filmov
tv
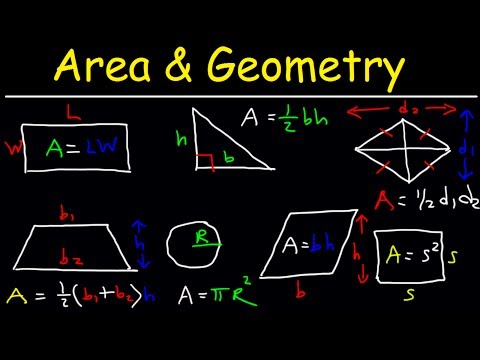
Find the area of a figure by decomposing it

Показать описание
Find the area of a figure by decomposing it
In this lesson, you will learn how to find the area of a figure by decomposing and finding the sum.
ADDITIONAL MATERIALS
STANDARDS
CCSS.4.MD.A.3 Apply the area and perimeter formulas for rectangles in real world and mathematical problems. For example, find the width of a rectangular room given the area of the flooring and the length, by viewing the area formula as a multiplication equation with an unknown factor.
TEKS.4.5.D solve problems related to perimeter and area of rectangles where dimensions are whole numbers.
TEKS.6.8.C write equations that represent problems related to the area of rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and triangles and volume of right rectangular prisms where dimensions are positive rational numbers; and
TEKS.6.8.D determine solutions for problems involving the area of rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and triangles and volume of right rectangular prisms where dimensions are positive rational numbers.
TEKS.7.9.C determine the area of composite figures containing combinations of rectangles, squares, parallelograms, trapezoids, triangles, semicircles, and quarter circles; and
TEKS.3.6.C determine the area of rectangles with whole number side lengths in problems using multiplication related to the number of rows times the number of unit squares in each row;
TEKS.3.6.D decompose composite figures formed by rectangles into non-overlapping rectangles to determine the area of the original figure using the additive property of area; and
TEKS.3.7.B determine the perimeter of a polygon or a missing length when given perimeter and remaining side lengths in problems;
TEKS.5.4.H represent and solve problems related to perimeter and/or area and related to volume.
IN.3.M.6 Multiply side lengths to find areas of rectangles with whole-number side lengths to solve real-world problems and other mathematical problems, and represent whole-number products as rectangular areas in mathematical reasoning.
IN.4.M.4 Apply the area and perimeter formulas for rectangles to solve real-world problems and other mathematical problems. Recognize area as additive and find the area of complex shapes composed of rectangles by decomposing them into non-overlapping rectangles and adding the areas of the non-overlapping parts; apply this technique to solve real-world problems and other mathematical problems.
VA.MG.3.8.b count the number of square units needed to cover a given surface in order to determine its area.
VA.MG.8.10 The student will solve area and perimeter problems, including practical problems, involving composite plane figures.
VA.MG.4.7 The student will solve practical problems that involve determining perimeter and area in U.S. Customary and metric units.
VA.MG.6.7.c solve problems, including practical problems, involving area and perimeter of triangles and rectangles.
VA.MG.5.8.a solve practical problems that involve perimeter, area, and volume in standard units of measure; and
VA.MG.5.8.b differentiate among perimeter, area, and volume and identify whether the application of the concept of perimeter, area, or volume is appropriate for a given situation.
FL.MAFS.4.MD.1.3 Apply the area and perimeter formulas for rectangles in real world and mathematical problems. For example, find the width of a rectangular room given the area of the flooring and the length, by viewing the area formula as a multiplication equation with an unknown factor.
In this lesson, you will learn how to find the area of a figure by decomposing and finding the sum.
ADDITIONAL MATERIALS
STANDARDS
CCSS.4.MD.A.3 Apply the area and perimeter formulas for rectangles in real world and mathematical problems. For example, find the width of a rectangular room given the area of the flooring and the length, by viewing the area formula as a multiplication equation with an unknown factor.
TEKS.4.5.D solve problems related to perimeter and area of rectangles where dimensions are whole numbers.
TEKS.6.8.C write equations that represent problems related to the area of rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and triangles and volume of right rectangular prisms where dimensions are positive rational numbers; and
TEKS.6.8.D determine solutions for problems involving the area of rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and triangles and volume of right rectangular prisms where dimensions are positive rational numbers.
TEKS.7.9.C determine the area of composite figures containing combinations of rectangles, squares, parallelograms, trapezoids, triangles, semicircles, and quarter circles; and
TEKS.3.6.C determine the area of rectangles with whole number side lengths in problems using multiplication related to the number of rows times the number of unit squares in each row;
TEKS.3.6.D decompose composite figures formed by rectangles into non-overlapping rectangles to determine the area of the original figure using the additive property of area; and
TEKS.3.7.B determine the perimeter of a polygon or a missing length when given perimeter and remaining side lengths in problems;
TEKS.5.4.H represent and solve problems related to perimeter and/or area and related to volume.
IN.3.M.6 Multiply side lengths to find areas of rectangles with whole-number side lengths to solve real-world problems and other mathematical problems, and represent whole-number products as rectangular areas in mathematical reasoning.
IN.4.M.4 Apply the area and perimeter formulas for rectangles to solve real-world problems and other mathematical problems. Recognize area as additive and find the area of complex shapes composed of rectangles by decomposing them into non-overlapping rectangles and adding the areas of the non-overlapping parts; apply this technique to solve real-world problems and other mathematical problems.
VA.MG.3.8.b count the number of square units needed to cover a given surface in order to determine its area.
VA.MG.8.10 The student will solve area and perimeter problems, including practical problems, involving composite plane figures.
VA.MG.4.7 The student will solve practical problems that involve determining perimeter and area in U.S. Customary and metric units.
VA.MG.6.7.c solve problems, including practical problems, involving area and perimeter of triangles and rectangles.
VA.MG.5.8.a solve practical problems that involve perimeter, area, and volume in standard units of measure; and
VA.MG.5.8.b differentiate among perimeter, area, and volume and identify whether the application of the concept of perimeter, area, or volume is appropriate for a given situation.
FL.MAFS.4.MD.1.3 Apply the area and perimeter formulas for rectangles in real world and mathematical problems. For example, find the width of a rectangular room given the area of the flooring and the length, by viewing the area formula as a multiplication equation with an unknown factor.
 0:10:26
0:10:26
 0:04:43
0:04:43
 0:07:14
0:07:14
 0:04:33
0:04:33
 0:20:35
0:20:35
 0:22:10
0:22:10
 0:08:58
0:08:58
 0:06:39
0:06:39
 0:06:39
0:06:39
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:04:30
0:04:30
 0:06:37
0:06:37
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:02:48
0:02:48
 0:15:51
0:15:51
 0:11:38
0:11:38
 0:00:47
0:00:47
 0:03:20
0:03:20
 0:05:21
0:05:21
 0:04:57
0:04:57
 0:02:46
0:02:46
 0:06:57
0:06:57
 0:05:48
0:05:48