filmov
tv
Electric Current, An Explanation
Показать описание
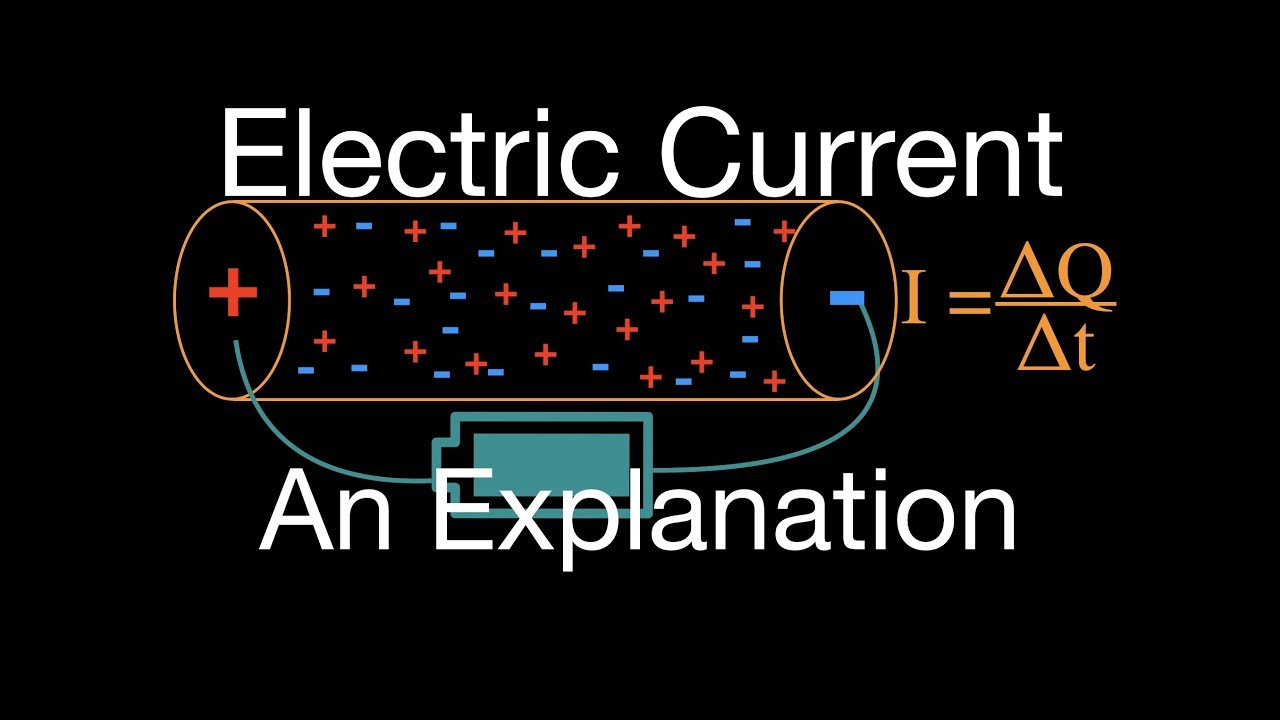
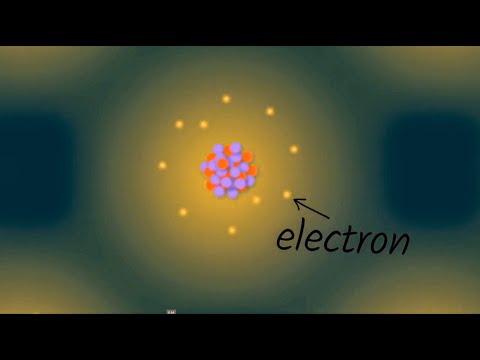
Electric current is the rate of flow of charge past a point in a closed circuit. In an electric circuit this charge is carried by electrons moving through a wire but it can also be carried by ions in an electrolyte.
The symbol for current is I, which originates from the French phrase intensité du courant (current intensity). The SI unit of electric current is the ampere (A). One ampere is equal to one coulomb per second. Electric current is measured using a device called an ammeter
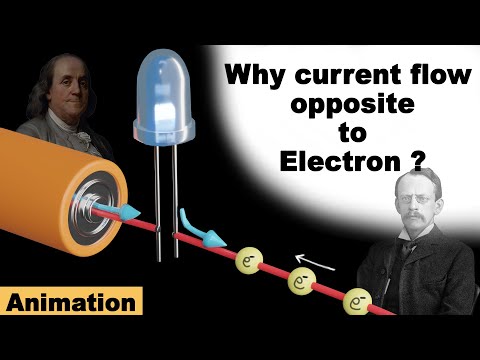
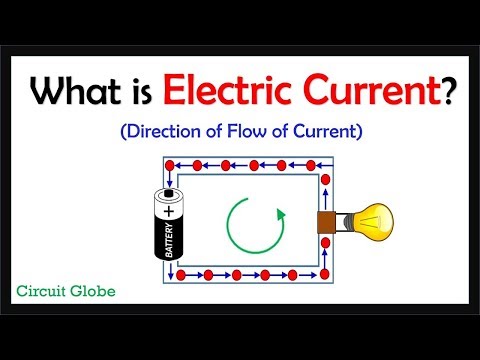
In a conductor the negatively charged electrons are the charge carriers and are free to move about in the metal. A flow of positive charges gives the same electric current, and has the same effect in a circuit, as an equal flow of negative charges in the opposite direction. The direction of conventional current is defined as the same direction as positive charges flow. Since electrons, the charge carriers in metal wires and most other parts of electric circuits, have a negative charge they flow in the opposite direction of conventional current flow in an electrical circuit.
Chapters:
0:00 Electric Current, An Explanation
0:30 What is Current
08:45 Equation and Calculation
09:45 Example Problem
Social Media for Step by Step Science:
Support my channel by doing all of the following:
(1) Subscribe, get all my physics, chemistry and math videos
(2) Give me a thumbs up for this video
(3) Leave me a positive comment
(4) Share is Caring, sharing this video with all of your friends
The symbol for current is I, which originates from the French phrase intensité du courant (current intensity). The SI unit of electric current is the ampere (A). One ampere is equal to one coulomb per second. Electric current is measured using a device called an ammeter
In a conductor the negatively charged electrons are the charge carriers and are free to move about in the metal. A flow of positive charges gives the same electric current, and has the same effect in a circuit, as an equal flow of negative charges in the opposite direction. The direction of conventional current is defined as the same direction as positive charges flow. Since electrons, the charge carriers in metal wires and most other parts of electric circuits, have a negative charge they flow in the opposite direction of conventional current flow in an electrical circuit.
Chapters:
0:00 Electric Current, An Explanation
0:30 What is Current
08:45 Equation and Calculation
09:45 Example Problem
Social Media for Step by Step Science:
Support my channel by doing all of the following:
(1) Subscribe, get all my physics, chemistry and math videos
(2) Give me a thumbs up for this video
(3) Leave me a positive comment
(4) Share is Caring, sharing this video with all of your friends
Комментарии
 0:11:40
0:11:40
 0:04:28
0:04:28
 0:18:10
0:18:10
 0:10:39
0:10:39
 0:05:52
0:05:52
 0:08:23
0:08:23
 0:10:08
0:10:08
 0:03:25
0:03:25
 0:38:55
0:38:55
 0:11:51
0:11:51
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:02:53
0:02:53
 0:14:48
0:14:48
 0:03:06
0:03:06
 0:04:22
0:04:22
 0:09:43
0:09:43
 0:03:49
0:03:49
 0:02:34
0:02:34
 0:07:49
0:07:49
 0:04:53
0:04:53
 0:21:06
0:21:06
 0:05:26
0:05:26
 0:21:08
0:21:08
 1:31:01
1:31:01