filmov
tv
Elementary Rate Laws - Unimolecular, Bimolecular and Termolecular Reactions - Chemical Kinetics
Показать описание
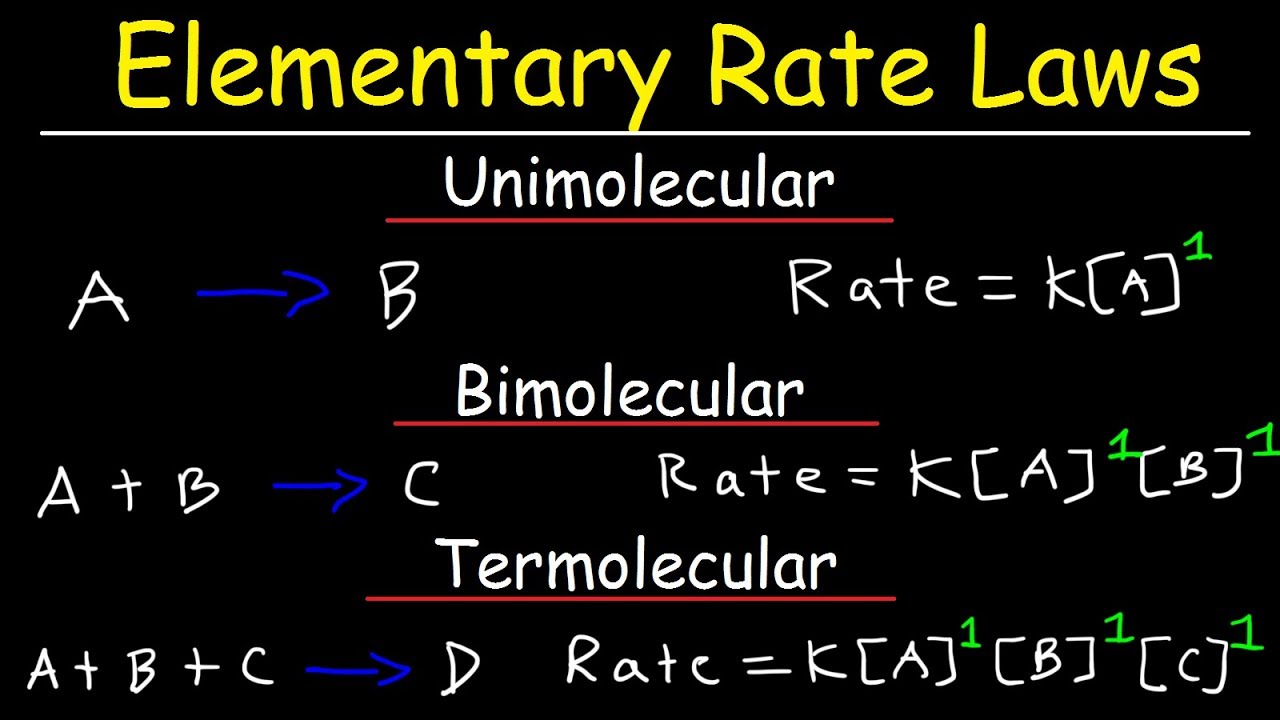
This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into elementary reactions and elementary rate laws. It explains the difference between unimolecular, bimolecular, and Termolecular reactions. An elementary reaction is one in which the rate law can be written from the coefficients of the balanced chemical equation and agrees with empirical data. A unimolecular reaction is a reaction that can proceed using a single molecule. A bimolecular reaction is one in which two molecules must collide in order to react. Termolecular reactions require the collision of three molecules.
Chem Kinetics Formula Sheet:
______________________________
Chemical Kinetics - Initial Rate Method:
Rate Constant k - Find The Units:
Integrated Rate Laws - 1st & 2nd Order:
Reaction Rate Factors:
Collision Theory & Activation Energy:
___________________________________
Potential Energy Diagrams:
Elementary Rate Laws:
Rate Laws of Reaction Mechanisms:
Intermediates & Catalysts:
Types of Catalysts:
____________________________________
The Equilibrium Expression:
Calculating Kp From Kc:
Chemical Equilibrium & Ice Tables:
Le Chatelier's Principle:
Acids and Bases - Introduction:
______________________________________
Final Exams and Video Playlists:
Full-Length Videos and Worksheets:
Chemistry PDF Worksheets:
Chem Kinetics Formula Sheet:
______________________________
Chemical Kinetics - Initial Rate Method:
Rate Constant k - Find The Units:
Integrated Rate Laws - 1st & 2nd Order:
Reaction Rate Factors:
Collision Theory & Activation Energy:
___________________________________
Potential Energy Diagrams:
Elementary Rate Laws:
Rate Laws of Reaction Mechanisms:
Intermediates & Catalysts:
Types of Catalysts:
____________________________________
The Equilibrium Expression:
Calculating Kp From Kc:
Chemical Equilibrium & Ice Tables:
Le Chatelier's Principle:
Acids and Bases - Introduction:
______________________________________
Final Exams and Video Playlists:
Full-Length Videos and Worksheets:
Chemistry PDF Worksheets:
Комментарии
 0:04:28
0:04:28
 0:09:10
0:09:10
 0:18:48
0:18:48
 0:08:42
0:08:42
 0:05:05
0:05:05
 0:05:35
0:05:35
 0:05:41
0:05:41
 0:01:46
0:01:46
 0:01:55
0:01:55
 0:10:14
0:10:14
 0:04:36
0:04:36
 0:06:17
0:06:17
 0:36:56
0:36:56
 0:06:13
0:06:13
 0:07:46
0:07:46
 0:01:11
0:01:11
 0:08:39
0:08:39
 0:02:33
0:02:33
 0:06:01
0:06:01
 0:02:40
0:02:40
 0:08:51
0:08:51
 0:04:12
0:04:12
 0:04:48
0:04:48
 0:10:01
0:10:01