filmov
tv
How to Use the Two Pointer Technique

Показать описание
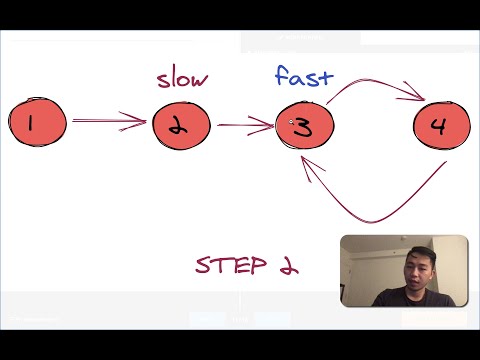
The two pointer technique is a near necessity in any software developer's toolkit, especially when it comes to technical interviews. In this guide, we'll cover the basics so that you know when and how to use this technique.
To / Too / Two - What is the Difference? | Homophones English Grammar ESL Mini Lesson
How to Use the Two Pointer Technique
The use of Two Handed Swords in Formations #sword #hema #zweihander
How to use WhatsApp on multiple phones | Two phones at once!
Use Same WhatsApp on Two Phones!
Use Two Apps At The Same Time
How I Use two computers with one keyboard.
How to Use Two Part Wood Filler #shorts
How to Use one WhatsApp Account on Two Phones
How to use two Facebook accounts in one phone without any app #shorts
Marques, How do you Use Two Phones?
why i use fortune two
Use TWO ROPES for Tricep extensions
How to Use WhatsApp Account On Two Phones!!
How to use one Facebook account on two phones
How to Use Two WhatsApp Accounts on One Phone (2024 Update)
How to use two WhatsApp accounts on the same phone
I use two compressors...
How to Use Same WhatsApp Account on Two Devices
Always Use Two Fingers! #motorcycle #shorts
How to use hybrid simcard slot with memory card || How use two simcard in hybrid slots
How to use two app in one time in half half screen
How to Use Two WhatsApp Accounts on One Phone
Use two straws to weave a beautiful love pendant. Pure milk straws can also be made. Come and try i
Комментарии
 0:02:47
0:02:47
 0:10:56
0:10:56
 0:00:28
0:00:28
 0:02:58
0:02:58
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:00:21
0:00:21
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:01:33
0:01:33
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:11:38
0:11:38
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:01:08
0:01:08
 0:03:44
0:03:44
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:02:49
0:02:49
 0:00:35
0:00:35
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:01:13
0:01:13
 0:00:25
0:00:25