filmov
tv
Homogeneous Differential Equations and its solution method

Показать описание
Introduction to Differential Equations
A differential equation is an equation that involves a function and its derivatives. In simpler terms, it relates a function with its rates of change. Differential equations are used to model a wide range of real-world phenomena, such as the motion of objects, electrical circuits, population growth, and much more.
General Form: - A differential equation can be represented as: F(x, y, dy/dx, d^2y/dx^2 .......) = 0.
where x is the independent variable, y is the dependent variable, and dy/dx, d^2y/dx^2, etc., are the derivatives of y with respect to x.
Order and Degree of a Differential Equation
Order: - The order of a differential equation is the highest order of the derivative present in the equation.
Degree: - The degree of a differential equation is the power of the highest order derivative, provided the equation is polynomial in derivatives.
Types of Differential Equations
Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs): - Involve one independent variable.
Example: dy/dx + y = x
Partial Differential Equations (PDEs): - Involve more than one independent variable.
Example: d^2x/dt^2 + d^2y/dt^2 = x – t\
Types of ordinary differential equations
Variable Separable
Reducible to Variable Separable
Homogeneous Differential Equations
Reducible to Homogeneous Differential Equations
Linear Differential Equations
Reducible to Linear Differential Equations
Important Formulas in Differential Equations
Solution of First-Order Differential Equation: - (Variable Separable Form):
If the equation is of the form dy/dx = g(x)h(y), separate variables:
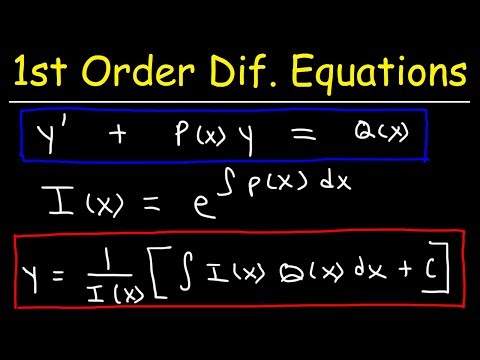
Linear Differential Equation (First Order): - General form: dy/dx + P(x)y = Q(x)
Homogeneous Differential Equations: - A first-order differential equation of the form dy/dx = y/x can be solved by substituting y = vx (where v is a new variable).
Steps to Solve a Differential Equation
Identify the order and degree
Classify the equation (linear, separable, homogeneous, etc.).
Use appropriate methods/formulas to solve the equation.
Differential Equations Class 12
First Order Differential Equations Class 12
Separation of Variables Method
Homogeneous Differential Equations Class 12
Linear Differential Equations Class 12
Formation of Differential Equations Class 12
General and Particular Solutions of Differential Equations
Applications of Differential Equations Class 12
Whatsapp No: - 9528824424
A differential equation is an equation that involves a function and its derivatives. In simpler terms, it relates a function with its rates of change. Differential equations are used to model a wide range of real-world phenomena, such as the motion of objects, electrical circuits, population growth, and much more.
General Form: - A differential equation can be represented as: F(x, y, dy/dx, d^2y/dx^2 .......) = 0.
where x is the independent variable, y is the dependent variable, and dy/dx, d^2y/dx^2, etc., are the derivatives of y with respect to x.
Order and Degree of a Differential Equation
Order: - The order of a differential equation is the highest order of the derivative present in the equation.
Degree: - The degree of a differential equation is the power of the highest order derivative, provided the equation is polynomial in derivatives.
Types of Differential Equations
Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs): - Involve one independent variable.
Example: dy/dx + y = x
Partial Differential Equations (PDEs): - Involve more than one independent variable.
Example: d^2x/dt^2 + d^2y/dt^2 = x – t\
Types of ordinary differential equations
Variable Separable
Reducible to Variable Separable
Homogeneous Differential Equations
Reducible to Homogeneous Differential Equations
Linear Differential Equations
Reducible to Linear Differential Equations
Important Formulas in Differential Equations
Solution of First-Order Differential Equation: - (Variable Separable Form):
If the equation is of the form dy/dx = g(x)h(y), separate variables:
Linear Differential Equation (First Order): - General form: dy/dx + P(x)y = Q(x)
Homogeneous Differential Equations: - A first-order differential equation of the form dy/dx = y/x can be solved by substituting y = vx (where v is a new variable).
Steps to Solve a Differential Equation
Identify the order and degree
Classify the equation (linear, separable, homogeneous, etc.).
Use appropriate methods/formulas to solve the equation.
Differential Equations Class 12
First Order Differential Equations Class 12
Separation of Variables Method
Homogeneous Differential Equations Class 12
Linear Differential Equations Class 12
Formation of Differential Equations Class 12
General and Particular Solutions of Differential Equations
Applications of Differential Equations Class 12
Whatsapp No: - 9528824424
 0:26:55
0:26:55
 0:07:59
0:07:59
 0:08:33
0:08:33
 1:05:45
1:05:45
 0:06:41
0:06:41
 0:01:47
0:01:47
 0:06:57
0:06:57
 0:03:35
0:03:35
 0:26:24
0:26:24
 0:25:41
0:25:41
 0:48:35
0:48:35
 1:55:11
1:55:11
 0:07:47
0:07:47
 0:18:50
0:18:50
 0:08:00
0:08:00
 0:16:18
0:16:18
 0:06:48
0:06:48
 0:13:34
0:13:34
 0:22:28
0:22:28
 0:05:22
0:05:22
 1:46:03
1:46:03
 0:30:35
0:30:35
 0:27:16
0:27:16
 0:00:52
0:00:52