filmov
tv
Where will the two balls collide? Vertical free fall with two objects, and a reference frame trick.
Показать описание
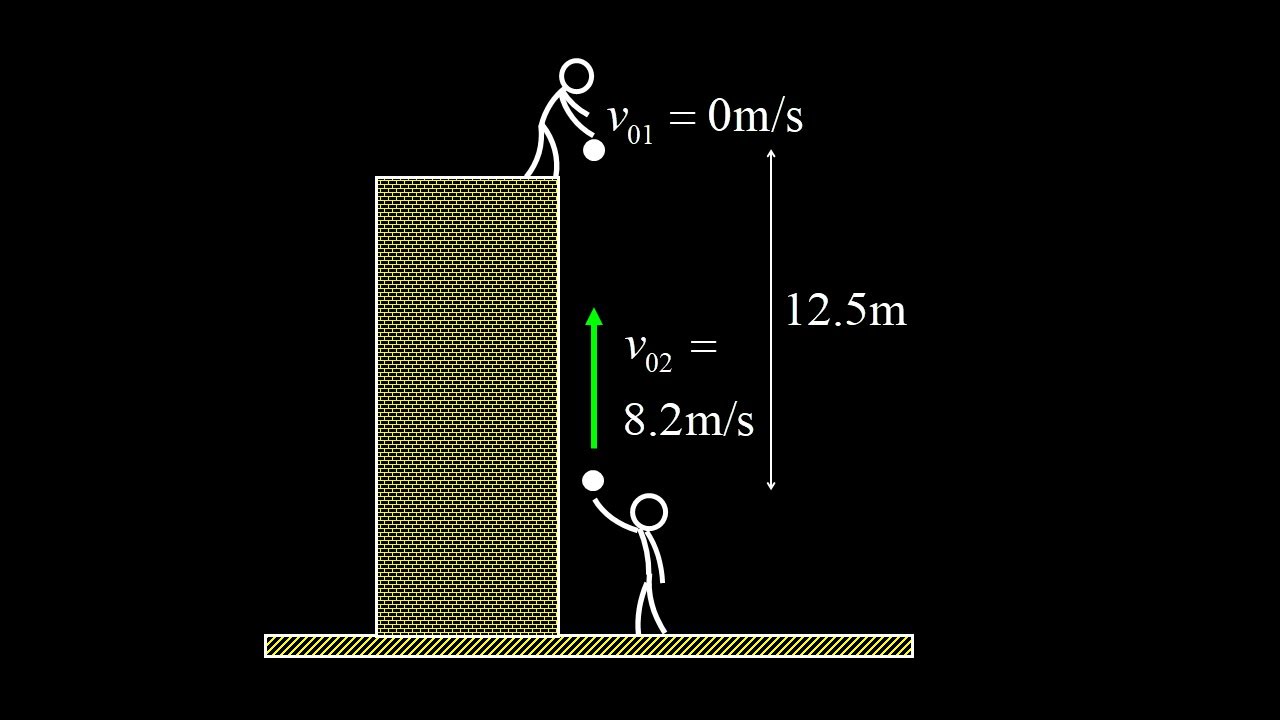
One ball is dropped from the top of a building, and the second ball is thrown straight upward: where will they collide?
In this vertical free fall problem, we are given two objects in free-fall. We solve for the time at which the balls collide, the height at which the balls collide and the relative velocity of the balls when they collide.
We notice a coincidence that's too important to ignore: the relative velocity at impact is the same as the initial relative velocity of the balls. To gain insight into this result, we use an accelerating reference frame analysis in which the origin itself is in free-fall!
The free-falling reference frame analysis makes it immediately clear that the relative velocity of the two balls never changes, so this part of the problem is trivial. We continue to solve for the time of collision using the accelerating reference frame, and this now reduces to constant velocity kinematics! Finally, we solve for the position of the collision by tracking the motion of the accelerated origin of coordinates, and we arrive at all the same solutions we got by using a standard stationary reference frame.
In this vertical free fall problem, we are given two objects in free-fall. We solve for the time at which the balls collide, the height at which the balls collide and the relative velocity of the balls when they collide.
We notice a coincidence that's too important to ignore: the relative velocity at impact is the same as the initial relative velocity of the balls. To gain insight into this result, we use an accelerating reference frame analysis in which the origin itself is in free-fall!
The free-falling reference frame analysis makes it immediately clear that the relative velocity of the two balls never changes, so this part of the problem is trivial. We continue to solve for the time of collision using the accelerating reference frame, and this now reduces to constant velocity kinematics! Finally, we solve for the position of the collision by tracking the motion of the accelerated origin of coordinates, and we arrive at all the same solutions we got by using a standard stationary reference frame.
Комментарии
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:10:06
0:10:06
 0:07:48
0:07:48
 0:00:22
0:00:22
 0:00:06
0:00:06
 0:00:05
0:00:05
 0:00:07
0:00:07
 0:08:29
0:08:29
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:00:27
0:00:27
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:00:24
0:00:24
 0:04:53
0:04:53
 0:03:50
0:03:50
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:03:50
0:03:50
 0:06:16
0:06:16
 0:00:22
0:00:22
 0:03:17
0:03:17
 0:00:19
0:00:19
 0:00:22
0:00:22
 0:02:01
0:02:01