filmov
tv
Mathematical Olympiad | Solve for a+b | Math Olympiad Preparation

Показать описание
Today I will teach you tips and tricks to solve the given olympiad math question in a simple and easy way. Learn how to prepare for Math Olympiad fast!
Need help with solving this Math Olympiad Question? You're in the right place!
I have over 20 years of experience teaching Mathematics at American schools, colleges, and universities. Learn more about me at
Mathematical Olympiad | Solve for a+b | Math Olympiad Preparation
#OlympiadMathematics #OlympiadPreparation #CollegeEntranceExam
#OlympiadMathematicalQuestion #HowToSolveOlympiadQuestion #MathOlympiadQuestion #MathOlympiadQuestions #OlympiadQuestion #Olympiad #AlgebraReview #Algebra #Mathematics #Math #Maths
#MathOlympiadPreparation #LearntipstosolveOlympiadMathQuestionfast #OlympiadMathematicsCompetition #MathOlympics #SolveSystemofEquations
#blackpenredpen #solveTheEquation #OlympiadMathematics #solveTheQuadraticEquation #MathematicalOlympiad
How to solve Olympiad Mathematical Question
How to prepare for Math Olympiad
How to Solve Olympiad Question
How to Solve international math olympiad questions
international math olympiad questions and solutions
international math olympiad questions and answers
olympiad mathematics competition
blackpenredpen
math olympics
olympiad exam
olympiad exam sample papers
math olympiad sample questions
math olympiad
British Math Olympiad
olympics math
olympics mathematics
olympics math activities
olympics math competition
Math Olympiad Training
How to win the International Math Olympiad | Po-Shen Loh and Lex Fridman
Po-Shen Loh and Lex Fridman
Number Theory
There is a ridiculously easy way to solve this Olympiad qualifier problem
This U.S. Olympiad Coach Has a Unique Approach to Math
The Map of Mathematics
mathcounts
math at work
exponential equation
system of equations
solve system of equations
solve the equation
solve the cubic equation
cubic equation
Po Shen Loh
pre math
Olympiad Mathematics
Mathematical Olympiad
Subscribe Now as the ultimate shots of Math doses are on their way to fill your minds with the knowledge and wisdom once again.
Комментарии
 0:02:34
0:02:34
 0:09:42
0:09:42
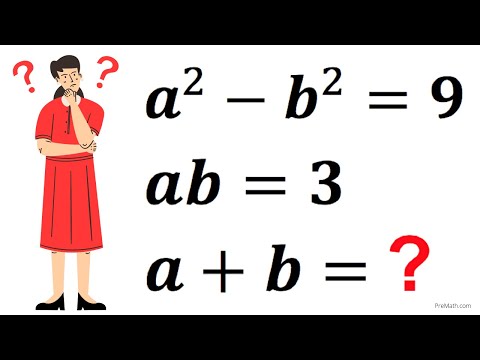 0:08:59
0:08:59
 0:08:03
0:08:03
 0:03:21
0:03:21
 0:06:40
0:06:40
 0:12:10
0:12:10
 0:02:51
0:02:51
 0:01:45
0:01:45
 0:01:54
0:01:54
 0:08:06
0:08:06
 0:08:40
0:08:40
 0:10:09
0:10:09
 0:16:03
0:16:03
 0:02:24
0:02:24
 0:09:33
0:09:33
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:03:20
0:03:20
 0:11:32
0:11:32
 0:11:59
0:11:59
 0:07:01
0:07:01
 0:00:50
0:00:50
 0:08:36
0:08:36
 0:00:52
0:00:52