filmov
tv
Understanding de Broglie Equation

Показать описание
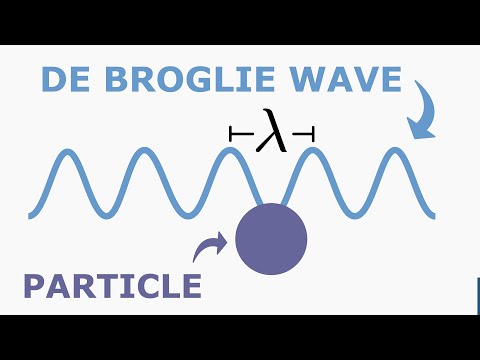
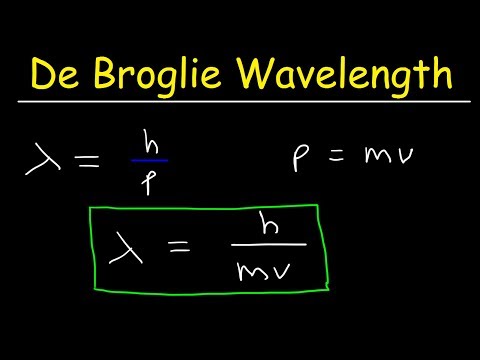
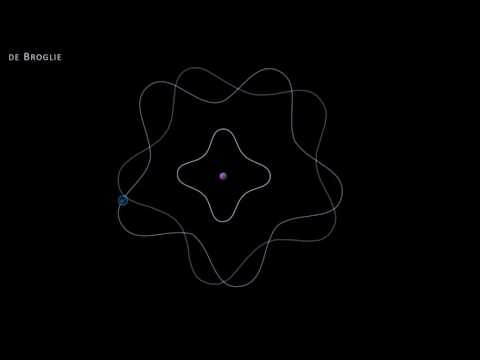
The early 20th century marked a revolutionary period in physics, with the development of quantum mechanics fundamentally altering our understanding of the physical world. Among the ground-breaking ideas introduced during this era, one of the most profound was Louis de Broglie's hypothesis of matter waves, encapsulated in what is now known as the de Broglie equation. This equation elegantly bridged the gap between the classical and quantum realms, suggesting that particles of matter, like photons, possess both wave-like and particle-like properties. The de Broglie equation is a fundamental principle in quantum mechanics that relates the wavelength of a particle to its momentum. It was proposed by the French physicist Louis de Broglie in 1924. The de Broglie equation is expressed as the wavelength of a particle being equal to Planck's constant divided by the particle's momentum. This equation suggests that all matter exhibits wave-like properties, a concept known as wave-particle duality. For macroscopic objects, the wavelength is so small that it's negligible, but for very small particles like electrons, this wavelength becomes significant and can be observed.
 0:11:20
0:11:20
 0:09:05
0:09:05
 0:01:16
0:01:16
 0:05:15
0:05:15
 0:10:37
0:10:37
 0:01:43
0:01:43
 0:11:21
0:11:21
 0:19:00
0:19:00
 0:11:53
0:11:53
 0:21:29
0:21:29
 0:08:12
0:08:12
 0:03:02
0:03:02
 0:07:35
0:07:35
 0:10:09
0:10:09
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:08:41
0:08:41
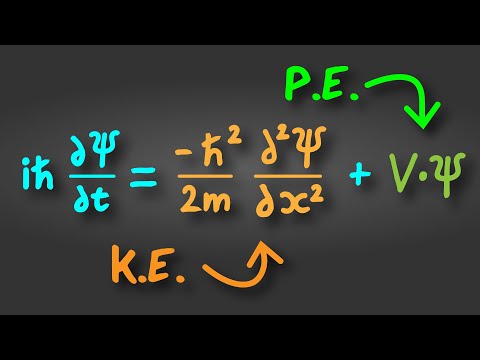 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:12:21
0:12:21
 0:04:58
0:04:58
 0:33:23
0:33:23
 0:08:33
0:08:33
 0:02:37
0:02:37
 0:01:39
0:01:39
 0:00:05
0:00:05