filmov
tv
3 tonsils

Показать описание
3- TONSILS
Histological structure:
The tonsils are masses of lymphatic tissue present in the lamina propria of a mucous membrane. These are:
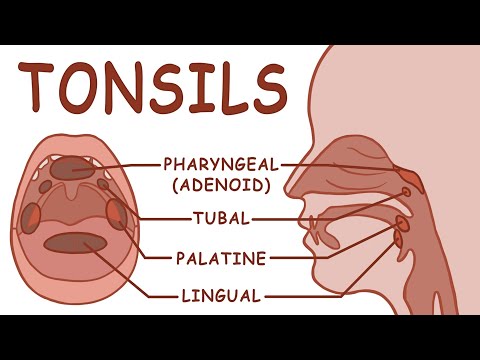
1- The palatine tonsils:
They re two masses of lymphatic tissue embedded in the C. T. under the mucous membrane of oro-pharynx. They consist of:
a- Stratified squamous ( non keratinized):
- Each tonsil is covered with stratified squamous epithelium which dips into the underlying lymphatic tissue to form primary and secondary tonsilar crypts.
- Lymphocytes may migrate from the lymphatic tissue through the epithelium to appear in the saliva. They are called salivary corpuscles.
b- Lymphatic tissue of two kinds:
- Lymphatic nodules (Primary or secondary) are located under the epithelium and around the crypts.
- Diffuse lymphatic tissue: formed of lymphocytes and plasma cells. It occupies the areas between the lymphatic nodules.
c- Capsule:
- Dense connective tissue, which separates the tonsils from the muscular wall of the pharynx.
- Some of mucous glands are present in the corium of the pharyngeal mucosa surrounding the tonsil.
2- The pharyngeal tonsils (adenoid):
• Single mass of lymphatic tissue present in nasopharynx.
• Covered by pseudo-stratified columnar ciliated epithelium which forms folds.
• The lymphatic tissue is more diffuse.
3- Lingual tonsils:
They are small collections of lymphatic tissue in the C. T. at the root of tongue.
Function of tonsils:
- Quick defense mechanism.
- They form antibodies against infective agents (antigens) which may be taken with food or air.
Histological structure:
The tonsils are masses of lymphatic tissue present in the lamina propria of a mucous membrane. These are:
1- The palatine tonsils:
They re two masses of lymphatic tissue embedded in the C. T. under the mucous membrane of oro-pharynx. They consist of:
a- Stratified squamous ( non keratinized):
- Each tonsil is covered with stratified squamous epithelium which dips into the underlying lymphatic tissue to form primary and secondary tonsilar crypts.
- Lymphocytes may migrate from the lymphatic tissue through the epithelium to appear in the saliva. They are called salivary corpuscles.
b- Lymphatic tissue of two kinds:
- Lymphatic nodules (Primary or secondary) are located under the epithelium and around the crypts.
- Diffuse lymphatic tissue: formed of lymphocytes and plasma cells. It occupies the areas between the lymphatic nodules.
c- Capsule:
- Dense connective tissue, which separates the tonsils from the muscular wall of the pharynx.
- Some of mucous glands are present in the corium of the pharyngeal mucosa surrounding the tonsil.
2- The pharyngeal tonsils (adenoid):
• Single mass of lymphatic tissue present in nasopharynx.
• Covered by pseudo-stratified columnar ciliated epithelium which forms folds.
• The lymphatic tissue is more diffuse.
3- Lingual tonsils:
They are small collections of lymphatic tissue in the C. T. at the root of tongue.
Function of tonsils:
- Quick defense mechanism.
- They form antibodies against infective agents (antigens) which may be taken with food or air.
Комментарии
 0:00:21
0:00:21
 0:03:41
0:03:41
 0:00:06
0:00:06
 0:01:29
0:01:29
 0:00:18
0:00:18
 0:03:11
0:03:11
 0:00:08
0:00:08
 0:00:41
0:00:41
 0:08:16
0:08:16
 0:01:15
0:01:15
 0:00:55
0:00:55
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:02:56
0:02:56
 0:00:08
0:00:08
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:01:43
0:01:43
 0:02:57
0:02:57
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:04:18
0:04:18
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:04:45
0:04:45
 0:02:16
0:02:16
 0:04:21
0:04:21