filmov
tv
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)

Показать описание
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a condition where a blood clot forms in a deep vein, typically in the legs. This can cause pain, swelling, and redness in the affected area, but sometimes it might not present noticeable symptoms. If the clot breaks loose, it can travel to the lungs and cause a serious condition called a pulmonary embolism.
How Vascular Surgeons Treat Deep Vein Thrombosis
1. Diagnosis and Evaluation: Vascular surgeons diagnose DVT using various methods:
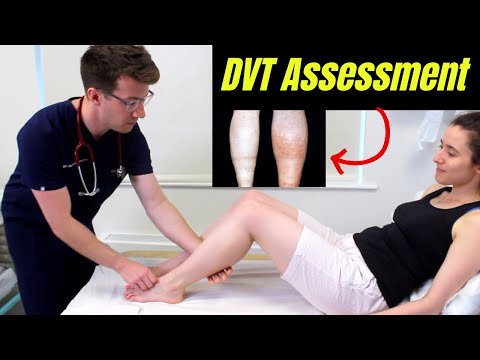
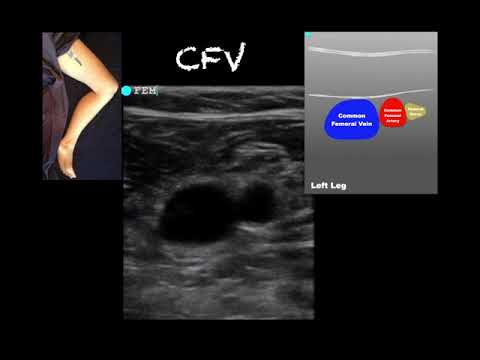
- Ultrasound: This imaging test uses sound waves to create images of the blood clots and check for their location.
- Computed Tomography Scan: This can be used to visualize the clot and assess its size and extent.
- Blood Tests: To check for markers that indicate clotting issues.
2. Medication Management: The primary treatment for DVT involves medications to:
- Anticoagulants: These drugs help prevent further clotting and allow the body to break down the existing clot.
- Thrombolytics: In more severe cases, these medications can help dissolve the clot more quickly.
3. Endovenous Procedures: For some cases, especially when medication alone is not effective:
- Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis: A catheter is inserted into the vein to deliver medication directly to the clot to dissolve it.
- Mechanical Thrombectomy: A procedure where a device is used to physically remove the clot from the vein.
4. Surgical Options: In rare, severe cases:
- Surgical Removal of the Clot: A surgical procedure to remove the clot from the vein if other treatments are not successful.
5. Post-Treatment Care: After treatment, vascular surgeons provide guidance on:
- Lifestyle Changes: Such as regular exercise and wearing compression stockings to prevent future clots.
- Ongoing Monitoring: To ensure the clot has dissolved and to manage any potential complications.
How Vascular Surgeons Treat Deep Vein Thrombosis
1. Diagnosis and Evaluation: Vascular surgeons diagnose DVT using various methods:
- Ultrasound: This imaging test uses sound waves to create images of the blood clots and check for their location.
- Computed Tomography Scan: This can be used to visualize the clot and assess its size and extent.
- Blood Tests: To check for markers that indicate clotting issues.
2. Medication Management: The primary treatment for DVT involves medications to:
- Anticoagulants: These drugs help prevent further clotting and allow the body to break down the existing clot.
- Thrombolytics: In more severe cases, these medications can help dissolve the clot more quickly.
3. Endovenous Procedures: For some cases, especially when medication alone is not effective:
- Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis: A catheter is inserted into the vein to deliver medication directly to the clot to dissolve it.
- Mechanical Thrombectomy: A procedure where a device is used to physically remove the clot from the vein.
4. Surgical Options: In rare, severe cases:
- Surgical Removal of the Clot: A surgical procedure to remove the clot from the vein if other treatments are not successful.
5. Post-Treatment Care: After treatment, vascular surgeons provide guidance on:
- Lifestyle Changes: Such as regular exercise and wearing compression stockings to prevent future clots.
- Ongoing Monitoring: To ensure the clot has dissolved and to manage any potential complications.
 0:12:53
0:12:53
 0:22:43
0:22:43
 0:08:38
0:08:38
 0:01:27
0:01:27
 0:27:39
0:27:39
 0:23:45
0:23:45
 0:13:00
0:13:00
 0:03:25
0:03:25
 0:19:31
0:19:31
 0:04:07
0:04:07
 0:10:48
0:10:48
 0:02:26
0:02:26
 0:01:10
0:01:10
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:04:52
0:04:52
 0:01:24
0:01:24
 0:08:30
0:08:30
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:00:37
0:00:37
 0:00:46
0:00:46
 0:02:14
0:02:14
 0:03:05
0:03:05
 0:00:49
0:00:49
 0:01:13
0:01:13