filmov
tv
What is the Nucleus | Nucleus Structure and Function

Показать описание
---RECOMMENDED STUDY GUIDES---
---STUDY RESOURCES---
---VIDEOS AND PLAYLISTS---
---DIVE IN---
---MY GEAR---
DISCLAIMER: This video and description contains affiliate links, which means that if you click on some of the product links, I’ll receive a small commission. This helps support the channel and allows us to continue to make videos like this. Thank you for the support!
Song: "New Tires" by Silent Partner
---TRANSCRIPT---
Thanks for stopping by, this is 2 minute classroom and today we are talking about the structure and function of the nucleus.
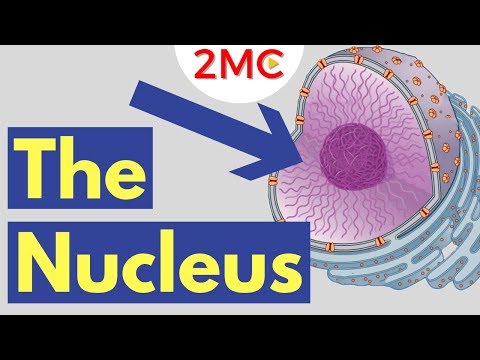
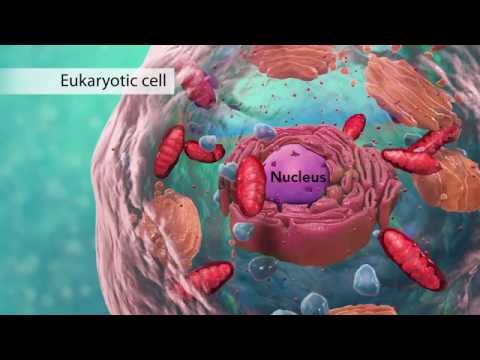
The nucleus sits in the center of eukaryotic cells and houses the DNA. It protects your genetic information and directs the synthesis of ribosomes and the expression of your genes. It’s also the location of transcription and DNA replication. You can think of it as the brain of the cell.
The nucleus has a very distinct structure.
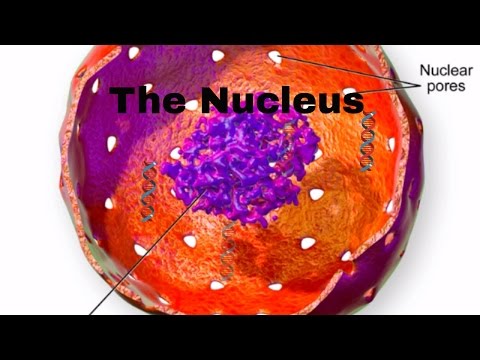
It’s surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope which contains special nuclear pores through which ribosomes and RNA exit. This nuclear envelope protects the DNA from nuclease enzymes in the cell whose job it is to destroy nucleotides, and you don’t want your DNA destroyed. The DNA never leaves the nucleus for the same reason.
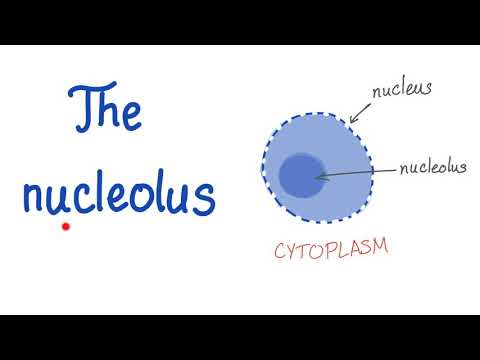
Within the nucleus there is a dark region called the nucleolus. This area is densely packed with RNA and proteins and is the location of ribosome assembly among other functions. Ribosomes have a big impact on cellular processes and I’ll create a separate video about ribosomes and link it here when it’s ready.
The nucleolus sits in the nucleoplasm, which encompasses the reamining contents of the nucleus. This is where the DNA is located. When the cell is getting ready to divide, the DNA forms chromosomes, these are structures you may be familiar with. Humans have 46 chromosomes in each cell.
However, most of the time the DNA is not in this chromosome structure, but is called chromatin, with the DNA being less compact and wrapped around special histone proteins.
If you are student interested in saving time in your studies, consider subscribing and hitting the bell to keep up with my content.
Here is a test prep playlist and some other videos you may enjoy. Thanks for watching, and I’ll catch you next time.
---STUDY RESOURCES---
---VIDEOS AND PLAYLISTS---
---DIVE IN---
---MY GEAR---
DISCLAIMER: This video and description contains affiliate links, which means that if you click on some of the product links, I’ll receive a small commission. This helps support the channel and allows us to continue to make videos like this. Thank you for the support!
Song: "New Tires" by Silent Partner
---TRANSCRIPT---
Thanks for stopping by, this is 2 minute classroom and today we are talking about the structure and function of the nucleus.
The nucleus sits in the center of eukaryotic cells and houses the DNA. It protects your genetic information and directs the synthesis of ribosomes and the expression of your genes. It’s also the location of transcription and DNA replication. You can think of it as the brain of the cell.
The nucleus has a very distinct structure.
It’s surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope which contains special nuclear pores through which ribosomes and RNA exit. This nuclear envelope protects the DNA from nuclease enzymes in the cell whose job it is to destroy nucleotides, and you don’t want your DNA destroyed. The DNA never leaves the nucleus for the same reason.
Within the nucleus there is a dark region called the nucleolus. This area is densely packed with RNA and proteins and is the location of ribosome assembly among other functions. Ribosomes have a big impact on cellular processes and I’ll create a separate video about ribosomes and link it here when it’s ready.
The nucleolus sits in the nucleoplasm, which encompasses the reamining contents of the nucleus. This is where the DNA is located. When the cell is getting ready to divide, the DNA forms chromosomes, these are structures you may be familiar with. Humans have 46 chromosomes in each cell.
However, most of the time the DNA is not in this chromosome structure, but is called chromatin, with the DNA being less compact and wrapped around special histone proteins.
If you are student interested in saving time in your studies, consider subscribing and hitting the bell to keep up with my content.
Here is a test prep playlist and some other videos you may enjoy. Thanks for watching, and I’ll catch you next time.
Комментарии
 0:01:58
0:01:58
 0:06:05
0:06:05
 0:31:17
0:31:17
 0:09:05
0:09:05
 0:07:22
0:07:22
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:04:42
0:04:42
 0:10:12
0:10:12
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:02:59
0:02:59
 0:01:14
0:01:14
 0:15:59
0:15:59
 0:04:18
0:04:18
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:08:51
0:08:51
 0:04:44
0:04:44
 0:02:19
0:02:19
 0:03:21
0:03:21
 0:04:00
0:04:00
 0:23:20
0:23:20
 0:03:42
0:03:42
 0:02:24
0:02:24
 0:09:46
0:09:46
 0:00:41
0:00:41