filmov
tv
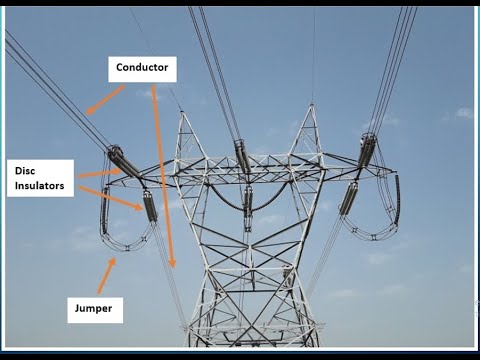
Power Line Transmission (400kv OHL) Horizontal and Vertical Clearance with Diagram in Urdu/Hindi

Показать описание
When it comes to 400 kV transmission lines, ensuring appropriate horizontal and vertical clearances is crucial for safety, operational efficiency, and reliability. These clearances are defined by regulatory standards in many countries, often referencing international standards like those from the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) or country-specific codes such as the Indian Electricity Rules or National Electric Safety Code (NESC) in the U.S.
Clearance Requirements for 400 kV Lines
Vertical Clearance:
The minimum vertical clearance is the distance from the ground or any object beneath the conductor to the lowest point of the conductor under maximum sag conditions.
Ground clearance:
For 400 kV lines, the typical vertical clearance from the ground is approximately 7.0 - 8.84 meters depending on factors like the terrain and specific regulatory standards.
Clearance from buildings:
For inhabited areas or buildings, the vertical clearance can be about 3-5 meters higher than the standard ground clearance.
Horizontal Clearance:
The horizontal clearance between conductors and objects such as trees, buildings, or other transmission structures is crucial to prevent electrical arcing.
From nearby structures:
The minimum horizontal clearance from the centerline of the transmission line to any building is usually about 8-12 meters.
Clearance between conductors:
The horizontal separation between the conductors themselves (phase-to-phase clearance) is also important for preventing short circuits and ensuring safe operation. Typically, the horizontal clearance between phases of a 400 kV transmission line is about 8-10 meters.
Clearance Requirements for 400 kV Lines
Vertical Clearance:
The minimum vertical clearance is the distance from the ground or any object beneath the conductor to the lowest point of the conductor under maximum sag conditions.
Ground clearance:
For 400 kV lines, the typical vertical clearance from the ground is approximately 7.0 - 8.84 meters depending on factors like the terrain and specific regulatory standards.
Clearance from buildings:
For inhabited areas or buildings, the vertical clearance can be about 3-5 meters higher than the standard ground clearance.
Horizontal Clearance:
The horizontal clearance between conductors and objects such as trees, buildings, or other transmission structures is crucial to prevent electrical arcing.
From nearby structures:
The minimum horizontal clearance from the centerline of the transmission line to any building is usually about 8-12 meters.
Clearance between conductors:
The horizontal separation between the conductors themselves (phase-to-phase clearance) is also important for preventing short circuits and ensuring safe operation. Typically, the horizontal clearance between phases of a 400 kV transmission line is about 8-10 meters.
 0:06:08
0:06:08
 0:03:28
0:03:28
 0:00:18
0:00:18
 0:03:15
0:03:15
 0:00:27
0:00:27
 0:04:23
0:04:23
 0:03:19
0:03:19
 0:10:25
0:10:25
 0:06:57
0:06:57
 0:13:03
0:13:03
 0:15:07
0:15:07
 0:03:05
0:03:05
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:06:07
0:06:07
 0:06:04
0:06:04
 0:09:15
0:09:15
 0:05:35
0:05:35
 0:03:05
0:03:05
 0:08:46
0:08:46
 0:00:21
0:00:21
 0:18:42
0:18:42
 0:05:40
0:05:40
 0:00:20
0:00:20
 0:00:32
0:00:32