filmov
tv
Introduction to Buffer System || Regulation of pH || Acid Base Balance || Buffers in Biochemistry
Показать описание
Buffer system for the acid base balance and regulation of pH - This video is on the introduction to Acids, Bases, Buffers, physiological pH of blood and different types of extracellular buffer and intra cellular buffer which are first line of defense for the regulation of pH.
Acids, Bases and buffers - 00:24 minutes
Normal pH of the body fluids - 01:45 minutes
Why maintenance of a pH is important - 02:28 minutes
Fixed acids or Non volatile acids - 03:25 minutes
Volatile acids - 03:50 minutes
Metabolic Sources Of Bases - 04:05 minutes
Mechanism for the regulation of pH - 04:40 minutes
Buffering Capacity - 06:40 minutes
pKa - 06:48 minutes
Intracellular and Extracellular buffer - 07:42 minutes
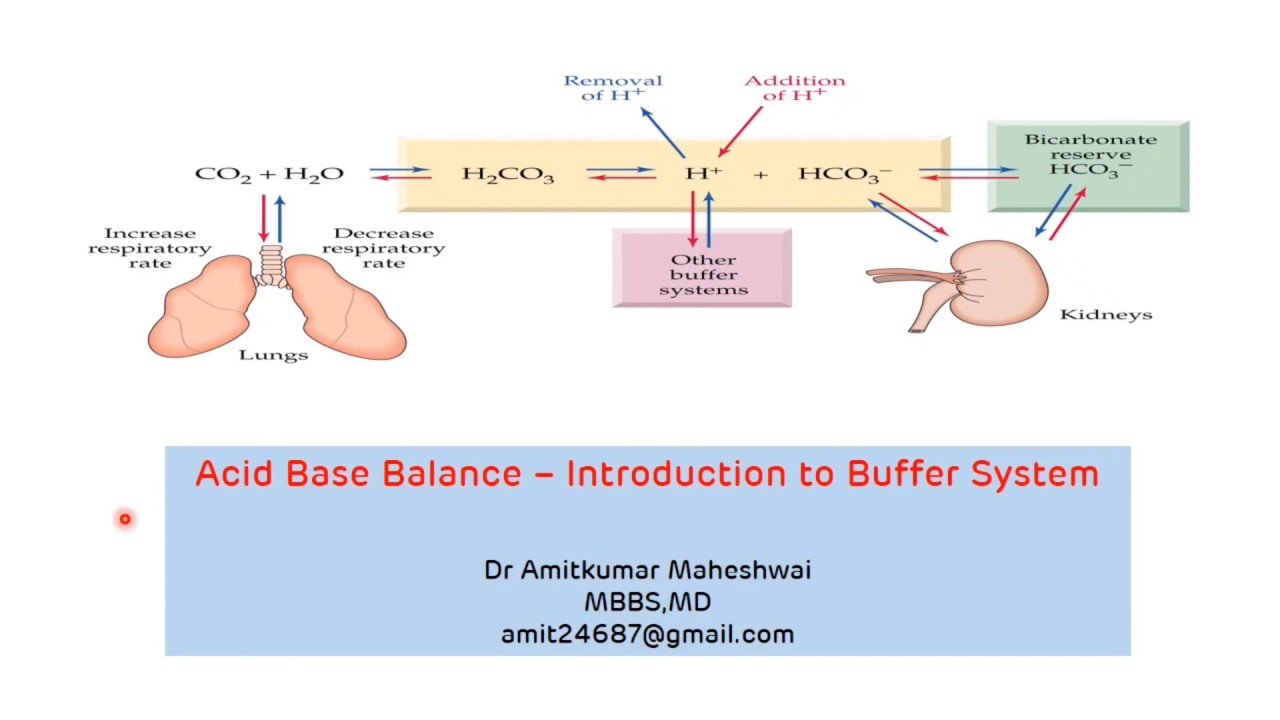
Bicarbonate Buffer system - 08:56 minutes
Mechanism of Bicarbonate buffer - 09:43 minutes
Phosphate buffer system - 12:47 minutes
Mechanism of phosphate buffer - 13:08 minutes
Protein buffer - 15:03 minutes
Hemoglobin buffer - 16:12 minutes
Mechanism of hemoglobin buffer - 17:14 minutes
Chloride Shift - 18:28 minutes
NEET PG Biochemistry MCQs - 21:03 minutes
ACIDS, BASES AND BUFFERS
An acid is defined as a substance that releases protons or hydrogen ions (H+), e.g. hydrochloric acid (HCI), carbonic acid (H2CO3).
base is a substance that accepts protons or hydrogen ions, e.g. bicarbonate ion (HCO3–), and HPO4– –
Buffer is a solution of weak acid and its corresponding salt which resists a change in pH when a small amount of acid or base is added to it.
By buffering mechanism a strong acid (or base) is replaced by a weaker one.
Normal pH Of The Body Fluids
The normal pH of arterial blood is 7.4
pH of venous blood and interstitial fluids is about 7.35
The pH of blood is maintained within a remarkable constant level of 7.35 to 7.45.
Regulatory Mechanisms to maintain normal Blood pH
Buffer mechanism: First line of defense
The respiratory mechanism: Second line of defense
Renal mechanism: Third line of defense.
Blood Buffer
Buffer System Extracellular buffer Intracellularbuffer
Bicarbonate NaHCO3/ H2CO3 KHCO3/H2CO3
Phosphate Na2HPO4/NaH2PO4 K2HPO4/KH2PO4
Protein Na Protein/H. Protein KHb/H.Hb
KHbO2/H.HbO2
#biochemistrybasicsbydramit #pHregulation #buffersystem #acidbasebalance #NEETPG #NEETPGbiochemistry #USMLE
Acids, Bases and buffers - 00:24 minutes
Normal pH of the body fluids - 01:45 minutes
Why maintenance of a pH is important - 02:28 minutes
Fixed acids or Non volatile acids - 03:25 minutes
Volatile acids - 03:50 minutes
Metabolic Sources Of Bases - 04:05 minutes
Mechanism for the regulation of pH - 04:40 minutes
Buffering Capacity - 06:40 minutes
pKa - 06:48 minutes
Intracellular and Extracellular buffer - 07:42 minutes
Bicarbonate Buffer system - 08:56 minutes
Mechanism of Bicarbonate buffer - 09:43 minutes
Phosphate buffer system - 12:47 minutes
Mechanism of phosphate buffer - 13:08 minutes
Protein buffer - 15:03 minutes
Hemoglobin buffer - 16:12 minutes
Mechanism of hemoglobin buffer - 17:14 minutes
Chloride Shift - 18:28 minutes
NEET PG Biochemistry MCQs - 21:03 minutes
ACIDS, BASES AND BUFFERS
An acid is defined as a substance that releases protons or hydrogen ions (H+), e.g. hydrochloric acid (HCI), carbonic acid (H2CO3).
base is a substance that accepts protons or hydrogen ions, e.g. bicarbonate ion (HCO3–), and HPO4– –
Buffer is a solution of weak acid and its corresponding salt which resists a change in pH when a small amount of acid or base is added to it.
By buffering mechanism a strong acid (or base) is replaced by a weaker one.
Normal pH Of The Body Fluids
The normal pH of arterial blood is 7.4
pH of venous blood and interstitial fluids is about 7.35
The pH of blood is maintained within a remarkable constant level of 7.35 to 7.45.
Regulatory Mechanisms to maintain normal Blood pH
Buffer mechanism: First line of defense
The respiratory mechanism: Second line of defense
Renal mechanism: Third line of defense.
Blood Buffer
Buffer System Extracellular buffer Intracellularbuffer
Bicarbonate NaHCO3/ H2CO3 KHCO3/H2CO3
Phosphate Na2HPO4/NaH2PO4 K2HPO4/KH2PO4
Protein Na Protein/H. Protein KHb/H.Hb
KHbO2/H.HbO2
#biochemistrybasicsbydramit #pHregulation #buffersystem #acidbasebalance #NEETPG #NEETPGbiochemistry #USMLE
Комментарии
 0:06:19
0:06:19
 0:24:25
0:24:25
 0:23:23
0:23:23
 0:04:27
0:04:27
 0:03:11
0:03:11
 0:07:18
0:07:18
 0:05:57
0:05:57
 0:02:43
0:02:43
 0:23:20
0:23:20
 0:06:28
0:06:28
 0:07:55
0:07:55
 0:02:11
0:02:11
 0:06:31
0:06:31
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:06:20
0:06:20
 0:07:31
0:07:31
 0:23:54
0:23:54
 0:33:21
0:33:21
 0:10:07
0:10:07
 0:05:04
0:05:04
 0:01:50
0:01:50
 0:13:56
0:13:56
 0:05:31
0:05:31
 1:21:17
1:21:17