filmov
tv
Diffusion Animation!
Показать описание
One of the most important processes in biology is diffusion, the movement of particles from high concentration to low concentration. This process is passive, meaning that NO energy is used by the cell to make it happen.
So, how does diffusion work?
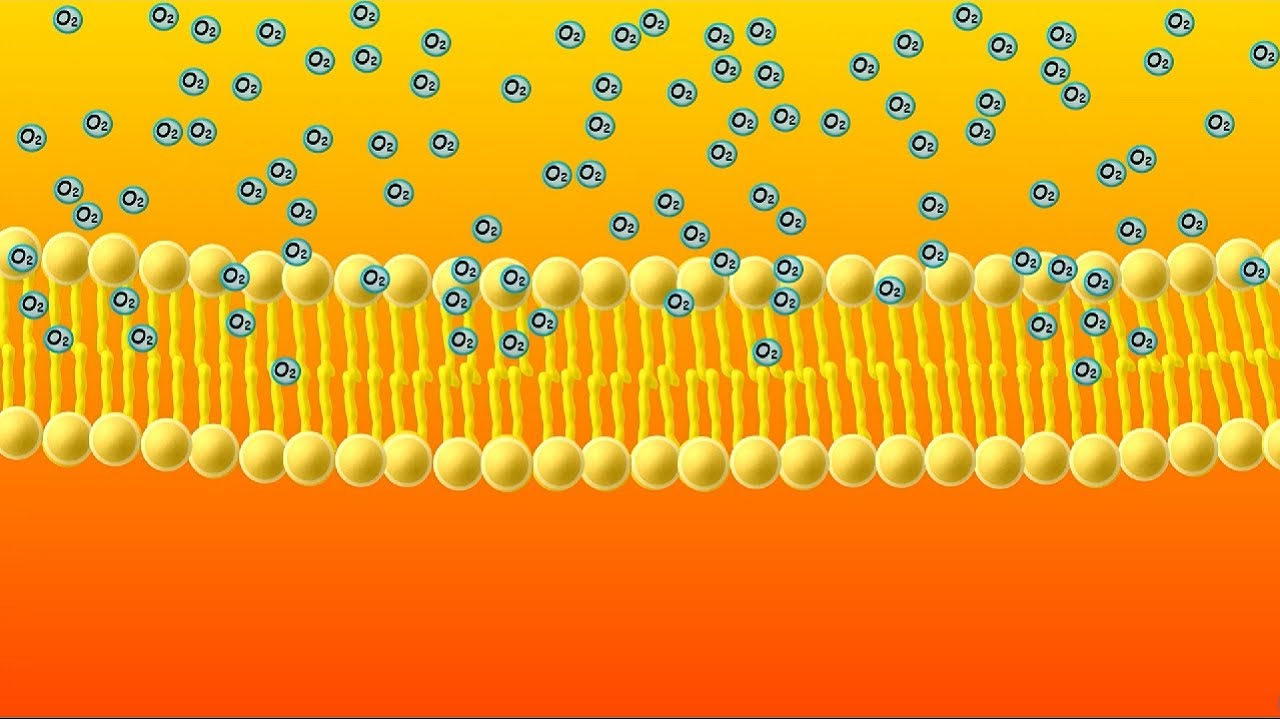
We will focus on simple diffusion across the phospholipid bilayer of a membrane, shown here. Notice that we have a high concentration of oxygen on one side of the membrane and a low concentration on the other side. I’m going to give you a second to think about this question: Which direction will the oxygen move? Make a hypothesis.
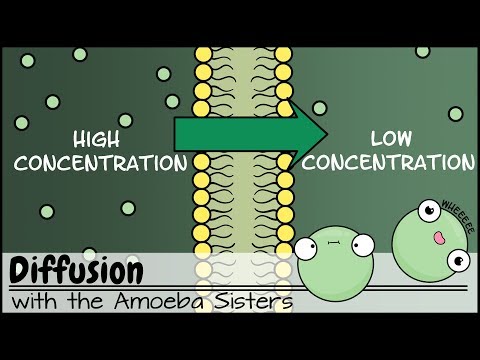
If you said that it will move down, toward the low concentration area, you are correct. Overall, molecules move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. Another way to say this is that they move DOWN THEIR CONCENTRATION GRADIENT.
But why do they do this? The answer is a bit more complex. Although we sometimes like to use analogies and say that molecules “want” to move from high to low, or that they “like” to have personal space and spread out to avoid being close to others, in reality molecules don’t really “like” or “want” anything.
Instead, diffusion happens because molecules are in constant random motion. Here is a model that shows this. Check it out.
Notice that the molecules move around randomly in every direction, but that overall they move from high to low concentration as they bounce around until there are roughly equal concentrations on both sides of the membrane. So, the net movement is from high to low concentration until equilibrium is reached. Equilibrium is when the concentrations on both sides are equal. But notice that movement continues even after equilibrium is reached. For this reason, we sometimes call this dynamic equilibrium. Molecules are still moving but there isn’t a net movement in any particular direction.
Now, let’s take a look at a model of a really important real-life use of diffusion, keeping you alive by getting oxygen into your blood. Take a deep breath and we’re going to look at what’s happening in your lungs as a result.
When you breathe in, oxygen rushes into your lungs producing a high concentration of oxygen in your lung tissues. This oxygen can then diffuse into your blood where it is picked up by red blood cells which carry the oxygen away. This ensures that the oxygen you breathed in can continue to diffuse down its concentration gradient (from high to low) into the bloodstream, keeping you alive.
Credits:
So, how does diffusion work?
We will focus on simple diffusion across the phospholipid bilayer of a membrane, shown here. Notice that we have a high concentration of oxygen on one side of the membrane and a low concentration on the other side. I’m going to give you a second to think about this question: Which direction will the oxygen move? Make a hypothesis.
If you said that it will move down, toward the low concentration area, you are correct. Overall, molecules move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. Another way to say this is that they move DOWN THEIR CONCENTRATION GRADIENT.
But why do they do this? The answer is a bit more complex. Although we sometimes like to use analogies and say that molecules “want” to move from high to low, or that they “like” to have personal space and spread out to avoid being close to others, in reality molecules don’t really “like” or “want” anything.
Instead, diffusion happens because molecules are in constant random motion. Here is a model that shows this. Check it out.
Notice that the molecules move around randomly in every direction, but that overall they move from high to low concentration as they bounce around until there are roughly equal concentrations on both sides of the membrane. So, the net movement is from high to low concentration until equilibrium is reached. Equilibrium is when the concentrations on both sides are equal. But notice that movement continues even after equilibrium is reached. For this reason, we sometimes call this dynamic equilibrium. Molecules are still moving but there isn’t a net movement in any particular direction.
Now, let’s take a look at a model of a really important real-life use of diffusion, keeping you alive by getting oxygen into your blood. Take a deep breath and we’re going to look at what’s happening in your lungs as a result.
When you breathe in, oxygen rushes into your lungs producing a high concentration of oxygen in your lung tissues. This oxygen can then diffuse into your blood where it is picked up by red blood cells which carry the oxygen away. This ensures that the oxygen you breathed in can continue to diffuse down its concentration gradient (from high to low) into the bloodstream, keeping you alive.
Credits:
Комментарии
 0:00:19
0:00:19
 0:02:55
0:02:55
 0:00:52
0:00:52
 0:01:36
0:01:36
 0:03:32
0:03:32
 0:00:24
0:00:24
 0:00:26
0:00:26
 0:09:46
0:09:46
 0:05:10
0:05:10
 0:02:17
0:02:17
 0:02:05
0:02:05
 0:07:40
0:07:40
 0:00:34
0:00:34
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:04:14
0:04:14
 0:00:09
0:00:09
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:00:41
0:00:41
 0:02:36
0:02:36
 0:06:24
0:06:24
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:10:25
0:10:25
 0:02:07
0:02:07
 0:01:56
0:01:56