filmov
tv
Why my sodium level is low? How to prevent low sodium level?

Показать описание
Sodium is an electrolyte that helps regulate the amount of water in the circulation and tissues. Sodium helps maintain normal blood pressure. Sodium also plays an important role in how nerves and muscles function.
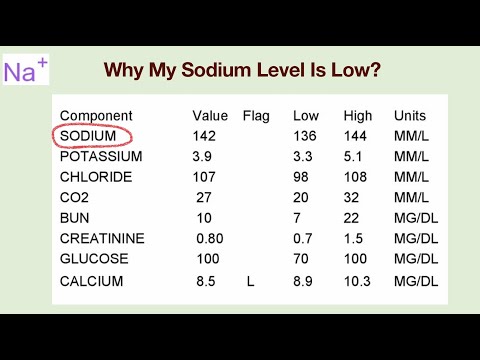
A normal blood sodium level is between 135 and 145 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L). When sodium level in the blood drops to below 135 mEq/L, it is called Hyponatremia or abnormally low sodium level in the blood.
When hyponatremia occurs, the water in the circulation and tissues enter body cells resulting in cell swelling. Cell swelling causes a wide range of signs and symptoms which may include:
* Nausea and vomiting
* Headache
* Confusion
* Loss of energy, drowsiness
* Restlessness and irritability
* Muscle weakness and cramps
* Seizures
* Coma
When sodium levels drop gradually over 3 days or longer, the symptoms and complications of hyponatremia are usually less severe.
When sodium levels drop quickly, rapid brain swelling can occur which can lead to seizures,coma and even death.
Many conditions can cause hyponatremia:
Medications such as certain water pills, antidepressants and pain pills can cause hyponatremia.
The use of Ecstasy or MDMA, a recreational drug, can lead to hyponatremia.
Congestive heart failure, kidney disease, liver disease can cause fluids to accumulate in your body. Fluid accumulation dilutes the sodium in your body and thus lowers the sodium level.
Syndrome of inappropriate anti-diuretic hormone which can cause your body to retain water and lower the sodium level.
Conditions that cause dehydration such as severe vomiting or diarrhea.
Drinking too much water.
Alcohol consumption.
Adrenal gland insufficiency
Underactive thyroid
Hyponatremia can be diagnosed with simple blood tests that measure the sodium level in the bloodstream.
Prevention of Hyponatremia
The following measures may help you prevent the occurrence of hyponatremia:
* Check blood tests regularly when you are taking medications that can cause Hyponatremia
* Follow your physician’s advice for the treatment of medical conditions that can contribute to hyponatremia, for example, adrenal gland insufficiency, underactive thyroid, congestive heart failure, kidney disease, liver disease etc.
* Take precautions during high-intensity activities. Athletes should drink only as much fluid as they lose due to sweating during a race.
* Consider drinking sports beverages during demanding activities such as marathons, triathlons.
* Drink water in moderation. If you do not feel thirsty and your urine is pale yellow, you are likely getting adequate fluid.
* Maintain adequate hydration if you have severe vomiting or diarrhea
* Drink alcohol in moderation. It is recommended that men should not drink more than 2 drinks a day and women should not drink more than 1 drink a day.
* Avoid using recreational drug, Ecstasy.
Treatment of Hyponatremia
If you develop severe signs and symptoms of hyponatremia, such as nausea and vomiting, confusion, seizures, or lost consciousness, you should seek emergency care immediately.
Severe Hyponatremia should be treated with intravenous infusion of hypertonic saline. Sodium level should be raised gradually over 24 to 72 hours. Rapid correction of sodium level is dangerous.
A new medication, Tolvaptan, can be used to treat hyponatremia in patients with heart failure or syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone.
Less severe Hyponatremia can be managed in an outpatient setting. Addressing the underlying medical conditions, restriction of fluid intake, adjusting diuretic use, cutting down alcohol intake, discontinuation of contributing medications can help correct Hyponatremia
A normal blood sodium level is between 135 and 145 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L). When sodium level in the blood drops to below 135 mEq/L, it is called Hyponatremia or abnormally low sodium level in the blood.
When hyponatremia occurs, the water in the circulation and tissues enter body cells resulting in cell swelling. Cell swelling causes a wide range of signs and symptoms which may include:
* Nausea and vomiting
* Headache
* Confusion
* Loss of energy, drowsiness
* Restlessness and irritability
* Muscle weakness and cramps
* Seizures
* Coma
When sodium levels drop gradually over 3 days or longer, the symptoms and complications of hyponatremia are usually less severe.
When sodium levels drop quickly, rapid brain swelling can occur which can lead to seizures,coma and even death.
Many conditions can cause hyponatremia:
Medications such as certain water pills, antidepressants and pain pills can cause hyponatremia.
The use of Ecstasy or MDMA, a recreational drug, can lead to hyponatremia.
Congestive heart failure, kidney disease, liver disease can cause fluids to accumulate in your body. Fluid accumulation dilutes the sodium in your body and thus lowers the sodium level.
Syndrome of inappropriate anti-diuretic hormone which can cause your body to retain water and lower the sodium level.
Conditions that cause dehydration such as severe vomiting or diarrhea.
Drinking too much water.
Alcohol consumption.
Adrenal gland insufficiency
Underactive thyroid
Hyponatremia can be diagnosed with simple blood tests that measure the sodium level in the bloodstream.
Prevention of Hyponatremia
The following measures may help you prevent the occurrence of hyponatremia:
* Check blood tests regularly when you are taking medications that can cause Hyponatremia
* Follow your physician’s advice for the treatment of medical conditions that can contribute to hyponatremia, for example, adrenal gland insufficiency, underactive thyroid, congestive heart failure, kidney disease, liver disease etc.
* Take precautions during high-intensity activities. Athletes should drink only as much fluid as they lose due to sweating during a race.
* Consider drinking sports beverages during demanding activities such as marathons, triathlons.
* Drink water in moderation. If you do not feel thirsty and your urine is pale yellow, you are likely getting adequate fluid.
* Maintain adequate hydration if you have severe vomiting or diarrhea
* Drink alcohol in moderation. It is recommended that men should not drink more than 2 drinks a day and women should not drink more than 1 drink a day.
* Avoid using recreational drug, Ecstasy.
Treatment of Hyponatremia
If you develop severe signs and symptoms of hyponatremia, such as nausea and vomiting, confusion, seizures, or lost consciousness, you should seek emergency care immediately.
Severe Hyponatremia should be treated with intravenous infusion of hypertonic saline. Sodium level should be raised gradually over 24 to 72 hours. Rapid correction of sodium level is dangerous.
A new medication, Tolvaptan, can be used to treat hyponatremia in patients with heart failure or syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone.
Less severe Hyponatremia can be managed in an outpatient setting. Addressing the underlying medical conditions, restriction of fluid intake, adjusting diuretic use, cutting down alcohol intake, discontinuation of contributing medications can help correct Hyponatremia
Комментарии
 0:04:22
0:04:22
 0:00:22
0:00:22
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:02:10
0:02:10
 0:01:21
0:01:21
 0:01:55
0:01:55
 0:03:20
0:03:20
 0:09:19
0:09:19
 0:27:08
0:27:08
 0:01:28
0:01:28
 0:13:37
0:13:37
 0:00:44
0:00:44
 0:01:35
0:01:35
 0:01:09
0:01:09
 0:03:51
0:03:51
 0:06:24
0:06:24
 0:00:27
0:00:27
 0:03:12
0:03:12
 0:12:30
0:12:30
 0:01:19
0:01:19
 0:06:26
0:06:26
 0:28:18
0:28:18
 0:17:18
0:17:18
 0:03:05
0:03:05