filmov
tv
Hund Rule and Aufbau Principle || Chemistry

Показать описание
#chemistry
For More details visit
Hund's Rule:
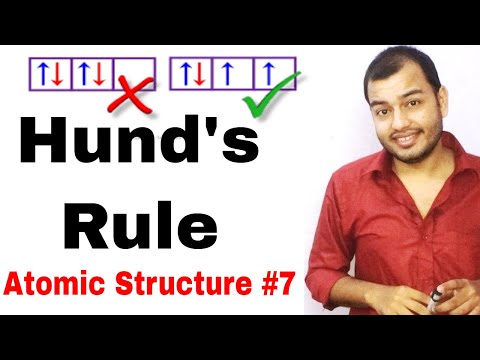
- States that when filling orbitals of equal energy (degenerate orbitals), electrons will occupy each orbital singly before pairing up in any orbital.
- Applies to atomic orbitals with the same energy level (degenerate orbitals).
- Electrons will occupy each available orbital singly before filling any orbital with a second electron.
- All the electrons in the singly occupied orbitals will have the same spin (either all up or all down).
Key Points:
- Hund's Rule applies to degenerate orbitals, which have the same energy level.
- Electrons will occupy each orbital singly before pairing up in any orbital.
- This rule helps explain the electron configuration of atoms.
- It is named after the German physicist Friedrich Hund, who formulated it around 1925.
Example:
- Consider the carbon atom (Z=6), which has two 2p orbitals (2px and 2py) of equal energy.
- According to Hund's Rule, the two electrons in the 2p orbitals will occupy each orbital singly, with the same spin (up or down).
- The electron configuration of carbon will be 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1, with the two 2p electrons having the same spin.
Hund's Rule is an important principle in atomic physics and chemistry, helping to explain the electron configuration of atoms and the behavior of electrons in degenerate orbitals.
Aufbau Principle:
- States that electrons in an atom occupy the lowest available energy levels (orbitals) first.
- Electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy.
- Each electron occupies the lowest available orbital that is not already occupied by another electron.
- This principle applies to the ground state of an atom (the most stable electron configuration).
Key Points:
- The Aufbau Principle is used to build the electron configuration of an atom.
- Electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels (orbitals) first.
- The principle applies to the ground state of an atom.
- It is named after the German word "Aufbau," meaning "building up."
Steps to apply the Aufbau Principle:
1. Determine the number of electrons in the atom.
2. Start with the lowest energy level (1s orbital).
3. Fill each orbital with the maximum number of electrons (2 electrons for s and p orbitals, 6 electrons for d orbitals, and 14 electrons for f orbitals).
4. Move to the next higher energy level and repeat step 3 until all electrons are assigned.
Example:
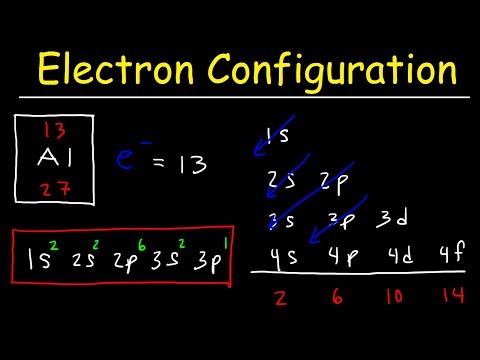
- Consider the carbon atom (Z=6) with 6 electrons.
- The electron configuration will be: 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1 (in order of increasing energy).
The Aufbau Principle is a fundamental principle in atomic physics and chemistry, helping to explain the electron configuration of atoms and the structure of the periodic table.
For More details visit
Hund's Rule:
- States that when filling orbitals of equal energy (degenerate orbitals), electrons will occupy each orbital singly before pairing up in any orbital.
- Applies to atomic orbitals with the same energy level (degenerate orbitals).
- Electrons will occupy each available orbital singly before filling any orbital with a second electron.
- All the electrons in the singly occupied orbitals will have the same spin (either all up or all down).
Key Points:
- Hund's Rule applies to degenerate orbitals, which have the same energy level.
- Electrons will occupy each orbital singly before pairing up in any orbital.
- This rule helps explain the electron configuration of atoms.
- It is named after the German physicist Friedrich Hund, who formulated it around 1925.
Example:
- Consider the carbon atom (Z=6), which has two 2p orbitals (2px and 2py) of equal energy.
- According to Hund's Rule, the two electrons in the 2p orbitals will occupy each orbital singly, with the same spin (up or down).
- The electron configuration of carbon will be 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1, with the two 2p electrons having the same spin.
Hund's Rule is an important principle in atomic physics and chemistry, helping to explain the electron configuration of atoms and the behavior of electrons in degenerate orbitals.
Aufbau Principle:
- States that electrons in an atom occupy the lowest available energy levels (orbitals) first.
- Electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy.
- Each electron occupies the lowest available orbital that is not already occupied by another electron.
- This principle applies to the ground state of an atom (the most stable electron configuration).
Key Points:
- The Aufbau Principle is used to build the electron configuration of an atom.
- Electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels (orbitals) first.
- The principle applies to the ground state of an atom.
- It is named after the German word "Aufbau," meaning "building up."
Steps to apply the Aufbau Principle:
1. Determine the number of electrons in the atom.
2. Start with the lowest energy level (1s orbital).
3. Fill each orbital with the maximum number of electrons (2 electrons for s and p orbitals, 6 electrons for d orbitals, and 14 electrons for f orbitals).
4. Move to the next higher energy level and repeat step 3 until all electrons are assigned.
Example:
- Consider the carbon atom (Z=6) with 6 electrons.
- The electron configuration will be: 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1 (in order of increasing energy).
The Aufbau Principle is a fundamental principle in atomic physics and chemistry, helping to explain the electron configuration of atoms and the structure of the periodic table.
 0:05:24
0:05:24
 0:10:47
0:10:47
 0:03:54
0:03:54
 0:04:27
0:04:27
 0:08:07
0:08:07
 0:09:25
0:09:25
 0:09:56
0:09:56
 0:13:03
0:13:03
 0:12:13
0:12:13
 0:03:56
0:03:56
 0:00:33
0:00:33
 0:03:59
0:03:59
 0:06:54
0:06:54
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:01:37
0:01:37
 0:05:13
0:05:13
 0:13:17
0:13:17
 0:10:19
0:10:19
 0:00:10
0:00:10
 0:03:36
0:03:36
 0:05:43
0:05:43
 0:00:08
0:00:08
 0:02:48
0:02:48
 0:15:25
0:15:25