filmov
tv
How Autofocus Works - Computerphile
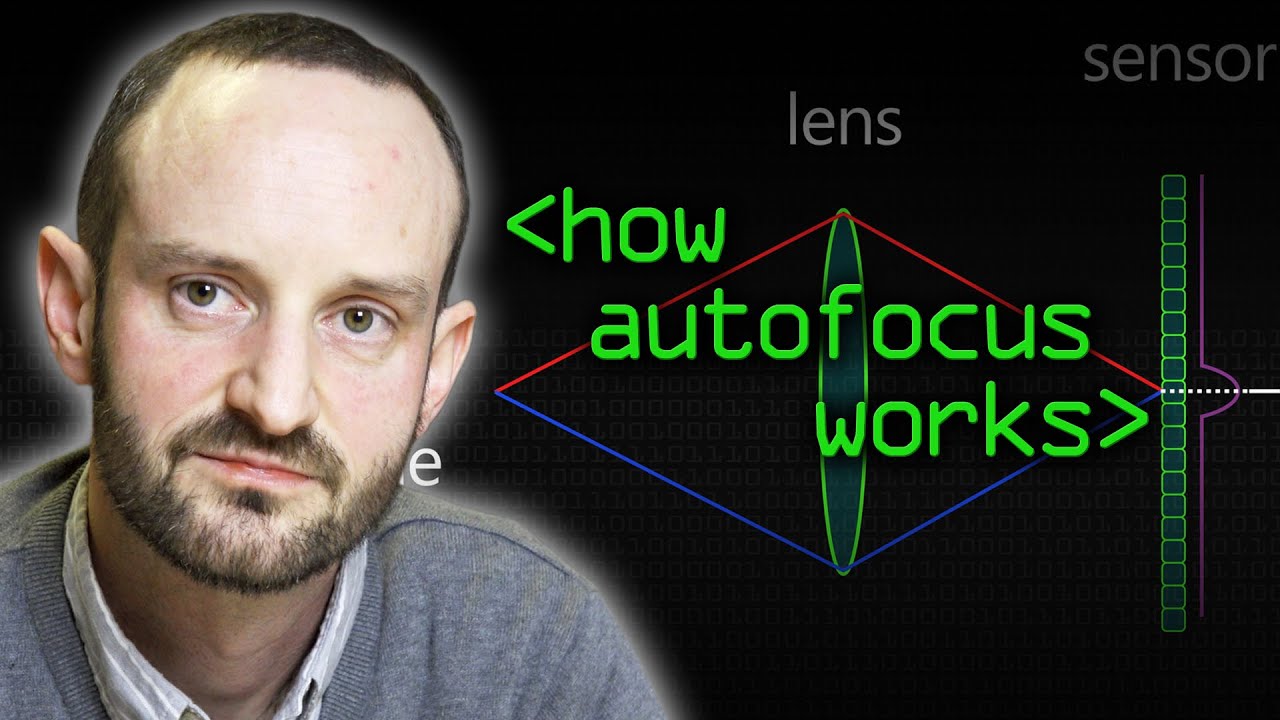
Показать описание
Why are some cameras faster to focus than others? Dr Andy French explains the different approaches the computers inside cameras use to focus.
This video was filmed and edited by Sean Riley.
This video was filmed and edited by Sean Riley.
How Autofocus Works - Computerphile
Atomic Auto-focus - Computerphile
Finding the Edges (Sobel Operator) - Computerphile
Light-field Camera - Computerphile
Industrial Light-field Magic - Computerphile
How do AUTO FOCUS systems ACTUALLY WORK? - Contrast Vs Phase Vs Hybrid
Taming Kerberos - Computerphile
Optical Flow - Computerphile
When your friend aks how autofocus works
The science behind how a digital camera works
Difference Between Phase Detection & Contrast Detection Auto Focus
Functional Parsing - Computerphile
AI Safety Gym - Computerphile
Data Analysis 6: Principal Component Analysis (PCA) - Computerphile
Contrast vs Phase Detection & Hybrid Autofocus (Simplified)
Using Regular Expressions - Computerphile
Gaming Museum - Computerphile
The new Lumix cameras have great phase detection autofocus! This is major for everyone! 🎬
The Joys of Updating & Upgrading - Computerphile
ALGOL 60 at 60 - Computerphile
Downsampling: Why I Use it and Why You Should Too | 4K
Talk Techy To Me - Can a digital camera save a life?
RegEx Roman Numerals - Computerphile
Data Compression as Fast As Possible
Комментарии
 0:18:24
0:18:24
 0:08:49
0:08:49
 0:07:46
0:07:46
 0:12:00
0:12:00
 0:04:26
0:04:26
 0:12:09
0:12:09
 0:16:06
0:16:06
 0:08:24
0:08:24
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:01:48
0:01:48
 0:05:53
0:05:53
 0:22:46
0:22:46
 0:16:00
0:16:00
 0:20:09
0:20:09
 0:07:13
0:07:13
 0:11:39
0:11:39
 0:10:35
0:10:35
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:13:06
0:13:06
 0:14:06
0:14:06
 0:09:05
0:09:05
 0:02:51
0:02:51
 0:17:14
0:17:14
 0:05:11
0:05:11