filmov
tv
Ionic Radius Trends, Basic Introduction, Periodic Table, Sizes of Isoelectric Ions, Chemistry

Показать описание
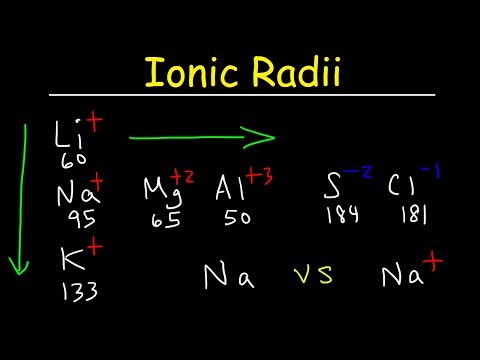
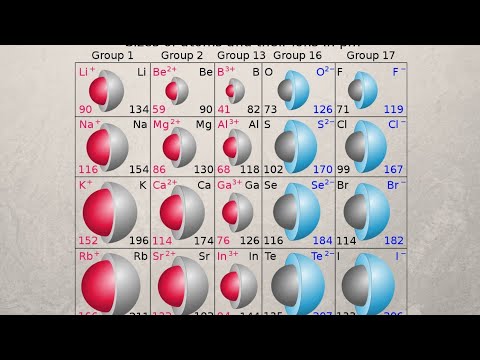
This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the periodic trends of the ionic radius of ions. It explains how to rank in order of increasing ionic radii - the sizes of isoelectric ions - which are ions that have the same number of electrons and the same electron configuration. Anions are usually bigger than cations.
Ionization Energy:
Electron Affinity:
Atomic Radius:
Bond Energy & Bond Length:
Electronegativity:
Periodic Trends:
__________________________________
Polar & Nonpolar Covalent Bonding:
Bond Polarity & Dipole Moment:
Ionic Radius:
Lattice Energy:
Born Haber Cycle:
Bond Energy Calculations:
___________________________________
Lewis Structures - Mega Review:
Final Exams and Video Playlists:
Full-Length Videos and Worksheets:
Ionization Energy:
Electron Affinity:
Atomic Radius:
Bond Energy & Bond Length:
Electronegativity:
Periodic Trends:
__________________________________
Polar & Nonpolar Covalent Bonding:
Bond Polarity & Dipole Moment:
Ionic Radius:
Lattice Energy:
Born Haber Cycle:
Bond Energy Calculations:
___________________________________
Lewis Structures - Mega Review:
Final Exams and Video Playlists:
Full-Length Videos and Worksheets:
Комментарии
 0:11:47
0:11:47
 0:09:00
0:09:00
 0:07:53
0:07:53
 0:06:32
0:06:32
 0:07:41
0:07:41
 0:07:38
0:07:38
 0:03:57
0:03:57
 0:14:04
0:14:04
 0:07:20
0:07:20
 0:05:48
0:05:48
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:03:23
0:03:23
 0:06:57
0:06:57
 0:07:33
0:07:33
 0:03:03
0:03:03
 0:07:27
0:07:27
 0:06:09
0:06:09
 0:18:06
0:18:06
 0:04:06
0:04:06
 0:06:53
0:06:53
 0:16:10
0:16:10
 0:04:40
0:04:40
 0:03:48
0:03:48
 0:13:30
0:13:30