filmov
tv
Thermodynamics: Non-ideal vapor-compression cycle, absorption refrigeration cycle (38 of 51)

Показать описание
0:00:39 - Reminder of vapor-compression refrigeration cycle devices
0:03:50 - Non-ideal vapor-compression refrigeration cycle
0:14:17 - Example: Non-ideal vapor compression refrigeration cycle
0:22:04 - Overview of absorption refrigeration cycle
0:44:28 - Preparation for midterm exam (summary of first third of course)
This lecture series was recorded live at Cal Poly Pomona during Spring 2018. The textbook is Cengel & Boles, "Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach (8th edition)."
0:03:50 - Non-ideal vapor-compression refrigeration cycle
0:14:17 - Example: Non-ideal vapor compression refrigeration cycle
0:22:04 - Overview of absorption refrigeration cycle
0:44:28 - Preparation for midterm exam (summary of first third of course)
This lecture series was recorded live at Cal Poly Pomona during Spring 2018. The textbook is Cengel & Boles, "Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach (8th edition)."
Thermodynamics: Non-ideal vapor-compression cycle, absorption refrigeration cycle (38 of 51)
Mechanical Engineering Thermodynamics - Lec 23, pt 4 of 4: Example - Ideal Vapor-Compression
Refrigeration Cycle | Vapor Compression Cycle | Animation | #Refrigerationcycle #HVAC
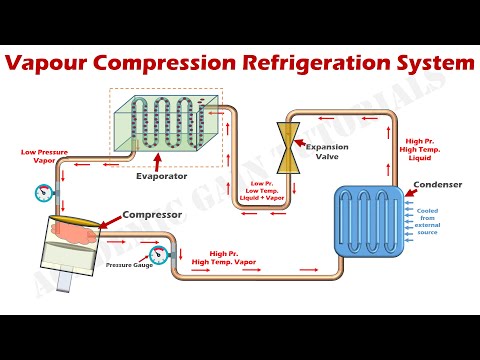
How Vapor Compression Refrigeration System Works - Parts & Function Explained.
Thermodynamics: Ideal Refrigeration Cycle
Refrigeration Cycle | Animation
The ideal vapor-compression refrigeration cycle
Mechanical Engineering Thermodynamics - Lec 23, pt 2 of 4: Vapor-Compression Refrigeration
Thermodynamic cycles -- Vapor compression refrigeration cycle
Ideal Vapour Compression Cycle Example 2
Refrigeration Cycles Lecture
Refrigeration Cycle Example
Numerical of Vapour Compression Refrigeration System
lecture 5 | type of questions | solved examples on vapour compression cycle #solvedexamples
How to read P h Chart explained with Numerical
Thermodynamics L12: Ideal Vapor-Compression Refrigeration Cycle Part-1
mod12lec88 - Thermodynamics cycles: vapor compression refrigeration cycle
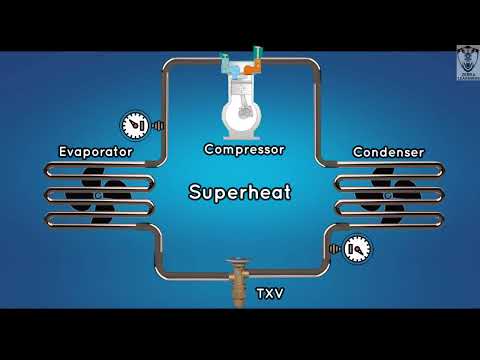
What is Superheat and Subcooling | Animation |#superheat #subcooling #hvac #chiller #thermodynamics
Example Problem - Simple Vapor Compression Refrigeration
Vapor-Compression Refrigeration Cycle (Interactive Simulation)
Thermodynamics L12: Ideal Vapor-Compression Refrigeration Cycle Part-2
The Ideal Vapor Compression Refrigeration Cycle Example, Chapter 11, Cengel Book, Part one
Thermodynamics: Closed feedwater heaters, Vapor-compression refrigeration cycle (37 of 51)
Vapour absorption refrigeration system
Комментарии
 1:05:10
1:05:10
 0:08:18
0:08:18
 0:05:13
0:05:13
 0:06:09
0:06:09
 0:42:31
0:42:31
 0:05:29
0:05:29
 0:09:42
0:09:42
 0:06:35
0:06:35
 0:33:29
0:33:29
 0:07:14
0:07:14
 0:47:19
0:47:19
 0:06:27
0:06:27
 0:16:10
0:16:10
 0:32:03
0:32:03
 0:10:13
0:10:13
 0:11:37
0:11:37
 0:25:17
0:25:17
 0:06:04
0:06:04
 0:43:24
0:43:24
 0:03:43
0:03:43
 0:06:20
0:06:20
 0:06:53
0:06:53
 1:05:19
1:05:19
 0:08:40
0:08:40