filmov
tv
Error Correcting Codes: What is Hamming Distance and Minimum Hamming Distance ?

Показать описание
In this video, the basics of the Error Correction Codes and the Concept of Hamming Distance, and the Minimum Hamming Distance is Explained with examples.
Timestamps:
0:00 Error-Correcting Codes (ECC)
1:23 Repetition Code
3:18 Hamming Distance and Minimum Hamming Distance
Error Correcting Codes:
When the data is sent over the noisy channel then the Error-Correcting Codes are used for correcting the errors in received data bits.
The Error Correcting Codes are used in computer memories, in satellite communication, in one-way communication links, and in multicast systems.
The Repetition Code is the very basic type of Error-Correcting Code. In this video, the triple repetition code is explained and the issues of the repetition code are also explained.
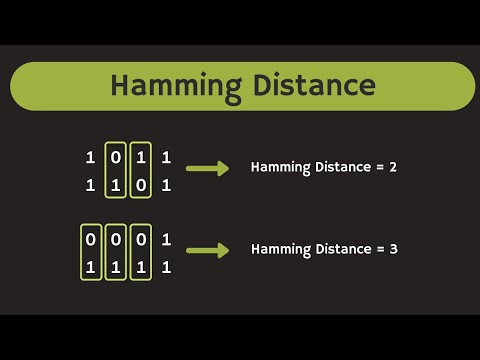
What is Hamming Distance?
The Hamming Distance is the number of bit positions at which the two codes differ.
What is Minimum Hamming Distance?
It is the smallest Hamming Distance between all possible codes in the given encoding scheme.
The link for the other useful videos:
1) Error Detecting Code: Parity Explained | Odd Parity and Even Parity
2) Gray Code:
This video will be helpful to all the students of science and engineering in understanding the concept of Hamming Distance and Minimum Hamming Distance.
#ALLABOUTELECTRONICS
#HammingDistance
Support the channel through membership program:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Follow my second channel:
Follow me on Facebook:
Follow me on Instagram:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Timestamps:
0:00 Error-Correcting Codes (ECC)
1:23 Repetition Code
3:18 Hamming Distance and Minimum Hamming Distance
Error Correcting Codes:
When the data is sent over the noisy channel then the Error-Correcting Codes are used for correcting the errors in received data bits.
The Error Correcting Codes are used in computer memories, in satellite communication, in one-way communication links, and in multicast systems.
The Repetition Code is the very basic type of Error-Correcting Code. In this video, the triple repetition code is explained and the issues of the repetition code are also explained.
What is Hamming Distance?
The Hamming Distance is the number of bit positions at which the two codes differ.
What is Minimum Hamming Distance?
It is the smallest Hamming Distance between all possible codes in the given encoding scheme.
The link for the other useful videos:
1) Error Detecting Code: Parity Explained | Odd Parity and Even Parity
2) Gray Code:
This video will be helpful to all the students of science and engineering in understanding the concept of Hamming Distance and Minimum Hamming Distance.
#ALLABOUTELECTRONICS
#HammingDistance
Support the channel through membership program:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Follow my second channel:
Follow me on Facebook:
Follow me on Instagram:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Комментарии
 0:20:05
0:20:05
 0:06:01
0:06:01
 0:07:34
0:07:34
 0:16:53
0:16:53
 0:22:31
0:22:31
 0:11:30
0:11:30
 0:09:01
0:09:01
 0:17:46
0:17:46
 0:05:25
0:05:25
 0:04:42
0:04:42
 0:10:44
0:10:44
 0:10:59
0:10:59
 0:07:27
0:07:27
 0:11:56
0:11:56
 0:10:25
0:10:25
 0:05:20
0:05:20
 0:13:45
0:13:45
 0:04:16
0:04:16
 1:14:52
1:14:52
 0:08:08
0:08:08
 0:07:01
0:07:01
 0:12:32
0:12:32
 1:09:55
1:09:55
 0:47:37
0:47:37