filmov
tv
Alcohols to Alkyl Bromides, Part 1: Hydrogen Bromide

Показать описание
In this first part of my video playlist about the best methods to convert aliphatic alcohols into alkyl bromides the use of hydrogen bromide as deoxybrominating reagent is described. In the second part, the use of reagents containing phosphorus-bromine bonds and some other, more exotic reagents will be discussed.
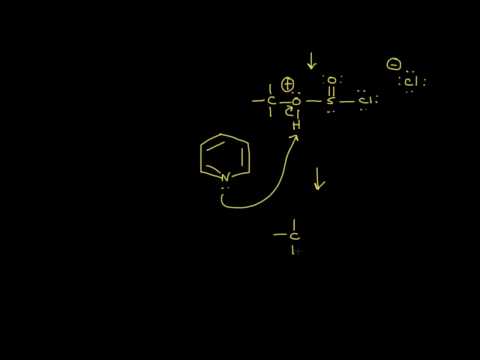
Depending on the reactivity of the alcohol and on the solvent chosen, deoxybromination by HBr can proceed by carbocation formation or by an SN2-type displacement of a protonated hydroxyl group.
In addition to carbocation rearrangements, typical side reactions include the formation of ethers or of olefins by elimination. Olefins can also be converted into alkyl bromides by treatment with HBr, but bromide usually adds to the more stable secondary or tertiary carbocation, and primary alkyl bromides can therefore not be prepared from terminal olefins. Only terminal electron-deficient alkenes will add bromide at the methylene group and yield primary alkyl bromides.
Further examples:
Org. Proc. Res. Dev. 2010, 14, 1215-1220; 544-552; 2003, 7, 339-340;
Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 3727-3728 (ionic liquids);
Org. Syn. . 1993, 71, 220 (Ar3COH); 1987, 65, 119 (PhtNCH2OH);
J. Chem. Soc. Perkin 1 1987, 2157-2158 (continuous);
GB 1212240 (1970; Br2, P(OH)3);
Org. Syn. 1965, 45, 42 (g-butyrolactone); 1958, 38, 68 (pentaerythritol);
GB 730682 (1955, Br2, sulfur, MeOH to MeBr);
J. Chem. Edu. 1949, 26, 329 (KBr, H2SO4);
Org. Syn. 1940, 20, 24; 1938, 18, 13 (2-aminoethanol); 1935, 15, 24 (dodecanol); 1921, 1, 3.
Depending on the reactivity of the alcohol and on the solvent chosen, deoxybromination by HBr can proceed by carbocation formation or by an SN2-type displacement of a protonated hydroxyl group.
In addition to carbocation rearrangements, typical side reactions include the formation of ethers or of olefins by elimination. Olefins can also be converted into alkyl bromides by treatment with HBr, but bromide usually adds to the more stable secondary or tertiary carbocation, and primary alkyl bromides can therefore not be prepared from terminal olefins. Only terminal electron-deficient alkenes will add bromide at the methylene group and yield primary alkyl bromides.
Further examples:
Org. Proc. Res. Dev. 2010, 14, 1215-1220; 544-552; 2003, 7, 339-340;
Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 3727-3728 (ionic liquids);
Org. Syn. . 1993, 71, 220 (Ar3COH); 1987, 65, 119 (PhtNCH2OH);
J. Chem. Soc. Perkin 1 1987, 2157-2158 (continuous);
GB 1212240 (1970; Br2, P(OH)3);
Org. Syn. 1965, 45, 42 (g-butyrolactone); 1958, 38, 68 (pentaerythritol);
GB 730682 (1955, Br2, sulfur, MeOH to MeBr);
J. Chem. Edu. 1949, 26, 329 (KBr, H2SO4);
Org. Syn. 1940, 20, 24; 1938, 18, 13 (2-aminoethanol); 1935, 15, 24 (dodecanol); 1921, 1, 3.
 0:16:07
0:16:07
 0:11:09
0:11:09
 0:12:28
0:12:28
 0:07:27
0:07:27
 0:09:20
0:09:20
 0:05:48
0:05:48
 0:04:36
0:04:36
 0:16:34
0:16:34
 0:08:54
0:08:54
 0:03:45
0:03:45
 0:08:26
0:08:26
 0:10:42
0:10:42
 0:26:56
0:26:56
 0:06:27
0:06:27
 0:11:23
0:11:23
 0:05:36
0:05:36
 0:16:30
0:16:30
 0:12:37
0:12:37
 0:45:19
0:45:19
 0:14:28
0:14:28
 0:14:56
0:14:56
 0:11:54
0:11:54
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:37:34
0:37:34