filmov
tv
Respiration | Transport of Carbon Dioxide in Blood & Body Fluids Part 2

Показать описание
#drnajeeb #medicines #pharmacology #medicaleducation #drnajeeblectures #respiration
Respiration | Transport of Carbon Dioxide in Blood & Body Fluids Part 2
to access 800+ Exclusive videos on Basic Medical Sciences & Clinical Medicine. These are premium videos (NOT FROM YOUTUBE). All these videos come with English subtitles & download options. Sign up now! Get Lifetime Access for a one-time payment of $99 ONLY!
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Why sign up for premium membership? Here's why!
Membership Features for premium website members.
1. More than 800+ Medical Lectures.
2. Basic Medical Sciences & Clinical Medicine.
3. Mobile-friendly interface with android and iOS apps.
4. English subtitles and new videos every week.
5. Download option for offline video playback.
6. Fanatic customer support and that's 24/7.
7. Fast video playback option to learn faster.
8. Trusted by over 2M+ students in 190 countries.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(0:00-7:45)
Discussion of transport & partial pressure of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) in blood & body tissues.
Comparison of solubility of CO2 & Oxygen (O2) in blood & body tissues.
Discrepancy in amount of O2 going into (250ml) and CO2 coming out (200ml) of the body cells per minute; its explanation.
PCO2 in arterial and venous blood.
(7:46-14:34)
Total CO2 content in arterial and venous blood per deciliter [100ml]; difference equals amount of CO2 transported per deciliter.
Comparison of pO2 & pCO2 in arterial & venous blood.
Comparison of total O2 & CO2 content in arterial & venous blood.
(14:35-21:44)
Functions of Hb summarized:
1-O2 transport
2-CO2 transport
3-Function as Buffering Proteins; maintaining Acid Base balance/pH
4-Binding with Nitric Oxide (NO) arriving from the lungs; which helps in dilatation of small arterioles.
(21:45-32:10)
PERIPHERAL TISSUES:
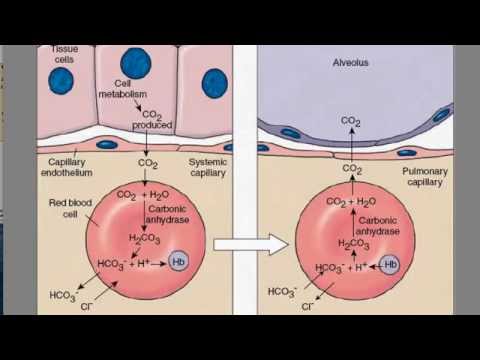
RBCs carrying out most of CO2 transport from body tissues back to lungs; role of pCO2, protons (H+), bicarbonate (HCO3-), carbonic Acid (H2CO3) and CARBONIC ANHYDRASE enzyme (CA enzyme) inside RBCs.
Role of Bicarbonate-Chloride Exchanger/Band-3 protein in maintaining electrical balance inside the RBCs while they are transporting CO2; explanation of slight difference of Hematocrit values between venous & arterial blood in this context.
“Buffering function” of Hemoglobin (Hb) in maintaining acid-base balance within RBCs that are transporting CO2.
(32:11-37:10)
Transport of small amount of CO2 in dissolved form in the plasma.
Transport of small amount of CO2 as Carbamino-proteins; especially as CARBAMINOHEMOGLOBIN.
(37:11-41:15)
Summary of forms in which CO2 is transported:
1-90% as Bicarbonate ions; which are formed in RBCs but transported in plasma.
2-5% is in dissolved form; under pCO2 of 46mmHg
3-5% in form of Carbamino-compounds.
Explanation of BOHR’S EFFECT; role of protonated Hb & their reduced affinity for O2; effect on Oxygen-Hemoglobin Dissociation curve.
(41:16-54:12)
PULMONARY TISSUES:
Mechanism of release of dissolved CO2 and CO2 stored as Carbamino proteins into the pulmonary tissues.
Mechanism of release of CO2 transported as HCO3- into the pulmonary tissues; role of CA enzyme and Band-3 proteins inside RBCs in releasing CO2 into the alveoli.
Explanation of HALDANE EFFECT; as reverse of Bohr effect.
Comparison of Bohr effect and Haldane effect.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Join this channel to get access to perks:
Respiration | Transport of Carbon Dioxide in Blood & Body Fluids Part 2
to access 800+ Exclusive videos on Basic Medical Sciences & Clinical Medicine. These are premium videos (NOT FROM YOUTUBE). All these videos come with English subtitles & download options. Sign up now! Get Lifetime Access for a one-time payment of $99 ONLY!
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Why sign up for premium membership? Here's why!
Membership Features for premium website members.
1. More than 800+ Medical Lectures.
2. Basic Medical Sciences & Clinical Medicine.
3. Mobile-friendly interface with android and iOS apps.
4. English subtitles and new videos every week.
5. Download option for offline video playback.
6. Fanatic customer support and that's 24/7.
7. Fast video playback option to learn faster.
8. Trusted by over 2M+ students in 190 countries.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(0:00-7:45)
Discussion of transport & partial pressure of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) in blood & body tissues.
Comparison of solubility of CO2 & Oxygen (O2) in blood & body tissues.
Discrepancy in amount of O2 going into (250ml) and CO2 coming out (200ml) of the body cells per minute; its explanation.
PCO2 in arterial and venous blood.
(7:46-14:34)
Total CO2 content in arterial and venous blood per deciliter [100ml]; difference equals amount of CO2 transported per deciliter.
Comparison of pO2 & pCO2 in arterial & venous blood.
Comparison of total O2 & CO2 content in arterial & venous blood.
(14:35-21:44)
Functions of Hb summarized:
1-O2 transport
2-CO2 transport
3-Function as Buffering Proteins; maintaining Acid Base balance/pH
4-Binding with Nitric Oxide (NO) arriving from the lungs; which helps in dilatation of small arterioles.
(21:45-32:10)
PERIPHERAL TISSUES:
RBCs carrying out most of CO2 transport from body tissues back to lungs; role of pCO2, protons (H+), bicarbonate (HCO3-), carbonic Acid (H2CO3) and CARBONIC ANHYDRASE enzyme (CA enzyme) inside RBCs.
Role of Bicarbonate-Chloride Exchanger/Band-3 protein in maintaining electrical balance inside the RBCs while they are transporting CO2; explanation of slight difference of Hematocrit values between venous & arterial blood in this context.
“Buffering function” of Hemoglobin (Hb) in maintaining acid-base balance within RBCs that are transporting CO2.
(32:11-37:10)
Transport of small amount of CO2 in dissolved form in the plasma.
Transport of small amount of CO2 as Carbamino-proteins; especially as CARBAMINOHEMOGLOBIN.
(37:11-41:15)
Summary of forms in which CO2 is transported:
1-90% as Bicarbonate ions; which are formed in RBCs but transported in plasma.
2-5% is in dissolved form; under pCO2 of 46mmHg
3-5% in form of Carbamino-compounds.
Explanation of BOHR’S EFFECT; role of protonated Hb & their reduced affinity for O2; effect on Oxygen-Hemoglobin Dissociation curve.
(41:16-54:12)
PULMONARY TISSUES:
Mechanism of release of dissolved CO2 and CO2 stored as Carbamino proteins into the pulmonary tissues.
Mechanism of release of CO2 transported as HCO3- into the pulmonary tissues; role of CA enzyme and Band-3 proteins inside RBCs in releasing CO2 into the alveoli.
Explanation of HALDANE EFFECT; as reverse of Bohr effect.
Comparison of Bohr effect and Haldane effect.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Join this channel to get access to perks:
Комментарии
 0:05:04
0:05:04
 0:13:28
0:13:28
 0:13:52
0:13:52
 0:07:59
0:07:59
 0:11:23
0:11:23
 0:07:35
0:07:35
 0:11:25
0:11:25
 0:09:34
0:09:34
 2:36:30
2:36:30
 0:03:47
0:03:47
 0:24:11
0:24:11
 0:33:30
0:33:30
 0:54:13
0:54:13
 0:08:01
0:08:01
 0:18:50
0:18:50
 0:08:47
0:08:47
 0:12:27
0:12:27
 0:11:52
0:11:52
 0:03:25
0:03:25
 0:03:58
0:03:58
 0:07:15
0:07:15
 0:22:24
0:22:24
 0:19:58
0:19:58
 0:10:53
0:10:53