filmov
tv
What is Pi? | Circles | Circumference | Don't Memorise

Показать описание
In this video, we will learn:
0:00 Introduction
0:12 Circumference
0:29 Diameter of the Circle
1:11 Value of Pi
2:04 Circumference Formula
3:06 Why do we use π Symbol for Pi?
3:59 Pi is the Ratio of the Circumference to the Diameter
Don’t Memorise brings learning to life through its captivating educational videos.
Register on our website to gain access to all videos and quizzes:
#Pi #PiArmy #Circles #neet2024 #infinityLearnNEET #neetsyllabus #neet2025
Math Antics - Circles, What Is PI?
What is Pi? | Circles | Circumference | Don't Memorise
Why is π = 3.14…??? #pivalue #circle #circles #geometry #maths #mathematics
Finding Pi Circles
Circles: What is Pi?
Math Antics - Circles, Circumference And Area
What is Pi? | Circles
What is pi ?I Understanding Circles and the Circumference
Make Circles For Any Occasion in Build A Boat For Treasure
Circles: radius, diameter, circumference and Pi | Geometry | Khan Academy
The infinite life of pi - Reynaldo Lopes
Circles - Area, Circumference, Radius & Diameter Explained!
Circles and Pi
e^(iπ) in 3.14 minutes, using dynamics | DE5
What is the Circumference of a Circle? | Perimeter of a Circle | Don't Memorise
What is Pi? | Circles & Circumference | Coding for Kids | Math for Kids | Havi
The History of Circles and the Origin of Pi 𝝅 (Made with Stop-Motion) | Verzon Homeschool Project |...
Exploring How Pi Works The Irrational Number Behind Circles
GCSE Maths from Scratch 21.04a Circles: Leaving answers in terms of Pi
Introduction to Circles: radius, diameter, circumference and pi
Proof Pi Exists, circumference over diameter is constant for all circles
Why is a Circle 360 Degrees, Why Not a Simpler Number, like 100?
Circles - Origins of Pi
Why is Circumference formula of a circle equal 2πr??? #pivalue #circle #circles #geometry #maths
Комментарии
 0:07:58
0:07:58
 0:04:45
0:04:45
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:04:54
0:04:54
 0:08:15
0:08:15
 0:07:56
0:07:56
 0:01:52
0:01:52
 0:03:00
0:03:00
 0:03:39
0:03:39
 0:11:05
0:11:05
 0:03:45
0:03:45
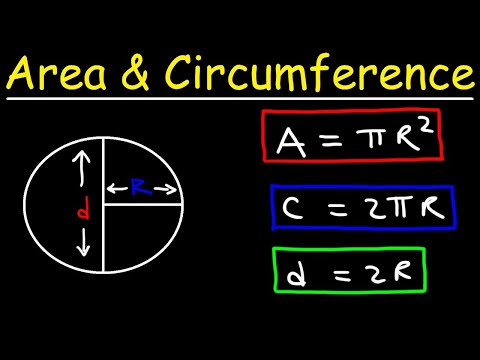 0:17:20
0:17:20
 0:09:43
0:09:43
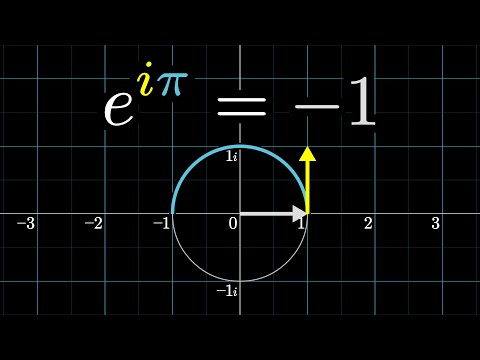 0:04:08
0:04:08
 0:03:44
0:03:44
 0:29:13
0:29:13
 0:03:58
0:03:58
 0:02:26
0:02:26
 0:01:50
0:01:50
 0:08:40
0:08:40
 0:02:36
0:02:36
 0:03:54
0:03:54
 0:06:30
0:06:30
 0:00:30
0:00:30