filmov
tv
Primary hemostasis | Advanced hematologic system physiology | Health & Medicine | Khan Academy

Показать описание
During primary hemostasis, a platelet plug is formed to rapidly stop the initial bleeding after injury. Learn about the different steps involved in primary hemostasis: vasoconstriction, platelet adhesion, activation and degranulation, platelet aggregation. Created by Gricelda Gomez.
Health & Medicine on Khan Academy: No organ quite symbolizes love like the heart. One reason may be that your heart helps you live, by moving ~5 liters (1.3 gallons) of blood through almost 100,000 kilometers (62,000 miles) of blood vessels every single minute! It has to do this all day, everyday, without ever taking a vacation! Now that is true love. Learn about how the heart works, how blood flows through the heart, where the blood goes after it leaves the heart, and what your heart is doing when it makes the sound “Lub Dub.”
For free. For everyone. Forever. #YouCanLearnAnything
Health & Medicine on Khan Academy: No organ quite symbolizes love like the heart. One reason may be that your heart helps you live, by moving ~5 liters (1.3 gallons) of blood through almost 100,000 kilometers (62,000 miles) of blood vessels every single minute! It has to do this all day, everyday, without ever taking a vacation! Now that is true love. Learn about how the heart works, how blood flows through the heart, where the blood goes after it leaves the heart, and what your heart is doing when it makes the sound “Lub Dub.”
For free. For everyone. Forever. #YouCanLearnAnything
Primary hemostasis | Advanced hematologic system physiology | Health & Medicine | Khan Academy
Hemostasis | Advanced hematologic system physiology | Health & Medicine | Khan Academy
Hematology | Hemostasis: Coagulation Cascade
Primary Hemostasis - Part 1: Platelet Adhesion
Secondary hemostasis | Advanced hematologic system physiology | Health & Medicine | Khan Academy
Primary vs Secondary Hemostasis - Blood Clotting (Coagulation) - Hematology
🥧 🥕 WHILE I COOK | Platelet Plug | Primary Hemostasis | Basic Hematologic Physiology Animation
Primary Hemostasis: FUN and SIMPLE!
Platelet Plug - Primary Hemostasis - Platelet Adhesion & Aggregation - How The Clot Forms!
Primary Hemostasis - Platelet Plug & Blood Clot- Mnemonic
1. Primary hemostasis
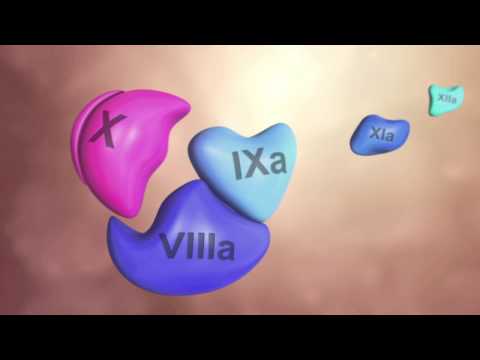
Coagulation Cascade Animation - Physiology of Hemostasis
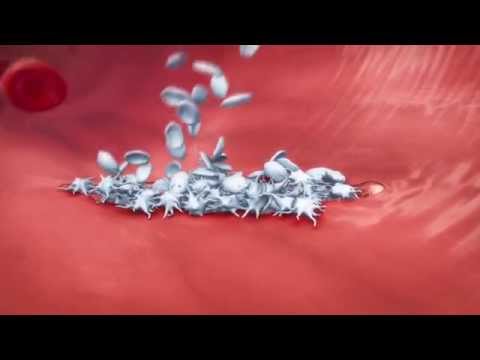
Primary Hemostasis: Platelet Plug Formation [Step-by-Step Animation]
Hemostasis, Types of hemostasis, Primary Hemostasis, Secondary Hemostasis, Physiology Made Easy
PRIMARY HEMOSTASIS (PLATELETS FUNCTION) D&N Medical Series
Platelet Plug Formation - Mechanisms
Platelet Activation and Factors for Clot Formation
Primary hemostasis | Advanced hematologic system physiology | Khan Academy Urdu
Hematologic System: Blood Components and Hemostasis - Medical-Surgical- Cardiovascular |@LevelUpRN
Primary Hemostasis - Part 2: Platelet Activation
Coagulation Cascade and Fibrinolysis - clotting factors, regulation and control mechanism
Primary Hemostasis Physiology of Platelets Adhesion and Aggregation | V-Learning™
Bleeding disorders (Primary Hemostasis)
Blood Clotting (Hemostasis)
Комментарии
 0:10:51
0:10:51
 0:06:25
0:06:25
 0:43:13
0:43:13
 0:07:47
0:07:47
 0:03:57
0:03:57
 0:12:32
0:12:32
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:03:30
0:03:30
 0:15:27
0:15:27
 0:04:45
0:04:45
 0:03:46
0:03:46
 0:02:30
0:02:30
 0:08:36
0:08:36
 0:01:28
0:01:28
 0:07:21
0:07:21
 0:04:19
0:04:19
 0:02:08
0:02:08
 0:10:12
0:10:12
 0:04:59
0:04:59
 0:08:08
0:08:08
 0:09:58
0:09:58
 0:12:01
0:12:01
 0:12:03
0:12:03
 0:04:38
0:04:38