filmov
tv
Collision domain Vs Broadcast domain in English/Hindi II Networking Video II CCNA(Cisco)

Показать описание
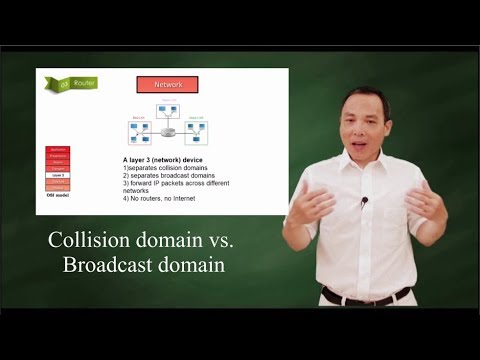
A collision domain is a network segment connected by a shared medium or through repeaters where simultaneous data transmissions collide with one another. The collision domain applies particularly in wireless networks, but also affected early versions of Ethernet. A network collision occurs when more than one device attempts to send a packet on a network segment at the same time. Members of a collision domain may be involved in collisions with one another. Devices outside the collision domain do not have collisions with those inside.
Only one device in the collision domain may transmit at any one time, and the other devices in the domain listen to the network and refrain from transmitting while others are already transmitting in order to avoid collisions. Because only one device may be transmitting at any one time, total network bandwidth is shared among all devices on the collision domain. Collisions also decrease network efficiency on a collision domain as collisions require devices to abort transmission and retransmit at a later time.
Since data bits are propagated at a finite speed, simultaneously is to be defined in terms of the size of the collision domain and the minimum packet size allowed. A smaller packet size or a larger dimension would make it possible for a sender to finish sending the packet without the first bits of the message being able to reach the most remote node. So, that node could start sending as well, without a clue to the transmission already taking place and destroying the first packet. Unless the size of the collision domain allows the initial sender to receive the second transmission attempt – the collision – within the time it takes to send the packet he would neither be able to detect the collision nor to repeat the transmission – this is called a late collision.
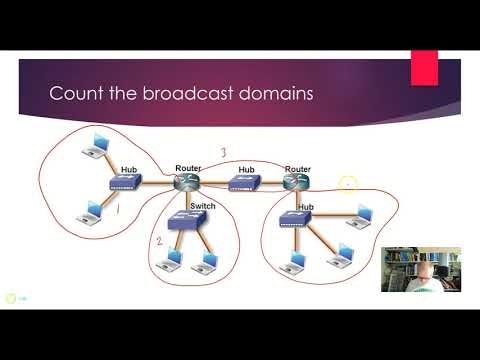
A broadcast domain is a logical division of a computer network, in which all nodes can reach each other by broadcast at the data link layer. A broadcast domain can be within the same LAN segment or it can be bridged to other LAN segments.
In terms of current popular technologies, any computer connected to the same Ethernet repeater or switch is a member of the same broadcast domain. Further, any computer connected to the same set of inter-connected switches/repeaters is a member of the same broadcast domain. Routers and other higher-layer devices form boundaries between broadcast domains.
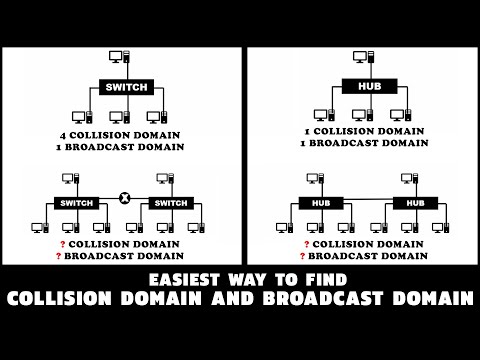
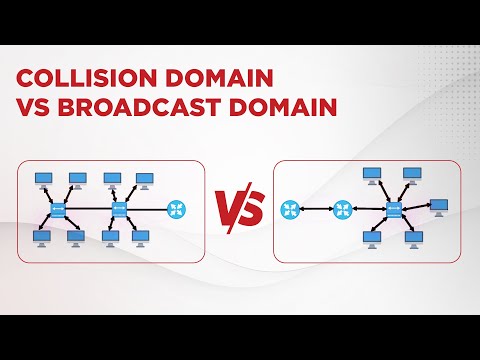
This is as compared to a collision domain, which would be all nodes on the same set of inter-connected repeaters, divided by switches and learning bridges. Collision domains are generally smaller than, and contained within, broadcast domains.
While some layer two network devices are able to divide the collision domains, broadcast domains are only divided by layer 3 network devices such as routers or layer 3 switches. Separating VLANs divides broadcast domains as well.
Video link
Only one device in the collision domain may transmit at any one time, and the other devices in the domain listen to the network and refrain from transmitting while others are already transmitting in order to avoid collisions. Because only one device may be transmitting at any one time, total network bandwidth is shared among all devices on the collision domain. Collisions also decrease network efficiency on a collision domain as collisions require devices to abort transmission and retransmit at a later time.
Since data bits are propagated at a finite speed, simultaneously is to be defined in terms of the size of the collision domain and the minimum packet size allowed. A smaller packet size or a larger dimension would make it possible for a sender to finish sending the packet without the first bits of the message being able to reach the most remote node. So, that node could start sending as well, without a clue to the transmission already taking place and destroying the first packet. Unless the size of the collision domain allows the initial sender to receive the second transmission attempt – the collision – within the time it takes to send the packet he would neither be able to detect the collision nor to repeat the transmission – this is called a late collision.
A broadcast domain is a logical division of a computer network, in which all nodes can reach each other by broadcast at the data link layer. A broadcast domain can be within the same LAN segment or it can be bridged to other LAN segments.
In terms of current popular technologies, any computer connected to the same Ethernet repeater or switch is a member of the same broadcast domain. Further, any computer connected to the same set of inter-connected switches/repeaters is a member of the same broadcast domain. Routers and other higher-layer devices form boundaries between broadcast domains.
This is as compared to a collision domain, which would be all nodes on the same set of inter-connected repeaters, divided by switches and learning bridges. Collision domains are generally smaller than, and contained within, broadcast domains.
While some layer two network devices are able to divide the collision domains, broadcast domains are only divided by layer 3 network devices such as routers or layer 3 switches. Separating VLANs divides broadcast domains as well.
Video link
 0:06:40
0:06:40
 0:05:54
0:05:54
 0:04:29
0:04:29
 0:04:06
0:04:06
 0:05:18
0:05:18
 0:10:02
0:10:02
 0:04:28
0:04:28
 0:13:52
0:13:52
 0:14:36
0:14:36
 0:09:58
0:09:58
 0:05:25
0:05:25
 0:04:02
0:04:02
 0:10:39
0:10:39
 0:04:22
0:04:22
 0:04:56
0:04:56
 0:05:49
0:05:49
 0:02:52
0:02:52
 0:01:03
0:01:03
 0:01:55
0:01:55
 0:04:16
0:04:16
 0:04:23
0:04:23
 0:01:37
0:01:37
 0:04:22
0:04:22
 0:06:23
0:06:23