filmov
tv
Learn English News: Why did ethnic Serbs attack NATO peacekeepers in Kosovo? Here’s what we know

Показать описание
Learn English Through News: Why did ethnic Serbs attack NATO peacekeepers in Kosovo? Here’s what we know
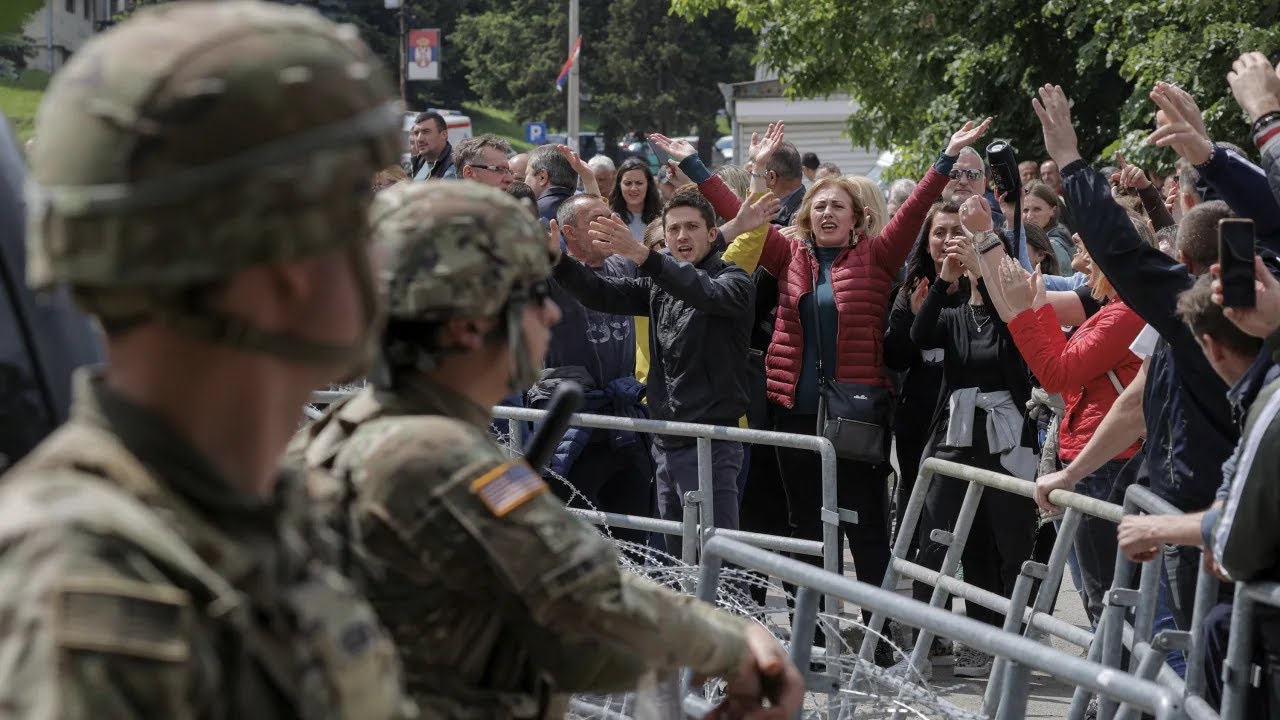
Dozens of NATO peacekeepers were injured after they were attacked by ethnic Serbs in northern Kosovo, during protests over the installation of ethnically Albanian mayors.
Violence broke out after Serbian demonstrators tried to block the newly elected mayors from taking office in the northern town of Zvecan on Monday, following a disputed election in April.
While this sort of violence against peacekeepers is rare, tensions have spiked in the region in recent months, fueled by deep historical rifts.
Here’s what you need to know.
What’s the background?
Kosovo declared independence from Serbia in 2008, following the 1998-99 war in which Kosovar Albanians attempted to break from what was then the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, made up of today’s Serbia and Montenegro. NATO intervened in the war to protect Kosovo’s Albanian majority.
Serbia views Kosovo as a breakaway state and does not recognize its independence. Kosovo’s Serbs view themselves as part of Serbia, and see Belgrade as their capital, rather than Pristina.
The majority of Kosovo’s Serbs – less than a tenth of the overall population – live in the northern regions, and have increasingly demanded greater autonomy from the ethnic Albanian majority.
The EU-brokered 2013 Brussels Agreement attempted to normalize relations between the two countries. Under this deal, Serbia could create autonomous municipalities in the northern region, but these would have to operate under the Kosovar legal system, with Kosovar police remaining the only police force.
More than a decade on, these municipalities have not been created, leaving disputes over the degree of autonomy for Kosovo’s Serbs to fester.
Even seemingly small details can cause huge flare-ups. For years, Kosovo has wanted Serbs to switch their Serbian car license plates to ones issued by Pristina. Last year, Kosovo’s government announced a two-month window in which plates had to be changed – but pushed the date back after protests.
Ethnic Serb mayors in northern municipalities, along with local judges and some 600 police officers, resigned in November in protest against the looming switch, according to Reuters.
What caused the fresh violence?
In March, the two countries signed a fresh deal in Ohrin, North Macedonia, aiming again to normalize ties. But this was followed by controversial local elections in four municipalities of northern Kosovo.
Serbian President Aleksandar Vucic called on ethnic Serbs in the region to boycott the elections, saying that they should no longer tolerate a foreign “occupation.”
Serbian List, the main political party in the region, called on the Serb community not to vote in the elections and on its candidates not to stand – leaving ethnically Albanian candidates to run unchallenged.
Fearing potential violence, Kosovo’s central election commission changed plans to put voting booths in local schools, instead setting up mobile huts patrolled by NATO peacekeepers.
Kosovo’s Prime Minister Albin Kurti said there had been a “threatening campaign orchestrated by Belgrade and executed through intimidation, pressure and blackmail by criminal groups.”
After polls closed, election officials said only around 1,567 had voted across the four municipalities – a turnout of 3.5%, according to local media.
The diminished turnout was a mark of the boycott’s success in these majority Serb regions. The Zvecan municipality has a population of around 16,800. Of these, more than 16,000 are ethnic Serbs – with only around 500 ethnic Albanians.
The newly-elected Albanian mayor in Zvecan won with scarcely over 100 votes, prompting cries that his authority is illegitimate.
What happened Monday?
Ethnic Serb protesters threw Molotov cocktails at NATO’s Kosovo Force (KFOR) troops and used batons to beat their riot shields, as the peacekeepers defended the municipal office in Zvecan.
KFOR said 30 of its peacekeepers – mostly from its Italian and Hungarian contingents – were wounded.
The soldiers suffered from “fractures and burns from improvised explosive incendiary devices,” while three soldiers were “wounded by the use of firearms,” according to KFOR.
The peacekeeping mission said that it had increased its presence in northern Kosovo after the newly elected ethnically Albanian mayors took office in majority Kosovo Serb areas. Its aim was to “reduce the risk of escalation,” KFOR said, but troops were “subsequently attacked by increasingly aggressive crowds.”
Kurti condemned the “outrageous attacks” on the peacekeepers. “In a democracy there is no place for fascist violence – not appeal from ballot to bullet,” he tweeted Monday.
In a statement, Serbian Prime Minister Ana Brnabic said the situation in northern Kosovo has “never been more difficult.”
Dozens of NATO peacekeepers were injured after they were attacked by ethnic Serbs in northern Kosovo, during protests over the installation of ethnically Albanian mayors.
Violence broke out after Serbian demonstrators tried to block the newly elected mayors from taking office in the northern town of Zvecan on Monday, following a disputed election in April.
While this sort of violence against peacekeepers is rare, tensions have spiked in the region in recent months, fueled by deep historical rifts.
Here’s what you need to know.
What’s the background?
Kosovo declared independence from Serbia in 2008, following the 1998-99 war in which Kosovar Albanians attempted to break from what was then the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, made up of today’s Serbia and Montenegro. NATO intervened in the war to protect Kosovo’s Albanian majority.
Serbia views Kosovo as a breakaway state and does not recognize its independence. Kosovo’s Serbs view themselves as part of Serbia, and see Belgrade as their capital, rather than Pristina.
The majority of Kosovo’s Serbs – less than a tenth of the overall population – live in the northern regions, and have increasingly demanded greater autonomy from the ethnic Albanian majority.
The EU-brokered 2013 Brussels Agreement attempted to normalize relations between the two countries. Under this deal, Serbia could create autonomous municipalities in the northern region, but these would have to operate under the Kosovar legal system, with Kosovar police remaining the only police force.
More than a decade on, these municipalities have not been created, leaving disputes over the degree of autonomy for Kosovo’s Serbs to fester.
Even seemingly small details can cause huge flare-ups. For years, Kosovo has wanted Serbs to switch their Serbian car license plates to ones issued by Pristina. Last year, Kosovo’s government announced a two-month window in which plates had to be changed – but pushed the date back after protests.
Ethnic Serb mayors in northern municipalities, along with local judges and some 600 police officers, resigned in November in protest against the looming switch, according to Reuters.
What caused the fresh violence?
In March, the two countries signed a fresh deal in Ohrin, North Macedonia, aiming again to normalize ties. But this was followed by controversial local elections in four municipalities of northern Kosovo.
Serbian President Aleksandar Vucic called on ethnic Serbs in the region to boycott the elections, saying that they should no longer tolerate a foreign “occupation.”
Serbian List, the main political party in the region, called on the Serb community not to vote in the elections and on its candidates not to stand – leaving ethnically Albanian candidates to run unchallenged.
Fearing potential violence, Kosovo’s central election commission changed plans to put voting booths in local schools, instead setting up mobile huts patrolled by NATO peacekeepers.
Kosovo’s Prime Minister Albin Kurti said there had been a “threatening campaign orchestrated by Belgrade and executed through intimidation, pressure and blackmail by criminal groups.”
After polls closed, election officials said only around 1,567 had voted across the four municipalities – a turnout of 3.5%, according to local media.
The diminished turnout was a mark of the boycott’s success in these majority Serb regions. The Zvecan municipality has a population of around 16,800. Of these, more than 16,000 are ethnic Serbs – with only around 500 ethnic Albanians.
The newly-elected Albanian mayor in Zvecan won with scarcely over 100 votes, prompting cries that his authority is illegitimate.
What happened Monday?
Ethnic Serb protesters threw Molotov cocktails at NATO’s Kosovo Force (KFOR) troops and used batons to beat their riot shields, as the peacekeepers defended the municipal office in Zvecan.
KFOR said 30 of its peacekeepers – mostly from its Italian and Hungarian contingents – were wounded.
The soldiers suffered from “fractures and burns from improvised explosive incendiary devices,” while three soldiers were “wounded by the use of firearms,” according to KFOR.
The peacekeeping mission said that it had increased its presence in northern Kosovo after the newly elected ethnically Albanian mayors took office in majority Kosovo Serb areas. Its aim was to “reduce the risk of escalation,” KFOR said, but troops were “subsequently attacked by increasingly aggressive crowds.”
Kurti condemned the “outrageous attacks” on the peacekeepers. “In a democracy there is no place for fascist violence – not appeal from ballot to bullet,” he tweeted Monday.
In a statement, Serbian Prime Minister Ana Brnabic said the situation in northern Kosovo has “never been more difficult.”
 0:26:36
0:26:36
 0:13:21
0:13:21
 0:14:18
0:14:18
 0:29:12
0:29:12
 0:16:14
0:16:14
 0:18:49
0:18:49
 0:33:01
0:33:01
 0:08:15
0:08:15
 0:06:22
0:06:22
 0:10:22
0:10:22
 1:07:07
1:07:07
 0:06:15
0:06:15
 0:08:07
0:08:07
 0:09:02
0:09:02
 0:06:22
0:06:22
 1:00:56
1:00:56
 0:28:17
0:28:17
 0:12:54
0:12:54
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:20:21
0:20:21
 0:29:21
0:29:21
 0:06:15
0:06:15
 0:16:47
0:16:47
 0:46:05
0:46:05