filmov
tv
Staphylococcus Aureus

Показать описание
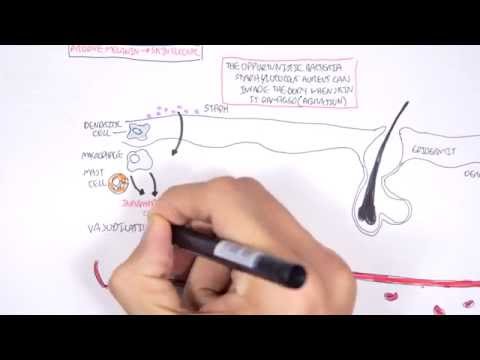
Staphylococcus aureus, often referred to as S. aureus, is a type of bacteria that can cause a wide range of infections in humans. It is a gram-positive bacterium, which means it retains a violet stain when subjected to a Gram stain, indicating a thick peptidoglycan layer in its cell wall. S. aureus is a member of the Staphylococcaceae family and is a common resident of the human skin and nasal passages.
While many people carry S. aureus on their skin and mucous membranes without any harm, it can become opportunistic and cause infections under certain circumstances, particularly when the immune system is compromised or when there is a breach in the skin barrier. Some common infections caused by S. aureus include:
1. Skin Infections: S. aureus can cause various skin infections, such as boils, impetigo, cellulitis, and folliculitis. These infections can range from mild to severe and are often characterized by redness, swelling, pain, and sometimes the presence of pus.
2. Surgical Site Infections: S. aureus can cause infections at surgical incision sites, leading to complications after surgeries.
3. Bloodstream Infections: S. aureus can enter the bloodstream, causing a serious condition known as bacteremia or septicemia. When the bacteria spread throughout the body, it can lead to life-threatening infections such as sepsis.
4. Pneumonia: S. aureus can cause pneumonia, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems or underlying respiratory conditions.
5. Endocarditis: This is an infection of the inner lining of the heart chambers and valves, which can be caused by S. aureus entering the bloodstream and lodging in these areas.
6. Osteomyelitis: S. aureus can infect bones and bone marrow, leading to a condition called osteomyelitis. This often occurs as a result of an open wound or surgery.
7. Toxin-Mediated Illnesses: S. aureus can produce toxins that cause illnesses such as toxic shock syndrome (TSS) and food poisoning. TSS can be a severe, life-threatening condition, while S. aureus-associated food poisoning results in symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
One of the challenges associated with S. aureus infections is its ability to develop resistance to antibiotics. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a strain of S. aureus that has become resistant to many commonly used antibiotics, making infections harder to treat.
Preventive measures to reduce the risk of S. aureus infections include practicing good hygiene, properly cleaning and caring for wounds, using antibiotics responsibly to prevent the development of antibiotic-resistant strains, and following infection control practices in healthcare settings.
If you suspect you have an S. aureus infection, it's important to seek medical attention, especially if the symptoms are severe or if you have underlying health conditions that could make the infection more serious.
While many people carry S. aureus on their skin and mucous membranes without any harm, it can become opportunistic and cause infections under certain circumstances, particularly when the immune system is compromised or when there is a breach in the skin barrier. Some common infections caused by S. aureus include:
1. Skin Infections: S. aureus can cause various skin infections, such as boils, impetigo, cellulitis, and folliculitis. These infections can range from mild to severe and are often characterized by redness, swelling, pain, and sometimes the presence of pus.
2. Surgical Site Infections: S. aureus can cause infections at surgical incision sites, leading to complications after surgeries.
3. Bloodstream Infections: S. aureus can enter the bloodstream, causing a serious condition known as bacteremia or septicemia. When the bacteria spread throughout the body, it can lead to life-threatening infections such as sepsis.
4. Pneumonia: S. aureus can cause pneumonia, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems or underlying respiratory conditions.
5. Endocarditis: This is an infection of the inner lining of the heart chambers and valves, which can be caused by S. aureus entering the bloodstream and lodging in these areas.
6. Osteomyelitis: S. aureus can infect bones and bone marrow, leading to a condition called osteomyelitis. This often occurs as a result of an open wound or surgery.
7. Toxin-Mediated Illnesses: S. aureus can produce toxins that cause illnesses such as toxic shock syndrome (TSS) and food poisoning. TSS can be a severe, life-threatening condition, while S. aureus-associated food poisoning results in symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
One of the challenges associated with S. aureus infections is its ability to develop resistance to antibiotics. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a strain of S. aureus that has become resistant to many commonly used antibiotics, making infections harder to treat.
Preventive measures to reduce the risk of S. aureus infections include practicing good hygiene, properly cleaning and caring for wounds, using antibiotics responsibly to prevent the development of antibiotic-resistant strains, and following infection control practices in healthcare settings.
If you suspect you have an S. aureus infection, it's important to seek medical attention, especially if the symptoms are severe or if you have underlying health conditions that could make the infection more serious.
Комментарии
 0:14:46
0:14:46
 1:01:18
1:01:18
 0:20:18
0:20:18
 0:09:19
0:09:19
 0:31:39
0:31:39
 0:05:13
0:05:13
 0:06:08
0:06:08
 0:03:48
0:03:48
 0:00:55
0:00:55
 0:06:32
0:06:32
 0:01:31
0:01:31
 0:08:49
0:08:49
 0:10:56
0:10:56
 0:14:13
0:14:13
 0:13:59
0:13:59
 0:43:46
0:43:46
 0:18:03
0:18:03
 0:01:49
0:01:49
 0:12:24
0:12:24
 0:03:10
0:03:10
 0:01:46
0:01:46
 0:00:55
0:00:55
 0:12:53
0:12:53
 0:02:10
0:02:10