filmov
tv
Dynein Motor Protein

Показать описание
Dyneins are a family of cytoskeletal motor proteins that move along microtubules in cells. They convert the chemical energy stored in ATP to mechanical work. Dynein transports various cellular cargos, provides forces and displacements important in mitosis, and drives the beat of eukaryotic cilia and flagella. All of these functions rely on dynein's ability to move towards the minus-end of the microtubules, known as retrograde transport; thus, they are called "minus-end directed motors". In contrast, most kinesin motor proteins move toward the microtubules' plus-end, in what is called anterograde transport.
Dynein Motor Protein
Kinesin protein walking on microtubule
Kinesin Motor Protein 3D Animation (with Labels)
Ron Vale (UCSF, HHMI) 2: Molecular Motor Proteins: The Mechanism of Dynein Motility
Tiny Motor Proteins
Motor Protein Driven Transport of Microtubules
A Day in the Life of a Motor Protein
Motor proteins | dynein, kinesin, myosin
Dynein Animation
Motor Proteins: Tiny Pirates in Your Cells
The protein molecule drags the endorphin hormone.
Ron Vale (UCSF, HHMI) 1: Molecular Motor Proteins
Mechanism and Regulation of Cytoplasmic Dynein: Supplemental Video 1
What is Kinesin? Ron Vale Explains
Dynein Transport Protein
The Microscopic Delivery Service: Kinesin Motor Protein #didyouknowfacts
Molecular Motor Struts Like Drunken Sailor
Structural insight into dynein motor protein
Motor protein- Dynein: Structure and Function
Molecular Motor 4k
MOTOR PROTEINS
What are motor proteins?
Your Body's Molecular Machines
Motor proteins caught “swinging on monkey bars”
Комментарии
 0:03:01
0:03:01
 0:00:22
0:00:22
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:39:37
0:39:37
 0:00:33
0:00:33
 0:00:18
0:00:18
 0:05:14
0:05:14
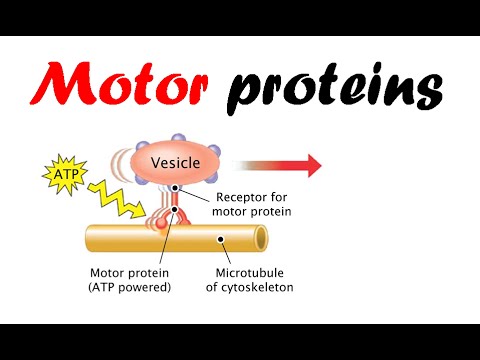 0:07:36
0:07:36
 0:01:42
0:01:42
 0:03:36
0:03:36
 0:00:06
0:00:06
 0:35:26
0:35:26
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:03:40
0:03:40
 0:00:21
0:00:21
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:01:12
0:01:12
 0:15:51
0:15:51
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:05:40
0:05:40
 0:00:03
0:00:03
 0:06:21
0:06:21
 0:04:09
0:04:09