filmov
tv
Cell Cycle Regulation | Basic Overview
Показать описание
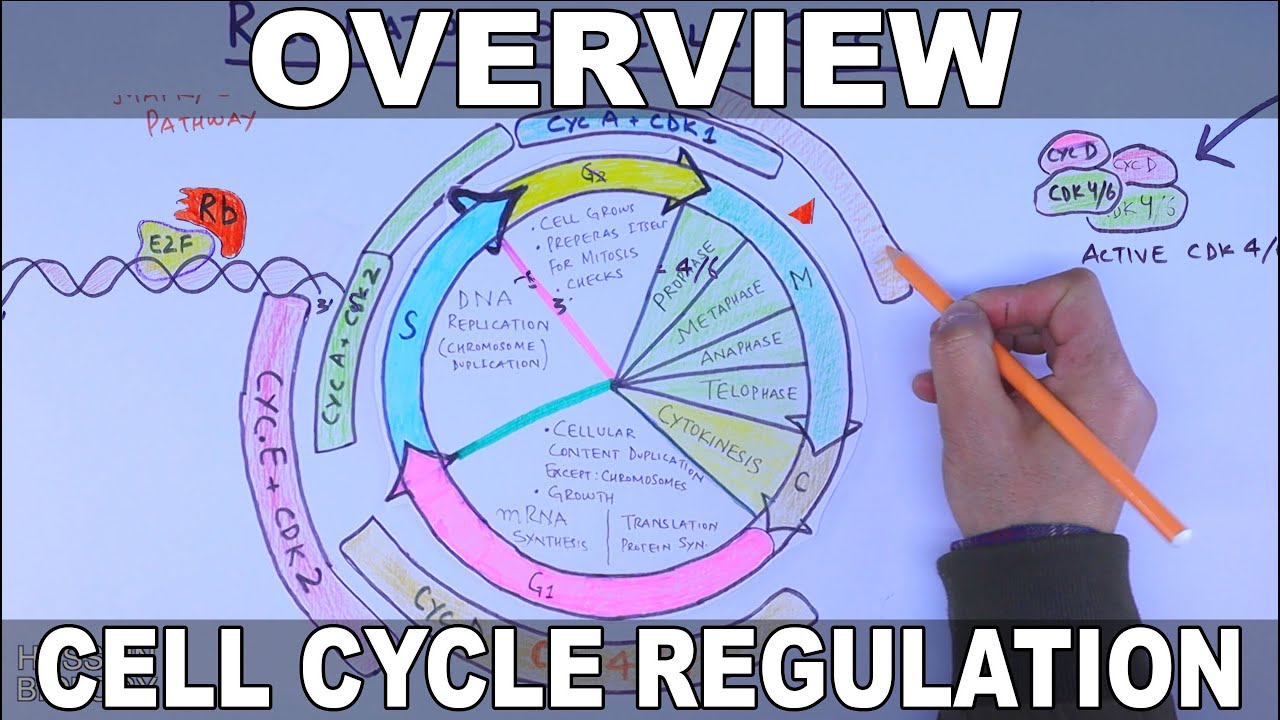
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and subsequently the partitioning of its cytoplasm and other components into two daughter cells in a process called cell division.
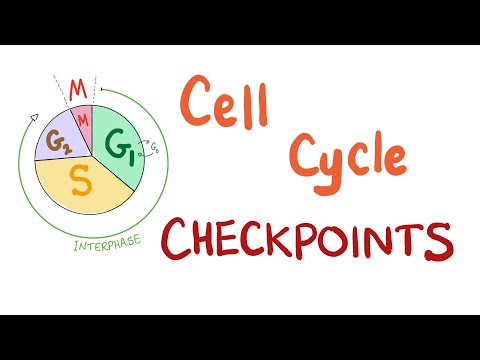
In cells with nuclei (eukaryotes), (i.e., animal, plant, fungal, and protist cells), the cell cycle is divided into two main stages: interphase and the mitotic (M) phase (including mitosis and cytokinesis). During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, and replicates its DNA and some of its organelles. During the mitotic phase, the replicated chromosomes, organelles, and cytoplasm separate into two new daughter cells. To ensure the proper replication of cellular components and division, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints after each of the key steps of the cycle that determine if the cell can progress to the next phase.
Two key classes of regulatory molecules, cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), determine a cell's progress through the cell cycle. Many of the genes encoding cyclins and CDKs are conserved among all eukaryotes, but in general more complex organisms have more elaborate cell cycle control systems that incorporate more individual components. Many of the relevant genes were first identified by studying yeast, The genetic nomenclature in yeast dubs many of these genes cdc (for "cell division cycle") followed by an identifying number, e.g. cdc25 or cdc20.
Cyclins form the regulatory subunits and CDKs the catalytic subunits of an activated heterodimer; cyclins have no catalytic activity and CDKs are inactive in the absence of a partner cyclin. When activated by a bound cyclin, CDKs perform a common biochemical reaction called phosphorylation that activates or inactivates target proteins to orchestrate coordinated entry into the next phase of the cell cycle. Different cyclin-CDK combinations determine the downstream proteins targeted. CDKs are constitutively expressed in cells whereas cyclins are synthesised at specific stages of the cell cycle, in response to various molecular signals.
Upon receiving a pro-mitotic extracellular signal, G1 cyclin-CDK complexes become active to prepare the cell for S phase, promoting the expression of transcription factors that in turn promote the expression of S cyclins and of enzymes required for DNA replication. The G1 cyclin-CDK complexes also promote the degradation of molecules that function as S phase inhibitors by targeting them for ubiquitination. Once a protein has been ubiquitinated, it is targeted for proteolytic degradation by the proteasome. However, results from a recent study of E2F transcriptional dynamics at the single-cell level argue that the role of G1 cyclin-CDK activities, in particular cyclin D-CDK4/6, is to tune the timing rather than the commitment of cell cycle entry
In cells with nuclei (eukaryotes), (i.e., animal, plant, fungal, and protist cells), the cell cycle is divided into two main stages: interphase and the mitotic (M) phase (including mitosis and cytokinesis). During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, and replicates its DNA and some of its organelles. During the mitotic phase, the replicated chromosomes, organelles, and cytoplasm separate into two new daughter cells. To ensure the proper replication of cellular components and division, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints after each of the key steps of the cycle that determine if the cell can progress to the next phase.
Two key classes of regulatory molecules, cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), determine a cell's progress through the cell cycle. Many of the genes encoding cyclins and CDKs are conserved among all eukaryotes, but in general more complex organisms have more elaborate cell cycle control systems that incorporate more individual components. Many of the relevant genes were first identified by studying yeast, The genetic nomenclature in yeast dubs many of these genes cdc (for "cell division cycle") followed by an identifying number, e.g. cdc25 or cdc20.
Cyclins form the regulatory subunits and CDKs the catalytic subunits of an activated heterodimer; cyclins have no catalytic activity and CDKs are inactive in the absence of a partner cyclin. When activated by a bound cyclin, CDKs perform a common biochemical reaction called phosphorylation that activates or inactivates target proteins to orchestrate coordinated entry into the next phase of the cell cycle. Different cyclin-CDK combinations determine the downstream proteins targeted. CDKs are constitutively expressed in cells whereas cyclins are synthesised at specific stages of the cell cycle, in response to various molecular signals.
Upon receiving a pro-mitotic extracellular signal, G1 cyclin-CDK complexes become active to prepare the cell for S phase, promoting the expression of transcription factors that in turn promote the expression of S cyclins and of enzymes required for DNA replication. The G1 cyclin-CDK complexes also promote the degradation of molecules that function as S phase inhibitors by targeting them for ubiquitination. Once a protein has been ubiquitinated, it is targeted for proteolytic degradation by the proteasome. However, results from a recent study of E2F transcriptional dynamics at the single-cell level argue that the role of G1 cyclin-CDK activities, in particular cyclin D-CDK4/6, is to tune the timing rather than the commitment of cell cycle entry
Комментарии
 0:12:40
0:12:40
 0:06:16
0:06:16
 0:39:36
0:39:36
 0:09:20
0:09:20
 0:05:26
0:05:26
 0:04:09
0:04:09
 0:13:59
0:13:59
 0:23:37
0:23:37
 0:36:17
0:36:17
 0:17:08
0:17:08
 0:03:04
0:03:04
 0:09:41
0:09:41
 0:14:33
0:14:33
 0:03:02
0:03:02
 0:48:19
0:48:19
 0:47:16
0:47:16
 0:17:47
0:17:47
 0:24:45
0:24:45
 0:05:38
0:05:38
 0:10:11
0:10:11
 0:14:57
0:14:57
 0:55:31
0:55:31
 0:13:30
0:13:30
 0:07:55
0:07:55