filmov
tv
Homogeneous Transformation Matrices | 3D robots | Robotics 201

Показать описание
In this video, we discuss how to construct the homogeneous transformation matrix and more importantly, what information it contains.
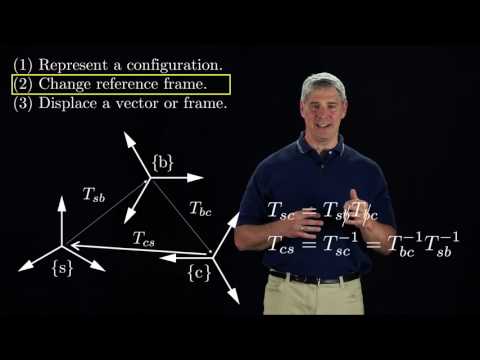
It is basically a 4x4 matrix for 3D robots which is comprised of a rotation matrix and a displacement vector coupled together. It is used for coordinate transformations.
Note: For coordinate transformation when using the Homogeneous matrix (X = H*x), remember that the points (X & x) are expressed in a homogenous form such that they are a 4x1 vector. The last element is a '1'.
❓ Do you have trouble understanding or find this concept difficult?
------
This video is part of the Robotics 201 tutorial series which covers kinematics and modeling of 3D robots.
This tutorial lesson series starts out from the very basics of robotics (assuming no prior knowledge) and gradually builds on in bite-sized videos of 10 minutes or less. By following along, you will soon become extremely good in the kinematics and modeling aspects of robots. And these will help you to design and build robots.
Here's what we will cover in this video series:
1. Co-ordinate Transformation for 3D robots
2. Homogeneous Transformations for 3D robots
3. Forward Kinematics
4. Inverse Kinematics
5. Robotic wrists (end-effector)
6. End-effector Velocities and Jacobians
7. Singularities of robots
8. Gimbal Locks
9. Forces & Torques
I will be uploading 1 video per week. If you find these helpful, don't forget to share and subscribe!
_____________________________
Robotics 201 - Robotics full course for beginners - Kinematics and Modeling
#roboticsforbeginners #roboticsTutorials #robotics #learnrobotics#homogenoustransformationmatrices #configuration #rotationmatrix #mechatronics #orientation #orientationinrobotics #transformationmatrices #displacementinrobotics #poseinrobotics #pose #translationandrotation
It is basically a 4x4 matrix for 3D robots which is comprised of a rotation matrix and a displacement vector coupled together. It is used for coordinate transformations.
Note: For coordinate transformation when using the Homogeneous matrix (X = H*x), remember that the points (X & x) are expressed in a homogenous form such that they are a 4x1 vector. The last element is a '1'.
❓ Do you have trouble understanding or find this concept difficult?
------
This video is part of the Robotics 201 tutorial series which covers kinematics and modeling of 3D robots.
This tutorial lesson series starts out from the very basics of robotics (assuming no prior knowledge) and gradually builds on in bite-sized videos of 10 minutes or less. By following along, you will soon become extremely good in the kinematics and modeling aspects of robots. And these will help you to design and build robots.
Here's what we will cover in this video series:
1. Co-ordinate Transformation for 3D robots
2. Homogeneous Transformations for 3D robots
3. Forward Kinematics
4. Inverse Kinematics
5. Robotic wrists (end-effector)
6. End-effector Velocities and Jacobians
7. Singularities of robots
8. Gimbal Locks
9. Forces & Torques
I will be uploading 1 video per week. If you find these helpful, don't forget to share and subscribe!
_____________________________
Robotics 201 - Robotics full course for beginners - Kinematics and Modeling
#roboticsforbeginners #roboticsTutorials #robotics #learnrobotics#homogenoustransformationmatrices #configuration #rotationmatrix #mechatronics #orientation #orientationinrobotics #transformationmatrices #displacementinrobotics #poseinrobotics #pose #translationandrotation
Комментарии
 0:18:05
0:18:05
 0:06:53
0:06:53
 0:15:24
0:15:24
 0:06:22
0:06:22
 0:09:24
0:09:24
 0:12:56
0:12:56
 0:10:02
0:10:02
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:00:19
0:00:19
 0:05:32
0:05:32
 0:09:56
0:09:56
 0:25:18
0:25:18
 0:11:55
0:11:55
 0:09:08
0:09:08
 0:11:14
0:11:14
 0:13:20
0:13:20
 0:10:59
0:10:59
 0:18:21
0:18:21
 0:15:44
0:15:44
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:12:39
0:12:39
 0:18:22
0:18:22
 1:03:48
1:03:48
 0:10:13
0:10:13