filmov
tv
Mass Spectrometry | A-level Chemistry | OCR, AQA, Edexcel

Показать описание
Mass Spectrometry in a Snap!
SnapRevise is the UK’s leading A-level and GCSE revision & exam preparation resource offering comprehensive video courses created by A* tutors. Our courses are designed around the OCR, AQA, SNAB, Edexcel B, WJEC, CIE and IAL exam boards, concisely covering all the important concepts required by each specification. In addition to all the content videos, our courses include hundreds of exam question videos, where we show you how to tackle questions and walk you through step by step how to score full marks.
Sign up today and together, let’s make A-level Chemistry a walk in the park!
The key points covered in this video include:
1. What is Mass Spectrometry?
2. TOF Mass Spectrometry
3. Low Resolution Mass Spec
4. Analysing Spectra
What is Mass Spectrometry?
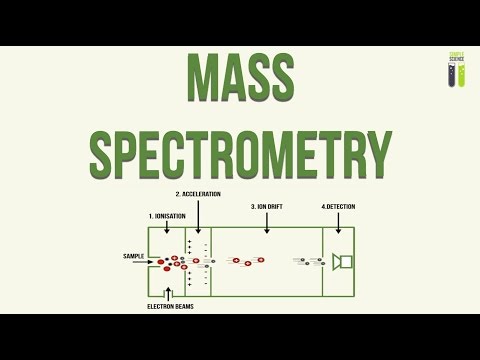
Mass Spectrometry is a form of molecular chemical analysis. There are many different types of mass spectrometer. All work on the same principle: 1. Form ions from sample, 2. Ions separated, According to Mass to Charge ratio, 3. Ions detected. Mass Spectrometry can be used to: Provide structural information, Identify an unknown compound, Determine the relative abundance of each isotope of an element.
Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry
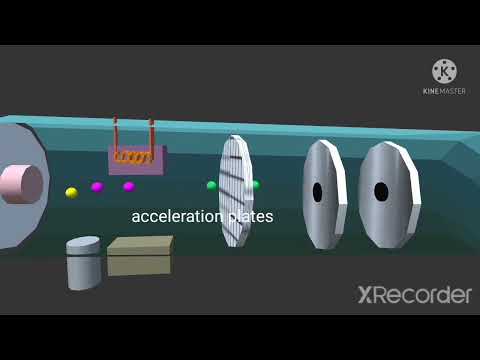
Apparatus under Vacuum. This excludes air, Prevents the ions from colliding with air. Step 1. Ionisation. The sample is dissolved in a volatile solvent, The vaporised solvent is forced through a hollow needle. This is connected to the +ve terminal of a high voltage supply, This produces tiny positively charged droplets. These tiny droplets have lost electrons, The solvent then evaporates, As a result of this, the droplets reduce in size. They are reduced single positively charged ion. Step 2. Acceleration. The positive ions are attracted towards an electric plate. This plate is negatively charged and causes the ions to accelerate, The ions accelerate towards the plate so that all ions have the same kinetic energy. Therefore the larger, heavier particles will have a lower speed. Speed 3. Ion Drift. The ions pass through a hole in the negatively charged plate. This forms a beam, The beam of ions travels along a tube. This is the Flight Tube. Step 4. Detections. When the ions arrive at the detector, their flight times are recorded. At the detector, the positive ions pick up an electron, This causes a current to flow. Step 5. Data Analysis. The detector passes a signal to the computer. This generates a mass spectrum.
Low Resolution Mass Spectrometry
Chlorine has 2 isotopes. Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons and different numbers of neutrons. Each isotope has a slightly different mass. Cl35, CCl37. As a result, the isotopes will have a different m/z ratio. They will be detected separately. Mass spectrometry can be carried out to a high level of precision. Up to 5 decimal places. When done to 1 decimal place, the process can be called Low Resolution Mass Spec.
SnapRevise is the UK’s leading A-level and GCSE revision & exam preparation resource offering comprehensive video courses created by A* tutors. Our courses are designed around the OCR, AQA, SNAB, Edexcel B, WJEC, CIE and IAL exam boards, concisely covering all the important concepts required by each specification. In addition to all the content videos, our courses include hundreds of exam question videos, where we show you how to tackle questions and walk you through step by step how to score full marks.
Sign up today and together, let’s make A-level Chemistry a walk in the park!
The key points covered in this video include:
1. What is Mass Spectrometry?
2. TOF Mass Spectrometry
3. Low Resolution Mass Spec
4. Analysing Spectra
What is Mass Spectrometry?
Mass Spectrometry is a form of molecular chemical analysis. There are many different types of mass spectrometer. All work on the same principle: 1. Form ions from sample, 2. Ions separated, According to Mass to Charge ratio, 3. Ions detected. Mass Spectrometry can be used to: Provide structural information, Identify an unknown compound, Determine the relative abundance of each isotope of an element.
Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry
Apparatus under Vacuum. This excludes air, Prevents the ions from colliding with air. Step 1. Ionisation. The sample is dissolved in a volatile solvent, The vaporised solvent is forced through a hollow needle. This is connected to the +ve terminal of a high voltage supply, This produces tiny positively charged droplets. These tiny droplets have lost electrons, The solvent then evaporates, As a result of this, the droplets reduce in size. They are reduced single positively charged ion. Step 2. Acceleration. The positive ions are attracted towards an electric plate. This plate is negatively charged and causes the ions to accelerate, The ions accelerate towards the plate so that all ions have the same kinetic energy. Therefore the larger, heavier particles will have a lower speed. Speed 3. Ion Drift. The ions pass through a hole in the negatively charged plate. This forms a beam, The beam of ions travels along a tube. This is the Flight Tube. Step 4. Detections. When the ions arrive at the detector, their flight times are recorded. At the detector, the positive ions pick up an electron, This causes a current to flow. Step 5. Data Analysis. The detector passes a signal to the computer. This generates a mass spectrum.
Low Resolution Mass Spectrometry
Chlorine has 2 isotopes. Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons and different numbers of neutrons. Each isotope has a slightly different mass. Cl35, CCl37. As a result, the isotopes will have a different m/z ratio. They will be detected separately. Mass spectrometry can be carried out to a high level of precision. Up to 5 decimal places. When done to 1 decimal place, the process can be called Low Resolution Mass Spec.
Комментарии
 0:10:46
0:10:46
 0:04:18
0:04:18
 0:10:02
0:10:02
 0:05:00
0:05:00
 0:11:34
0:11:34
 0:30:43
0:30:43
 0:20:11
0:20:11
 0:04:51
0:04:51
 0:51:32
0:51:32
 0:06:00
0:06:00
 0:09:07
0:09:07
 0:06:47
0:06:47
 0:03:51
0:03:51
 0:36:50
0:36:50
 0:14:13
0:14:13
 0:01:18
0:01:18
 0:13:45
0:13:45
 0:11:09
0:11:09
 0:08:01
0:08:01
 0:12:59
0:12:59
 0:13:51
0:13:51
 0:05:19
0:05:19
 0:05:30
0:05:30
 0:08:47
0:08:47