filmov
tv
What is a Capacitor? (Physics, Electricity)

Показать описание
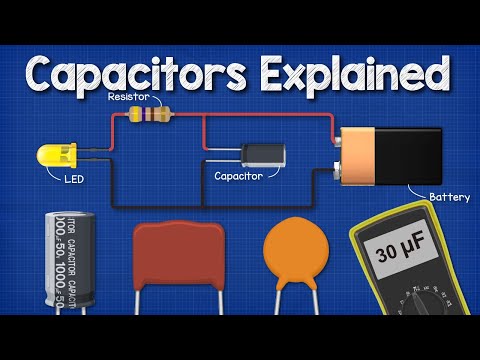
Capacitors are essential components of the electric and electronic circuits present in the technology we use every day. Students usually encounter capacitors for the first time in grade 12 physics class but often find capacitors and the way they work quite unclear.
In this video, we will dive into the fundamental knowledge related to capacitors: What are capacitors? What are capacitors used for? What is their role in a circuit and what happens physically during a charge or discharge of a capacitor.
This video is just an introduction to capacitors. It is not extensive. There are many relevant concepts we just mentioned without developing. These will be discussed in more detail in future videos (dielectric material, capacitance, time constant etc.).
#physics #capacitor #electricity
Structure of the video:
00:00 Introduction
00:30 What is a capacitor?
01:27 What are capacitors used for? (high power devices, phone chargers, signal filters)
04:11 What is an electric potential? What is a voltage? (Reminder of electricity basics)
05:08 What is an electric field? (Reminder of electricity basics)
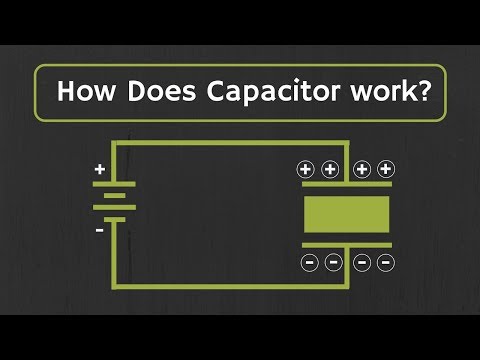
05:28 How does a capacitor work? (What physically happens during the charging of a capacitor)
06:51 How does a capacitor work? (How can a current flow through a capacitor?)
11:51 How does a capacitor work? (What physically happens during the discharging of a capacitor)
12:57 What is a capacitor? (Conclusion)
In order to fully grasp the content of this video, the viewer needs to be familiar with the following concepts already presented in a PME video.
_ Electric Potentials.
_ Electric Fields.
_ Work.
_ Energy.
Note about conventional notations in electric circuits:
In this video (and all other videos about electricity), we use a conventional representation of electric circuits. In that model, the charges that are free to move are positive. Those that are fixed are negative. This model is used in most textbook and by the scientific community initially for historical reasons, but mostly because it is more convenient (no negative signs to handle) and because this model is mathematically and energetically equivalent to reality.
- - - - - - - - -
This video is produced and presented by Edouard Reny, Ph.D. in solid state chemistry and private tutor in Physical Sciences.
In this video, we will dive into the fundamental knowledge related to capacitors: What are capacitors? What are capacitors used for? What is their role in a circuit and what happens physically during a charge or discharge of a capacitor.
This video is just an introduction to capacitors. It is not extensive. There are many relevant concepts we just mentioned without developing. These will be discussed in more detail in future videos (dielectric material, capacitance, time constant etc.).
#physics #capacitor #electricity
Structure of the video:
00:00 Introduction
00:30 What is a capacitor?
01:27 What are capacitors used for? (high power devices, phone chargers, signal filters)
04:11 What is an electric potential? What is a voltage? (Reminder of electricity basics)
05:08 What is an electric field? (Reminder of electricity basics)
05:28 How does a capacitor work? (What physically happens during the charging of a capacitor)
06:51 How does a capacitor work? (How can a current flow through a capacitor?)
11:51 How does a capacitor work? (What physically happens during the discharging of a capacitor)
12:57 What is a capacitor? (Conclusion)
In order to fully grasp the content of this video, the viewer needs to be familiar with the following concepts already presented in a PME video.
_ Electric Potentials.
_ Electric Fields.
_ Work.
_ Energy.
Note about conventional notations in electric circuits:
In this video (and all other videos about electricity), we use a conventional representation of electric circuits. In that model, the charges that are free to move are positive. Those that are fixed are negative. This model is used in most textbook and by the scientific community initially for historical reasons, but mostly because it is more convenient (no negative signs to handle) and because this model is mathematically and energetically equivalent to reality.
- - - - - - - - -
This video is produced and presented by Edouard Reny, Ph.D. in solid state chemistry and private tutor in Physical Sciences.
Комментарии
 0:08:42
0:08:42
 0:28:18
0:28:18
 0:10:57
0:10:57
 0:10:02
0:10:02
 0:00:54
0:00:54
 0:01:18
0:01:18
 0:09:23
0:09:23
 0:15:20
0:15:20
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:10:14
0:10:14
 0:00:42
0:00:42
 0:16:00
0:16:00
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:11:23
0:11:23
 0:14:51
0:14:51
 0:05:46
0:05:46
 0:38:44
0:38:44
 0:07:05
0:07:05
 0:25:49
0:25:49
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:10:38
0:10:38
 0:00:34
0:00:34
 0:28:26
0:28:26
 0:08:30
0:08:30