filmov
tv
Physics, Torque (10 of 13) Static Equilibrium, Hanging Sign at an Angle No. 4

Показать описание
Shows how to use static equilibrium to determine the tension in the cable supporting the beam from which the sign is hanging. To solve this problem we will set the sum of the torques equal to zero and solve for the force in the cable.
Torque is a rotating force. It is a measure of how much force is acting on an object that causes the object to rotate. The object will rotate about an axis, which is called the pivot point. It is labeled with the letter P or O. The distance from the pivot point to the point where the force acts is called the moment arm or the lever arm. This distance is labeled with the letter r. This distance r is also a vector, and points from the axis of rotation to the point where the force acts. The force is labeled with the letter F.
Support my channel by doing all of the following:
(1) Subscribe, get all my physics, chemistry and math videos
(2) Give me a thumbs up for this video
(3) Leave me a positive comment
(4) Share is Caring, sharing this video with all of your friends
Torque is a rotating force. It is a measure of how much force is acting on an object that causes the object to rotate. The object will rotate about an axis, which is called the pivot point. It is labeled with the letter P or O. The distance from the pivot point to the point where the force acts is called the moment arm or the lever arm. This distance is labeled with the letter r. This distance r is also a vector, and points from the axis of rotation to the point where the force acts. The force is labeled with the letter F.
Support my channel by doing all of the following:
(1) Subscribe, get all my physics, chemistry and math videos
(2) Give me a thumbs up for this video
(3) Leave me a positive comment
(4) Share is Caring, sharing this video with all of your friends
Physics, Torque (10 of 13) Static Equilibrium, Hanging Sign at an Angle No. 4
Physics 15 Torque Fundamentals (10 of 13) How to Calculate the Net Torque? Ex. 1
Torque, Basic Introduction, Lever Arm, Moment of Force, Simple Machines & Mechanical Advantage
Physics, Torque (4 of 13) Force Not at Right Angle to the Object
Physics, Torque (11 of 13) Static Equilibrium, Hanging Sign No. 5
JEE Advanced Physics 2021 Shift 1 #13 Torque and Angular Momentum
Solve ANY Torque Problem!! (Physics)
Physics 15 Torque Fundamentals (4 of 13) How to Calculate a Torque (Method 1)
System of Particles and Rotational Motion - Part 2 | Physics | JEE Main 2025 | @InfinityLearn-JEE
Physics, Torque (2 of 13) Force at Right Angle to Object
Physics, Torque (12 of 13) Static Equilibrium, Ladder Problem
Physics 15 Torque Fundamentals (9 of 13) How to Calculate a Torque (Basic Example 3)
Physics, Torque (13 of 13) Static Equilibrium, Mobile Calculations
Physics, Torque (1 of 13) An Explanation
What is Torque? - Torque basics explained
Physics 15 Torque Fundamentals (12 of 13) The Torque Wrench
Torque
Physics, Net Torque (5 of 13) Five Forces Applied to a Door
The Cross Product & Torque (Class 11 Physics)
A Tesla Turbine That Actually Works - Power, Torque, Low RPM
Physics 15 Torque Fundamentals (13 of 13) Torque and Angular Acceleration
Physics, Torque (7 of 13) Static Equilibrium, Hanging Sign No. 1
Physics, Torque (3 of 13) Balance Beam
Physics 15 Torque Fundamentals (1 of 13) What is Torque?
Комментарии
 0:09:10
0:09:10
 0:03:24
0:03:24
 0:21:17
0:21:17
 0:06:16
0:06:16
 0:11:56
0:11:56
 0:06:44
0:06:44
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:03:36
0:03:36
 3:24:32
3:24:32
 0:08:48
0:08:48
 0:10:09
0:10:09
 0:03:39
0:03:39
 0:09:13
0:09:13
 0:08:23
0:08:23
 0:02:10
0:02:10
 0:02:28
0:02:28
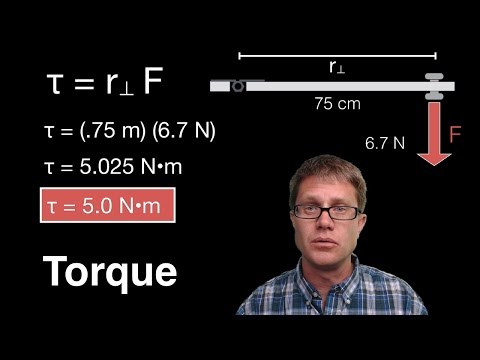 0:07:03
0:07:03
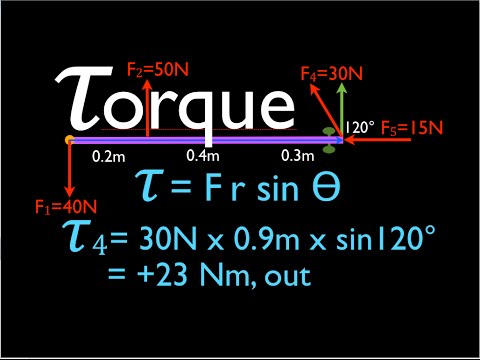 0:08:04
0:08:04
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:03:48
0:03:48
 0:06:58
0:06:58
 0:05:02
0:05:02
 0:03:10
0:03:10