filmov
tv
Integral of absolute value of x or abs(x)

Показать описание
This calculus video tutorial explains how to find the integral of absolute value of x or abs(x) using graphs and piecewise functions as well as the power rule for integration.
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Definite Integral with Absolute Value |2x - 7| from 0 to 7/2
Integral of absolute value of x or abs(x)
Absolute Value Integrals
Definite integral of absolute value function | AP Calculus AB | Khan Academy
How to evaluate the definite integral with absolute value
Absolute value integral
Definite Integral with Absolute Value (Example)
Integral of abs(x) in 44 seconds!
Integrals involving absolute value function - Integral of Absolute value - Calculus
Evaluate the definite integral with absolute value
Definite Integral of the Absolute Value of x from -1 to 2
Integral of The Absolute Value of Sine from 0 to 3pi/2
Evaluating Definite Integral with Absolute Value
Ex: Definite Integration of an Absolute Value Function Using Geometric Formula
Definite Integral of an Absolute Value Function ❖ Calculus
Definite Integral with Absolute Value
The TRUE Integral of |x|, the absolute value. | Shorts
Learn how to evaluate the definite integral of absolute value by graphing
Evaluating the integral of an absolute value function
Setting Up Definite Integral of Absolute Value Function
The Integral and Derivative of an Absolute Value
How to evaluate the definite integral of absolute value
Absolute Value Definite Integral - Example 1
Integral of absolute value of x (abs x)
Комментарии
 0:04:44
0:04:44
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:13:26
0:13:26
 0:06:52
0:06:52
 0:04:33
0:04:33
 0:16:09
0:16:09
 0:07:17
0:07:17
 0:00:44
0:00:44
 0:29:00
0:29:00
 0:03:00
0:03:00
 0:03:02
0:03:02
 0:04:51
0:04:51
 0:03:16
0:03:16
 0:04:21
0:04:21
 0:05:23
0:05:23
 0:08:25
0:08:25
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:02:22
0:02:22
 0:08:55
0:08:55
 0:03:06
0:03:06
 0:06:26
0:06:26
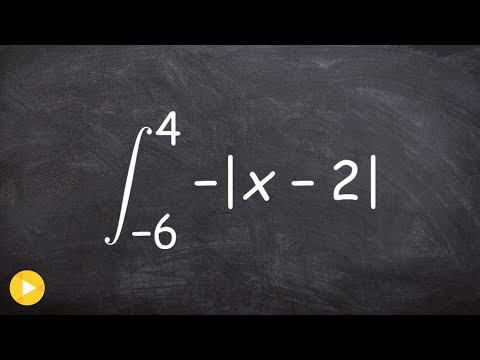 0:04:18
0:04:18
 0:10:36
0:10:36
 0:02:19
0:02:19