filmov
tv
Triple bottom line (3 pillars): sustainability in business

Показать описание
This whiteboard animation video presents the concept of the triple bottom line and uses science to suggest a different way to look at it. This provides businesses with new perspective on the rationale for integrating sustainability into who and how they are in the world. This is also known as the 3 pillars of sustainability.
2 great books to learn more about the triple bottom line & sustainability for businesses:
The triple bottom line is also related to corporate social responsibility (CSR), people planet profit, circular economy, natural capitalism, biomimicry.
**
Learn about sustainability for free with short animation videos!
Extra info & links below...
**
Thank you to The Natural Step Canada and all our patrons for supporting us.
Script by Sarah Brooks
Thanks to our subtitles volunteer:
Spanish & Catalan: Josep Simona
Portuguese: André Ribeiro Winter
Music by "Locally Sourced" by Jason Farnham
**
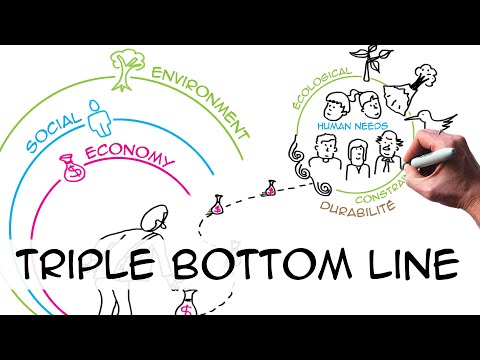
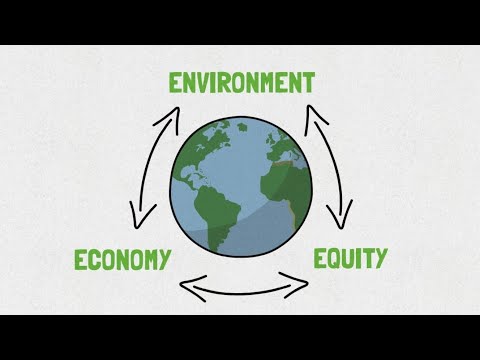
The triple bottom line (TBL or 3BL) is a concept that is used a lot when speaking about sustainable development, and particularly sustainability in business. John Elkington, a global authority on corporate responsibility and sustainability coined the phrase in a book in 1997. His argument was that the methods by which companies measure value should include not only a financial bottom line (profit or loss), but a social and environmental one as well. The concept has evolved into one that’s often described as three overlapping circles. You’ve probably seen this image before. Sustainability is typically defined as the place where economy, social realities and environmental health overlap.
The concept of the triple bottom line mainstreamed the idea of sustainability as including people, planet AND profit. It helped business to understand that long-term sustainability of an organization required more than just financial equity. It also helped to clarify that when businesses were considering what sustainability meant for them, it didn’t mean they had to give up the notion of financial success.
But this overlapping circles image of the triple bottom line can convey a lot more. The circles are all the same size. Does this indicate that the economy is the same relative size, or value, as the other two circles, which deal with society and the environment? Can we trade say “2 social and 3 environment for 5 economy” as long as we stay in the overlapping bit in the middle (sustainability)?
Science tells us that, left to its own devices, the planet operates in a balanced way. We call this the cycles of nature and they are powered by energy from the sun. Science also tells us that matter is not created or destroyed, while laws of thermodynamics tell us that everything tends toward dispersal (principle of entropy). Because plant cells are, for all intents and purposes, the only cells that can produce structure from energy, photosynthesis is the process by which matter is structured on our planet. This is why we say that photosynthesis pays the bills. Without it, creation of structure from energy would not occur, and entropy could rule the day.
How does this help us understand the triple bottom line?
Plant cells belong to the environment circle of the triple bottom line. If plant cells are the original creators of structure, then this is the circle on which everything else depends, or in which everything is embedded. Everything comes from nature at some point. Society, which is related to the social circle of the triple bottom line, exists within the environment. And economy is a by-product of society. Instead of three overlapping circles, we have three nested circles, where the economy is a wholly owned subsidiary of the environment.
To achieve sustainability, we need to comply with social and environmental conditions: meet human needs within ecological constraints. Does this mean that business has to put financial gain last? Of course not! But economic decisions are part of a strategy to make more money while getting closer to social and ecological sustainability. The economy is a means to an end. Not the end itself.
2 great books to learn more about the triple bottom line & sustainability for businesses:
The triple bottom line is also related to corporate social responsibility (CSR), people planet profit, circular economy, natural capitalism, biomimicry.
**
Learn about sustainability for free with short animation videos!
Extra info & links below...
**
Thank you to The Natural Step Canada and all our patrons for supporting us.
Script by Sarah Brooks
Thanks to our subtitles volunteer:
Spanish & Catalan: Josep Simona
Portuguese: André Ribeiro Winter
Music by "Locally Sourced" by Jason Farnham
**
The triple bottom line (TBL or 3BL) is a concept that is used a lot when speaking about sustainable development, and particularly sustainability in business. John Elkington, a global authority on corporate responsibility and sustainability coined the phrase in a book in 1997. His argument was that the methods by which companies measure value should include not only a financial bottom line (profit or loss), but a social and environmental one as well. The concept has evolved into one that’s often described as three overlapping circles. You’ve probably seen this image before. Sustainability is typically defined as the place where economy, social realities and environmental health overlap.
The concept of the triple bottom line mainstreamed the idea of sustainability as including people, planet AND profit. It helped business to understand that long-term sustainability of an organization required more than just financial equity. It also helped to clarify that when businesses were considering what sustainability meant for them, it didn’t mean they had to give up the notion of financial success.
But this overlapping circles image of the triple bottom line can convey a lot more. The circles are all the same size. Does this indicate that the economy is the same relative size, or value, as the other two circles, which deal with society and the environment? Can we trade say “2 social and 3 environment for 5 economy” as long as we stay in the overlapping bit in the middle (sustainability)?
Science tells us that, left to its own devices, the planet operates in a balanced way. We call this the cycles of nature and they are powered by energy from the sun. Science also tells us that matter is not created or destroyed, while laws of thermodynamics tell us that everything tends toward dispersal (principle of entropy). Because plant cells are, for all intents and purposes, the only cells that can produce structure from energy, photosynthesis is the process by which matter is structured on our planet. This is why we say that photosynthesis pays the bills. Without it, creation of structure from energy would not occur, and entropy could rule the day.
How does this help us understand the triple bottom line?
Plant cells belong to the environment circle of the triple bottom line. If plant cells are the original creators of structure, then this is the circle on which everything else depends, or in which everything is embedded. Everything comes from nature at some point. Society, which is related to the social circle of the triple bottom line, exists within the environment. And economy is a by-product of society. Instead of three overlapping circles, we have three nested circles, where the economy is a wholly owned subsidiary of the environment.
To achieve sustainability, we need to comply with social and environmental conditions: meet human needs within ecological constraints. Does this mean that business has to put financial gain last? Of course not! But economic decisions are part of a strategy to make more money while getting closer to social and ecological sustainability. The economy is a means to an end. Not the end itself.
Комментарии
 0:04:14
0:04:14
 0:03:20
0:03:20
 0:09:31
0:09:31
 0:09:13
0:09:13
 0:04:16
0:04:16
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:07:42
0:07:42
 0:06:46
0:06:46
 0:03:06
0:03:06
 0:10:36
0:10:36
 0:04:18
0:04:18
 0:01:21
0:01:21
 0:01:30
0:01:30
 0:10:57
0:10:57
 0:01:43
0:01:43
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:06:59
0:06:59
 0:08:17
0:08:17
 0:03:37
0:03:37
 1:16:02
1:16:02
 0:04:29
0:04:29
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:19:19
0:19:19
 0:04:45
0:04:45