filmov
tv
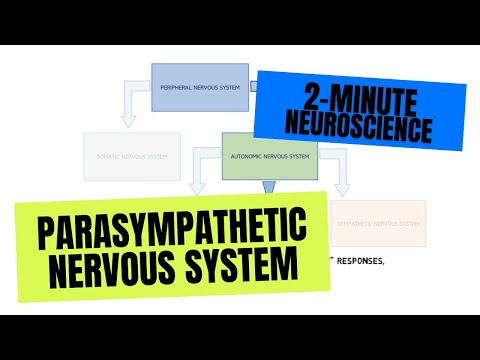
2-Minute Neuroscience: Parasympathetic Nervous System

Показать описание
The parasympathetic nervous system is the subdivision of the autonomic nervous system that is typically associated with conserving energy and the “rest and digest” response. In this video, I discuss the general anatomy and functions of the parasympathetic nervous system.
TRANSCRIPT:
The parasympathetic nervous system is a subdivision of the autonomic nervous system, which is the subdivision of the peripheral nervous system that controls automatic processes in the body like digestion, heart rate, and respiration. The parasympathetic nervous system is typically associated with energy conservation and processes like digestion and elimination of waste products from the body. Because of these functions, the parasympathetic nervous system is sometimes referred to as the “rest and digest” system, although this term is an oversimplification that does not accurately describe the full range of activities of the parasympathetic nervous system.
The nerves that make up the parasympathetic nervous system originate in the brainstem and the sacral spinal cord. Like most other neurons of the autonomic nervous system, they do not travel directly from the brainstem or spinal cord to their targets but instead extend first to clusters of neurons known as ganglia. The parasympathetic ganglia are typically found near or in the wall of the organs they supply. The neurons that travel from the brainstem and spinal cord to the parasympathetic ganglia are called preganglionic neurons, and they synapse with neurons in the ganglia called postganglionic neurons, which then extend to the targets of the parasympathetic nervous system. The preganglionic and postganglionic neurons of the parasympathetic nervous system primarily release the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
The preganglionic neurons that originate in the brainstem arise from the cranial nerve nuclei for the oculomotor, facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves. These preganglionic neurons travel with the cranial nerves to provide parasympathetic innervation to the head and neck, but the fibers that travel with the vagus nerve also supply the internal organs of the thorax and abdomen. The preganglionic neurons that originate in the sacral spinal cord come together to form the pelvic nerves, which supply the organs of the pelvis.
REFERENCE:
Wehrwein EA, Orer HS, Barman SM. Overview of the Anatomy, Physiology, and Pharmacology of the Autonomic Nervous System. Compr Physiol. 2016 Jun 13;6(3):1239-78. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c150037.
TRANSCRIPT:
The parasympathetic nervous system is a subdivision of the autonomic nervous system, which is the subdivision of the peripheral nervous system that controls automatic processes in the body like digestion, heart rate, and respiration. The parasympathetic nervous system is typically associated with energy conservation and processes like digestion and elimination of waste products from the body. Because of these functions, the parasympathetic nervous system is sometimes referred to as the “rest and digest” system, although this term is an oversimplification that does not accurately describe the full range of activities of the parasympathetic nervous system.
The nerves that make up the parasympathetic nervous system originate in the brainstem and the sacral spinal cord. Like most other neurons of the autonomic nervous system, they do not travel directly from the brainstem or spinal cord to their targets but instead extend first to clusters of neurons known as ganglia. The parasympathetic ganglia are typically found near or in the wall of the organs they supply. The neurons that travel from the brainstem and spinal cord to the parasympathetic ganglia are called preganglionic neurons, and they synapse with neurons in the ganglia called postganglionic neurons, which then extend to the targets of the parasympathetic nervous system. The preganglionic and postganglionic neurons of the parasympathetic nervous system primarily release the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
The preganglionic neurons that originate in the brainstem arise from the cranial nerve nuclei for the oculomotor, facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves. These preganglionic neurons travel with the cranial nerves to provide parasympathetic innervation to the head and neck, but the fibers that travel with the vagus nerve also supply the internal organs of the thorax and abdomen. The preganglionic neurons that originate in the sacral spinal cord come together to form the pelvic nerves, which supply the organs of the pelvis.
REFERENCE:
Wehrwein EA, Orer HS, Barman SM. Overview of the Anatomy, Physiology, and Pharmacology of the Autonomic Nervous System. Compr Physiol. 2016 Jun 13;6(3):1239-78. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c150037.
Комментарии
 0:02:00
0:02:00
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:02:00
0:02:00
 0:02:00
0:02:00
 0:01:55
0:01:55
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:02:00
0:02:00
 0:02:00
0:02:00
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:02:00
0:02:00
 0:01:53
0:01:53
 0:02:00
0:02:00
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:02:00
0:02:00
 0:02:00
0:02:00
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:11:31
0:11:31
 0:02:00
0:02:00
 0:02:00
0:02:00
 0:02:00
0:02:00
 0:01:58
0:01:58
 0:02:00
0:02:00
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:02:02
0:02:02