filmov
tv
How to derive cosine rule formula

Показать описание
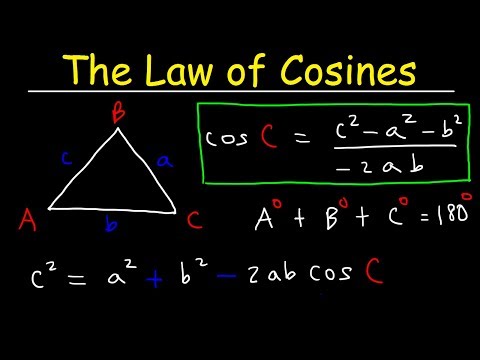
The Cosine Rule, also known as the Law of Cosines, is another key theorem in trigonometry, used primarily in non-right-angled triangles. It relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. The formula is particularly useful for solving triangles when you know two sides and the included angle (SAS) or when you know all three sides (SSS).
The Cosine Rule is stated as:
c² = a² + b² - 2ab•cos(C)
Where:
a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides of the triangle,
C is the angle opposite side c .
Similarly, for the other angles, the rule can be written as:
a² = b² + c² - 2bc•cos(A)
b² = a² + c² - 2ac•cos(B)
The Cosine Rule is useful in two primary situations:
1. When you know two sides and the included angle (SAS) and want to find the third side.
2. When you know all three sides (SSS) and want to find an angle.
In the special case where the angle is 90° (right-angled triangle), the Cosine Rule simplifies to the Pythagorean Theorem.
The Cosine Rule is stated as:
c² = a² + b² - 2ab•cos(C)
Where:
a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides of the triangle,
C is the angle opposite side c .
Similarly, for the other angles, the rule can be written as:
a² = b² + c² - 2bc•cos(A)
b² = a² + c² - 2ac•cos(B)
The Cosine Rule is useful in two primary situations:
1. When you know two sides and the included angle (SAS) and want to find the third side.
2. When you know all three sides (SSS) and want to find an angle.
In the special case where the angle is 90° (right-angled triangle), the Cosine Rule simplifies to the Pythagorean Theorem.
Proof of the Cosine Rule
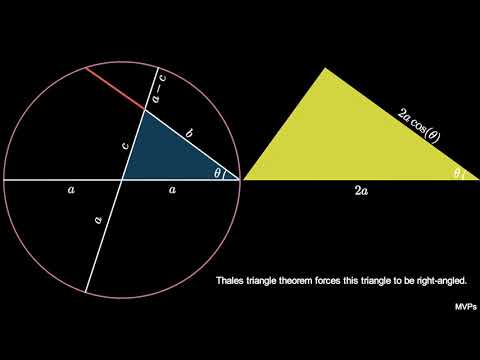
Law Of Cosines I (visual proof)
Proof of the cosine rule
Law Of Cosines II (visual proof)
Sine Or Cosine Rule? | Trigonometry | Maths | FuseSchool
How to derive cosine rule formula
The Cosine Rule (1 of 3: Proof of the Formula)
Proof of Cosine Rule - Grade 11
Double & Half Angle Identities (9 Examples)
Law of Cosines, Finding Angles & Sides, SSS & SAS Triangles - Trigonometry
Trigonometry (Sine/Cosine Rule)
Proof / Derivation Cosine Rule
Cosine Rule Proof (Derivation)
Proof of the law of cosines
Deriving the Law of Sines and Cosines
HOW TO DERIVE SINE LAW AND COSINE LAW?
Cosine rule|math trick
Sine Rule or Cosine Rule
Law of Sines Visual Proof
Derive cosine rule (law of cosines)
Proof of Cosine rule. How we derive cosine rule for different triangles.
Easy way to memorise cosine rule “The arrow”
DERIVATION OF COSINE LAW FOR TRIANGLE | Kamaldheeriya
Deriving Spherical Law of Cosines
Комментарии
 0:08:10
0:08:10
 0:02:31
0:02:31
 0:06:07
0:06:07
 0:02:42
0:02:42
 0:02:52
0:02:52
 0:07:27
0:07:27
 0:13:24
0:13:24
 0:20:27
0:20:27
 0:49:12
0:49:12
 0:10:18
0:10:18
 0:10:01
0:10:01
 0:01:46
0:01:46
 0:04:56
0:04:56
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:09:00
0:09:00
 0:10:20
0:10:20
 0:00:09
0:00:09
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:02:58
0:02:58
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:06:44
0:06:44
 0:00:22
0:00:22
 0:06:42
0:06:42
 0:15:17
0:15:17