filmov
tv
Athlete's Foot (Tinea pedis): Symptoms, Causes & Treatment - Foot Fungus

Показать описание
Athlete's Foot (Tinea pedis): Symptoms, Causes & Treatment - Foot Fungus
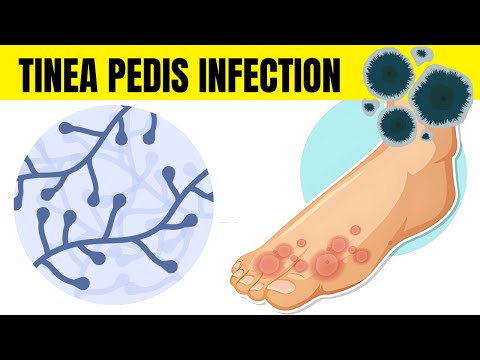
Athlete's foot, or tinea pedis, is a contagious fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet.
Athlete’s foot is a form of ringworm, typically characterized by skin fissures or scales that can be red and itchy. Sometimes, it can produce an unpleasant foot odor.
Risk Factors for Athlete's Foot (Tinea pedis);
• Underlying immunodeficiency or diabetes mellitus.
• Systemic corticosteroids or immune suppressive medications.
• Poor peripheral circulation or lymphoedema.
How is Athlete's Foot (Tinea pedis) Spread?
Athlete’s foot can be spread through direct through skin-to-skin contact of the infected part, or indirectly in which the fungi can infect people via contaminated surfaces, clothing, socks, shoes, bed sheets, and towels.
What Causes Athlete's Foot (Tinea pedis)?
• Trichophyton rubrum.
• Trichophyton interdigitale.
• Epidermophyton floccosum.
Signs & Symptoms of Athlete's Foot (Tinea pedis);
• Athlete's foot can affect one or both feet, and manifest as;
• Scaly, peeling or cracked skin between the toes, especially between 4th and 5th toes.
• Dry, scaly skin covering the sole and sides of the feet.
• Inflamed skin that might appear reddish, purplish or grayish.
• Itching, Burning, or stinging particularly after removing shoes and socks.
• Small to medium-sized blisters, usually affecting the inner aspect of the foot.
How is Athlete's Foot (Tinea pedis) Treated?
• General measures such as drying of feet, especially between the toes, avoidance of occlusive footwear, and the use of barrier protection like sandals will help your body fight the infection and heal on its own.
• Medical management involve the use of OTC medications - Topical antifungal therapy once or twice daily is usually sufficient. These include azoles, ciclopirox, allylamines, butenafine & tolnaftate.
• In severe cases and for those who do not respond to topical therapy, an oral antifungal agent is used – Griseofulvin, Itraconazole, Terbinafine & Fluconazole.
How can Athlete's Foot (Tinea pedis) be Prevented?
• Educating infected individuals not to expose others to their infection.
• Thoroughly wash your feet with soap.
• Keep feet dry.
• Apply antifungal powder to your feet to absorb moisture.
• Wear cotton or wool socks that absorb moisture.
• Put on your socks before your underwear to prevent the fungus from spreading to your groin.
• Wear loose-fitting, well-ventilated shoes, especially during the warmer months.
• Change shoes regularly so that footwear is relatively dry. Shoes need time to dry out.
• Do not share footwear.
What are the Complications of Athlete's Foot (Tinea pedis)?
• Fungal nail infection.
• Secondary bacterial infection.
• Cellulitis.
• Lymphangitis.
• Allergic reaction.
#tineapedis #Athlete'sFoot #athletesfoot #tineapedistreatment #tineapediscauses #tineapedissymptoms #athletesfoottreatment #athletesfootsymptoms #athletesfootcauses
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Check out our other videos
Pancreatitis (Acute Pancreatitis) – Causes, Signs & Symptoms, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Treatment
Haemorrhoids (Hemorrhoids) | Piles – Signs & Symptoms, Causes, Types, Diagnosis, Treatment
Hepatitis C – Symptoms, Causes, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Treatment, Complications | Viral Hepatitis
Anal Fissure - Signs & Symptoms, Causes, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Treatment
Gonorrhea – Symptoms, Causes, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Treatment, Complications
Bacterial Vaginosis – Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment
Chlamydia - Symptoms, Causes, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Treatment, Complications
Early Symptoms of HIV infection | Early Signs of HIV infection
Syphilis – Symptoms, Causes, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Treatment, Complications, Preventions
0:00 Tinea Pedis (Athlete's Foot)
0:25 Who Gets Athlete's Foot?
1:08 What Causes Athlete's Foot?
1:22 Symptoms of Athlete's Foot
1:45 Diagnosis of Athlete's Foot
2:12 How is Athlete's Foot Treated?
3:04 Prevention of Athlete's Foot
4:01 Complications of Athlete's Foot
4:13 Take Home Message
Athlete's foot, or tinea pedis, is a contagious fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet.
Athlete’s foot is a form of ringworm, typically characterized by skin fissures or scales that can be red and itchy. Sometimes, it can produce an unpleasant foot odor.
Risk Factors for Athlete's Foot (Tinea pedis);
• Underlying immunodeficiency or diabetes mellitus.
• Systemic corticosteroids or immune suppressive medications.
• Poor peripheral circulation or lymphoedema.
How is Athlete's Foot (Tinea pedis) Spread?
Athlete’s foot can be spread through direct through skin-to-skin contact of the infected part, or indirectly in which the fungi can infect people via contaminated surfaces, clothing, socks, shoes, bed sheets, and towels.
What Causes Athlete's Foot (Tinea pedis)?
• Trichophyton rubrum.
• Trichophyton interdigitale.
• Epidermophyton floccosum.
Signs & Symptoms of Athlete's Foot (Tinea pedis);
• Athlete's foot can affect one or both feet, and manifest as;
• Scaly, peeling or cracked skin between the toes, especially between 4th and 5th toes.
• Dry, scaly skin covering the sole and sides of the feet.
• Inflamed skin that might appear reddish, purplish or grayish.
• Itching, Burning, or stinging particularly after removing shoes and socks.
• Small to medium-sized blisters, usually affecting the inner aspect of the foot.
How is Athlete's Foot (Tinea pedis) Treated?
• General measures such as drying of feet, especially between the toes, avoidance of occlusive footwear, and the use of barrier protection like sandals will help your body fight the infection and heal on its own.
• Medical management involve the use of OTC medications - Topical antifungal therapy once or twice daily is usually sufficient. These include azoles, ciclopirox, allylamines, butenafine & tolnaftate.
• In severe cases and for those who do not respond to topical therapy, an oral antifungal agent is used – Griseofulvin, Itraconazole, Terbinafine & Fluconazole.
How can Athlete's Foot (Tinea pedis) be Prevented?
• Educating infected individuals not to expose others to their infection.
• Thoroughly wash your feet with soap.
• Keep feet dry.
• Apply antifungal powder to your feet to absorb moisture.
• Wear cotton or wool socks that absorb moisture.
• Put on your socks before your underwear to prevent the fungus from spreading to your groin.
• Wear loose-fitting, well-ventilated shoes, especially during the warmer months.
• Change shoes regularly so that footwear is relatively dry. Shoes need time to dry out.
• Do not share footwear.
What are the Complications of Athlete's Foot (Tinea pedis)?
• Fungal nail infection.
• Secondary bacterial infection.
• Cellulitis.
• Lymphangitis.
• Allergic reaction.
#tineapedis #Athlete'sFoot #athletesfoot #tineapedistreatment #tineapediscauses #tineapedissymptoms #athletesfoottreatment #athletesfootsymptoms #athletesfootcauses
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Check out our other videos
Pancreatitis (Acute Pancreatitis) – Causes, Signs & Symptoms, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Treatment
Haemorrhoids (Hemorrhoids) | Piles – Signs & Symptoms, Causes, Types, Diagnosis, Treatment
Hepatitis C – Symptoms, Causes, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Treatment, Complications | Viral Hepatitis
Anal Fissure - Signs & Symptoms, Causes, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Treatment
Gonorrhea – Symptoms, Causes, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Treatment, Complications
Bacterial Vaginosis – Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment
Chlamydia - Symptoms, Causes, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Treatment, Complications
Early Symptoms of HIV infection | Early Signs of HIV infection
Syphilis – Symptoms, Causes, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Treatment, Complications, Preventions
0:00 Tinea Pedis (Athlete's Foot)
0:25 Who Gets Athlete's Foot?
1:08 What Causes Athlete's Foot?
1:22 Symptoms of Athlete's Foot
1:45 Diagnosis of Athlete's Foot
2:12 How is Athlete's Foot Treated?
3:04 Prevention of Athlete's Foot
4:01 Complications of Athlete's Foot
4:13 Take Home Message
Комментарии
 0:10:01
0:10:01
 0:03:59
0:03:59
 0:03:59
0:03:59
 0:03:29
0:03:29
 0:01:14
0:01:14
 0:01:37
0:01:37
 0:04:51
0:04:51
 0:01:56
0:01:56
 0:03:03
0:03:03
 0:05:17
0:05:17
 0:03:24
0:03:24
 0:01:34
0:01:34
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:01:24
0:01:24
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:00:50
0:00:50
 0:04:47
0:04:47
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:01:12
0:01:12
 0:03:06
0:03:06
 0:01:17
0:01:17
 0:02:53
0:02:53
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 0:07:21
0:07:21