filmov
tv
Biomechanics of the foot: inversion and eversion

Показать описание
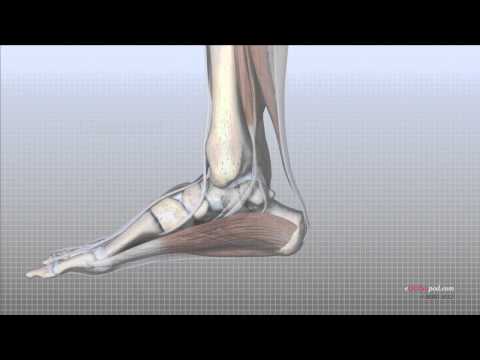
Inversion and eversion are movements of the foot that primarily occur at the subtalar and transverse tarsal joints. Inversion involves turning the sole of the foot inward so it faces toward the midline of the body. This movement lifts the inner edge of the foot and is essential for stabilizing the foot on uneven surfaces. Eversion is the opposite action, where the sole of the foot turns outward, away from the midline. This movement raises the outer edge of the foot, helping to adapt to varied terrain and balance. During inversion, the navicular and cuboid bones are drawn medially. Consequently, the forefoot moves medially and anteriorly. Also, the tarsal sinus opens to its widest during inversion. During eversion, the navicular and cuboid bones are drawn laterally so that the forefoot is drawn laterally and anteriorly. During eversion, the tarsal sinus closes. Both inversion and eversion are crucial for activities like walking, running, and adapting to different ground surfaces, providing stability and balance.
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:03:12
0:03:12
 0:00:35
0:00:35
 0:01:43
0:01:43
 0:01:19
0:01:19
 0:08:00
0:08:00
 0:00:35
0:00:35
 0:19:51
0:19:51
 0:01:37
0:01:37
 0:01:53
0:01:53
 0:06:05
0:06:05
 0:14:58
0:14:58
 0:16:22
0:16:22
 0:05:12
0:05:12
 0:00:25
0:00:25
 0:00:38
0:00:38
 0:00:47
0:00:47
 0:20:48
0:20:48
 0:14:12
0:14:12
 0:28:11
0:28:11
 0:01:07
0:01:07
 0:04:11
0:04:11
 0:02:47
0:02:47
 0:05:11
0:05:11