filmov
tv
Gestational Diabetes: Diagnosis and Treatment | Ohio State Medical Center

Показать описание
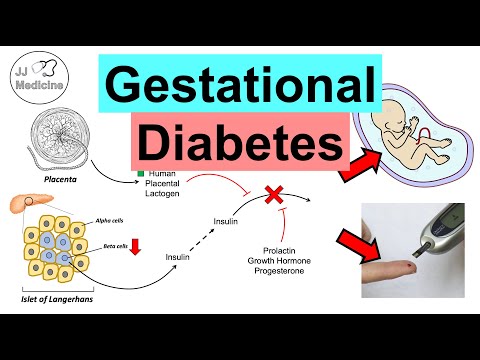
Because Gestational Diabetes typically doesn’t have symptoms, pregnant women are screened using a simple glucose tolerance test. Those at high risk will be screened earlier in pregnancy. Women are at greater risk for Gestational Diabetes if they have parents who had Type 2 Diabetes, are overweight, have had a large baby in the past, have sugar in their urine, have polycystic ovarian syndrome, or have had Gestational Diabetes before. In lower risk women, testing won’t occur until 24-28 weeks of a pregnancy. Complications of Gestational Diabetes include the baby becoming very large, causing a traumatic birth, and a higher lifetime risk for the baby of being overweight or developing diabetes themselves. Treatment of Gestational Diabetes typically involves a balanced diet and exercise, with medication only when required.
 0:03:45
0:03:45
 0:07:03
0:07:03
 0:16:55
0:16:55
 0:03:53
0:03:53
 0:05:06
0:05:06
 0:21:12
0:21:12
 0:02:52
0:02:52
 0:08:38
0:08:38
 0:39:30
0:39:30
 0:09:11
0:09:11
 0:02:36
0:02:36
 0:19:23
0:19:23
 0:08:02
0:08:02
 0:03:25
0:03:25
 0:06:01
0:06:01
 0:03:36
0:03:36
 0:02:19
0:02:19
 0:03:42
0:03:42
 0:00:55
0:00:55
 0:27:51
0:27:51
 0:09:21
0:09:21
 0:15:27
0:15:27
 0:02:52
0:02:52
 0:08:27
0:08:27