filmov
tv
Conditional Probability Example Problems
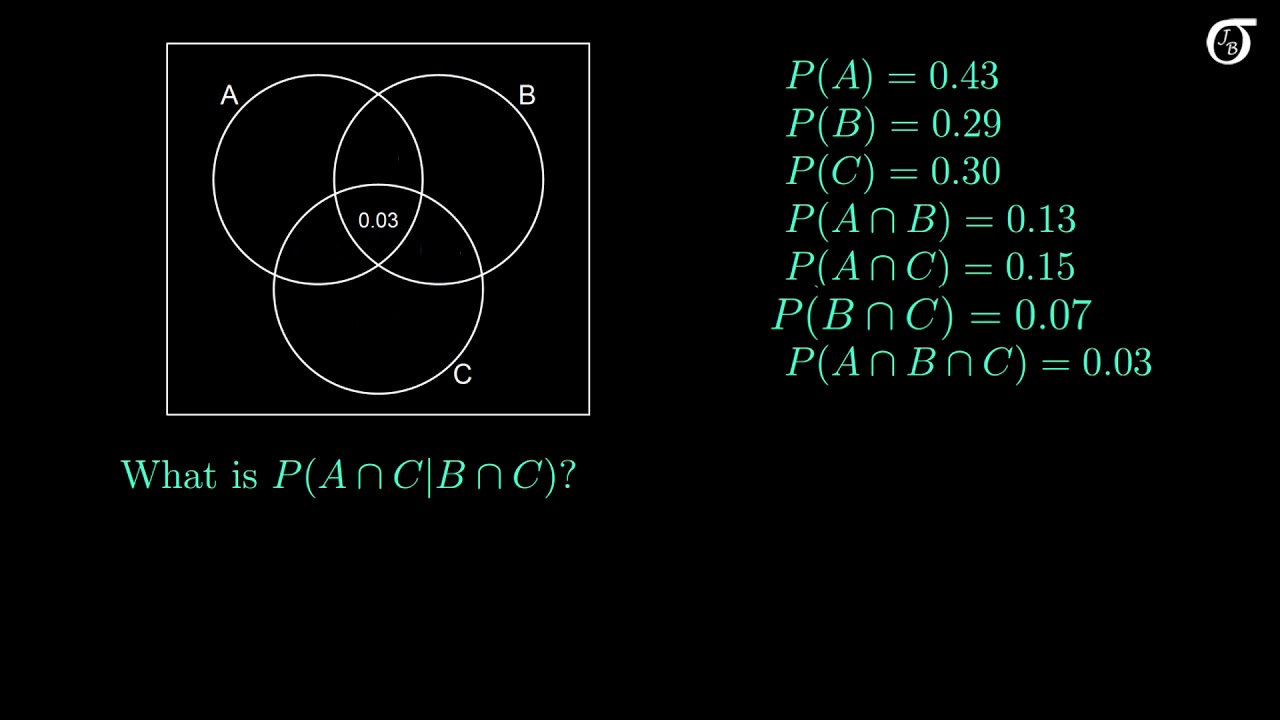
Показать описание
Conditional probability example problems, pitched at a level appropriate for a typical introductory statistics course. I assume that viewers have already been introduced to the concepts of conditional probability and independence, but I do review the concepts along the way. I work through some problems with the conditional probability formula explicitly, and some using the reduced sample space argument.
The sudden death data is slightly modified from:
Naneix et al. (2015). Sudden adult death: An autopsy series of 534 cases with gender and control comparison. Journal of Forensic and Legal Medicine, 32:10-15.
The data was pulled from their Figure 3, and I pooled the Abdominal/pelvian and undetermined groups into "other", to make the example work better visually and have it be easier to follow. I took some slight liberties here, as "undetermined" is not the same as "other". Conscious choice, y'all.
Examples:
0:58. An example using the conditional probability formula, where we are given P(A), P(B), and P(A U B).
3:06: Die rolling. Everybody's fave. P(AUB|C).
4:51. Two-way table, involving real data from above. Limited on interpretation, and focussing on finding various conditional probabilities.
8:05. Conditional probability involving 3 events, visualized with a Venn diagram. P(A n C | B n C), P(B^c|A U C).
11:21. Example of determining whether P(A|B) = P(A), P(A|B) is less than P(A), or P(A|B) is greater than P(A), based on common knowledge and without being given probabilities.
13:00. Informal illustration that if P(A|B) is greater than P(A) then P(B|A) is greater than P(B), and if P(A|B) is less than P(A) then P(B|A) is less than P(B).
14:40. If A is a subset of B, and P(A) is greater than 0, what can be said of P(A|B) and P(B|A)?
The sudden death data is slightly modified from:
Naneix et al. (2015). Sudden adult death: An autopsy series of 534 cases with gender and control comparison. Journal of Forensic and Legal Medicine, 32:10-15.
The data was pulled from their Figure 3, and I pooled the Abdominal/pelvian and undetermined groups into "other", to make the example work better visually and have it be easier to follow. I took some slight liberties here, as "undetermined" is not the same as "other". Conscious choice, y'all.
Examples:
0:58. An example using the conditional probability formula, where we are given P(A), P(B), and P(A U B).
3:06: Die rolling. Everybody's fave. P(AUB|C).
4:51. Two-way table, involving real data from above. Limited on interpretation, and focussing on finding various conditional probabilities.
8:05. Conditional probability involving 3 events, visualized with a Venn diagram. P(A n C | B n C), P(B^c|A U C).
11:21. Example of determining whether P(A|B) = P(A), P(A|B) is less than P(A), or P(A|B) is greater than P(A), based on common knowledge and without being given probabilities.
13:00. Informal illustration that if P(A|B) is greater than P(A) then P(B|A) is greater than P(B), and if P(A|B) is less than P(A) then P(B|A) is less than P(B).
14:40. If A is a subset of B, and P(A) is greater than 0, what can be said of P(A|B) and P(B|A)?
Комментарии
 0:16:39
0:16:39
 0:08:12
0:08:12
 0:06:14
0:06:14
 0:06:16
0:06:16
 0:06:43
0:06:43
 0:00:52
0:00:52
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:16:26
0:16:26
 0:35:35
0:35:35
 0:14:22
0:14:22
 0:04:07
0:04:07
 0:12:10
0:12:10
 0:03:55
0:03:55
 0:12:01
0:12:01
 0:10:44
0:10:44
 0:07:44
0:07:44
 0:05:52
0:05:52
 0:10:56
0:10:56
 0:14:49
0:14:49
 0:20:36
0:20:36
 0:04:07
0:04:07
 0:04:11
0:04:11
 0:06:23
0:06:23
 0:00:25
0:00:25