filmov
tv
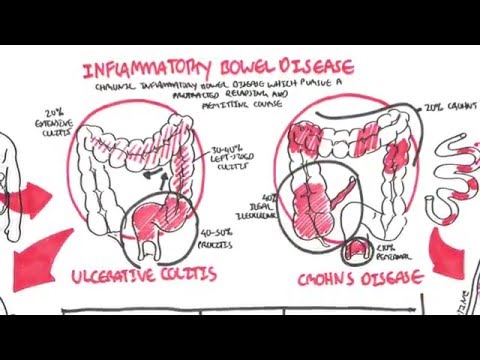
Inflammatory Bowel Disease

Показать описание
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are chronic inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) that can occur at any age but mostly affect young people. They are lifelong conditions with no known cure, characterised by periods of flare and remission.
Across the western world IBD current affects nearly 1% of the population; in newly industrialised countries the incidence is rising rapidly along with adoption of a western lifestyle. Environmental factors – notably diet, the gut microbiome and genetics are all involved in the development of IBD.
The symptoms of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis can be intrusive - pain, diarrhoea, bleeding, urgency, loss of appetite, weight loss, nausea and fatigue. IBD can significantly impact mental health, with high rates of anxiety & depression.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is NOT irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) but they can co-exist. In IBD the central process is gut inflammation – this requires treatment with anti-inflammation medicines as it may lead to irreversible bowel damage. These include steroids, immunosuppressants and biologic medicines. Newer therapies are increasingly effective and targeted. Whilst advanced therapies are typically expensive, biosimilar versions are increasingly available at a fraction of the cost. There is a disconnect between symptoms and gut inflammation - the goal is to treat and monitor both.
It is now possible in many newly diagnosed patients to completely induce remission and maintain this safely long term. However, all too commonly the drugs are ineffective or associated with side effects and many patients will require major surgery with portions of the intestine removed and stoma formation.
Across the western world IBD current affects nearly 1% of the population; in newly industrialised countries the incidence is rising rapidly along with adoption of a western lifestyle. Environmental factors – notably diet, the gut microbiome and genetics are all involved in the development of IBD.
The symptoms of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis can be intrusive - pain, diarrhoea, bleeding, urgency, loss of appetite, weight loss, nausea and fatigue. IBD can significantly impact mental health, with high rates of anxiety & depression.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is NOT irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) but they can co-exist. In IBD the central process is gut inflammation – this requires treatment with anti-inflammation medicines as it may lead to irreversible bowel damage. These include steroids, immunosuppressants and biologic medicines. Newer therapies are increasingly effective and targeted. Whilst advanced therapies are typically expensive, biosimilar versions are increasingly available at a fraction of the cost. There is a disconnect between symptoms and gut inflammation - the goal is to treat and monitor both.
It is now possible in many newly diagnosed patients to completely induce remission and maintain this safely long term. However, all too commonly the drugs are ineffective or associated with side effects and many patients will require major surgery with portions of the intestine removed and stoma formation.
Комментарии
 0:08:59
0:08:59
 0:13:33
0:13:33
 1:06:30
1:06:30
 0:06:39
0:06:39
 0:05:21
0:05:21
 0:03:34
0:03:34
 0:06:38
0:06:38
 0:27:27
0:27:27
 0:13:40
0:13:40
 0:54:26
0:54:26
 0:21:00
0:21:00
 0:02:37
0:02:37
 0:05:06
0:05:06
 0:46:38
0:46:38
 0:17:24
0:17:24
 0:01:31
0:01:31
 0:05:23
0:05:23
 0:04:39
0:04:39
 0:11:52
0:11:52
 0:06:07
0:06:07
 0:11:36
0:11:36
 0:09:52
0:09:52
 0:15:56
0:15:56
 0:00:38
0:00:38