filmov
tv
Part 3 | Functions | Python Malayalam Tutorial For Beginners | Python Coding Challenge

Показать описание
24/7 FREE Telegram Support! Sign Up Now:
In this tutorial we will discuss functions.
Link to 100K Coding Challenge:
00:40 Function
11:29 Global variable ,Local variable
16:18 key word argument
17:58 Default argument
21:29 Dictionaries
About us:
Subscribe to Kerala's leading tech-career YouTube channel for free programming tutorials and tech-career videos in Malayalam. Learn the skills and knowledge needed to build a high-income career in IT. Join our community of future tech experts today!
Transform your career with 'Brocamp'—our 12 month Offline & Online training program that places you in a real office environment to master coding and in-demand skills. With over 1700+ successful placements averaging ₹40,000/month, secure your future with our proven career-focused training programs.
Ready to start your journey?
Connect with us: Call/WhatsApp us at 7034395811
To know more about Brocamp, Visit:
In this tutorial we will discuss functions.
Link to 100K Coding Challenge:
00:40 Function
11:29 Global variable ,Local variable
16:18 key word argument
17:58 Default argument
21:29 Dictionaries
About us:
Subscribe to Kerala's leading tech-career YouTube channel for free programming tutorials and tech-career videos in Malayalam. Learn the skills and knowledge needed to build a high-income career in IT. Join our community of future tech experts today!
Transform your career with 'Brocamp'—our 12 month Offline & Online training program that places you in a real office environment to master coding and in-demand skills. With over 1700+ successful placements averaging ₹40,000/month, secure your future with our proven career-focused training programs.
Ready to start your journey?
Connect with us: Call/WhatsApp us at 7034395811
To know more about Brocamp, Visit:
Part 3 | Functions | Python Malayalam Tutorial For Beginners | Python Coding Challenge
Structures and Functions (Part 3)
Lesson #35 - Function Part 3 - Parameters
Leadership and Management | Part 3 of 4:The Four Functions of Management
All of Grade 12 Math - Advanced Functions - IN 1 HOUR!!! (part 3)
Tools and their functions part 3
Learn Basic SQL in 15 Minutes (PART 3/3) | SQL Functions Tutorial | Business Intelligence
C_86 Functions in C-part 3 |Function Definition in C
The Purpose and Functions of Prophetic Systems. Part #3
Placenta Part 3 - Functions of placenta - Pitfalls of placenta - Gestational Diabetes
Grade 10 Functions Exam Question PART 3
VEX Isn't Scary | Part 3 | Functions
Memorization Trick for Graphing Functions Part 1 | Algebra Math Hack #shorts #math #school
How REAL Men Integrate Functions
Subprograms Part 3 - Extra Custom Delphi Function Examples
Maths-Domain and Range-Understanding Simple and Easy (O-Level)
Moment Generating Functions (Part 3)
Fresh man mathematics | chapter 2 part 3 | Function | Review of Relations and Functions
Rational Functions Part 3
9 Functions - part 3 #JuliaProgramming #learnjulia
#20 [c++] - Function part 3 (built in functions)
PLUS ONE MATHS ONAM EXAM | TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS PART 3 | CHAPTER 3 | EXAM WINNER +1
Why “probability of 0” does not mean “impossible” | Probabilities of probabilities, part 2
Fresh man mathematics chapter 3 part 3/ Types of function
Комментарии
 0:25:06
0:25:06
 0:02:48
0:02:48
 0:08:43
0:08:43
 0:04:45
0:04:45
 0:23:08
0:23:08
 0:04:14
0:04:14
 0:16:40
0:16:40
 0:14:50
0:14:50
 1:20:05
1:20:05
 0:13:45
0:13:45
 0:23:33
0:23:33
 0:21:46
0:21:46
 0:00:15
0:00:15
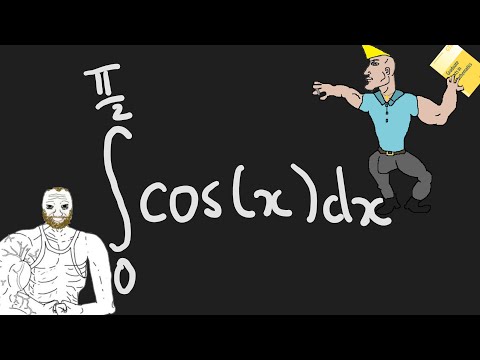 0:00:35
0:00:35
 0:22:02
0:22:02
 0:00:54
0:00:54
 0:06:38
0:06:38
 0:41:01
0:41:01
 0:06:22
0:06:22
 0:18:36
0:18:36
![#20 [c++] -](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/QjKUXcig4is/hqdefault.jpg) 0:13:40
0:13:40
 1:21:08
1:21:08
 0:10:01
0:10:01
 0:52:47
0:52:47