filmov
tv
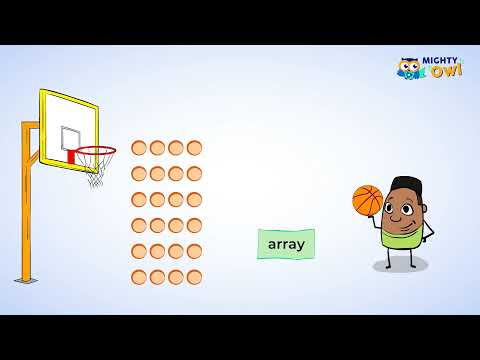
Solve multiplication problems by drawing an array

Показать описание
Solve multiplication problems by drawing an array
In this lesson you will learn how to solve multiplication problems by creating an array.
ADDITIONAL MATERIALS
STANDARDS
CCSS.3.OA.A.1 Interpret products of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 5 × 7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups of 7 objects each. For example, describe a context in which a total number of objects can be expressed as 5 × 7.
TEKS.3.4.K solve one-step and two-step problems involving multiplication and division within 100 using strategies based on objects; pictorial models, including arrays, area models, and equal groups; properties of operations; or recall of facts.
TEKS.3.4.E represent multiplication facts by using a variety of approaches such as repeated addition, equal-sized groups, arrays, area models, equal jumps on a number line, and skip counting;
TEKS.3.4.D determine the total number of objects when equally-sized groups of objects are combined or arranged in arrays up to 10 by 10;
IN.3.AT.4 Interpret a multiplication equation as equal groups (e.g., interpret 5 × 7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups of 7 objects each). Represent verbal statements of equal groups as multiplication equations.
VA.CE.4.4.d create and solve single-step and multistep practical problems involving addition, subtraction, and multiplication, and single-step practical problems involving division with whole numbers.
VA.CE.3.4.b create and solve single-step practical problems that involve multiplication and division through 10 x 10; and
VA.CE.3.4.a represent multiplication and division through 10 × 10, using a variety of approaches and models;
FL.MAFS.3.OA.1.1 Interpret products of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 5 × 7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups of 7 objects each. For example, describe a context in which a total number of objects can be expressed as 5 × 7.
In this lesson you will learn how to solve multiplication problems by creating an array.
ADDITIONAL MATERIALS
STANDARDS
CCSS.3.OA.A.1 Interpret products of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 5 × 7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups of 7 objects each. For example, describe a context in which a total number of objects can be expressed as 5 × 7.
TEKS.3.4.K solve one-step and two-step problems involving multiplication and division within 100 using strategies based on objects; pictorial models, including arrays, area models, and equal groups; properties of operations; or recall of facts.
TEKS.3.4.E represent multiplication facts by using a variety of approaches such as repeated addition, equal-sized groups, arrays, area models, equal jumps on a number line, and skip counting;
TEKS.3.4.D determine the total number of objects when equally-sized groups of objects are combined or arranged in arrays up to 10 by 10;
IN.3.AT.4 Interpret a multiplication equation as equal groups (e.g., interpret 5 × 7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups of 7 objects each). Represent verbal statements of equal groups as multiplication equations.
VA.CE.4.4.d create and solve single-step and multistep practical problems involving addition, subtraction, and multiplication, and single-step practical problems involving division with whole numbers.
VA.CE.3.4.b create and solve single-step practical problems that involve multiplication and division through 10 x 10; and
VA.CE.3.4.a represent multiplication and division through 10 × 10, using a variety of approaches and models;
FL.MAFS.3.OA.1.1 Interpret products of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 5 × 7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups of 7 objects each. For example, describe a context in which a total number of objects can be expressed as 5 × 7.
 0:04:24
0:04:24
 0:01:30
0:01:30
 0:04:48
0:04:48
 0:03:00
0:03:00
 0:02:07
0:02:07
 0:05:36
0:05:36
 0:03:34
0:03:34
 0:03:58
0:03:58
 0:45:03
0:45:03
 0:03:45
0:03:45
 0:00:28
0:00:28
 0:04:19
0:04:19
 0:07:31
0:07:31
 0:02:05
0:02:05
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:05:49
0:05:49
 0:00:27
0:00:27
 0:00:22
0:00:22
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:02:29
0:02:29
 0:00:18
0:00:18
 0:00:36
0:00:36
 0:05:19
0:05:19
 0:05:13
0:05:13