filmov
tv
Calcific Bursitis, Causes, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment.

Показать описание
.
Chapters
0:00 Introduction
0:36 causes of Calcific Bursitis
1:11 symptoms of Calcific Bursitis
1:32 Treatments of Calcific Bursitis
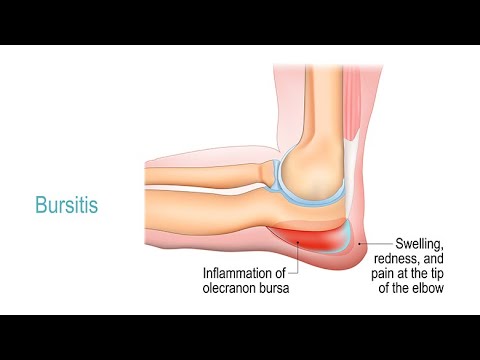
Calcific bursitis refers to calcium deposits within the bursae. This most occurs in the shoulder area. The most common bursa for calcific bursitis to occur is the subacromial bursa. A bursa is a small, fluid-filled sac that reduces friction, and facilitates movements between its adjacent tissues (i.e., between tendon and bone, two muscles or skin and bone). Inflammation of the bursae is called bursitis. Pain during rest
Tenderness on palpation
Stiffness (reducing joint range of motion)
Swelling
Causes
Calcific bursitis may be related to:[citation needed]
Calcific tendinitis. Sometimes calcium deposits of the involved tendons penetrate into the bursae.
Chronic bursitis. Lack of bursitis treatment or repetitive bursitis may lead to calcific bursitis.
Diagnosis
Diagnostic methods are the following[citation needed]
X-ray
MRI scan
Treatment
Management methods are the following[citation needed]
Ice (in the acute stage)
Rest (immobilization of the affected limb in the acute phase)
Non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Injections of steroid
Physical therapy
Surgical treatment
Chapters
0:00 Introduction
0:36 causes of Calcific Bursitis
1:11 symptoms of Calcific Bursitis
1:32 Treatments of Calcific Bursitis
Calcific bursitis refers to calcium deposits within the bursae. This most occurs in the shoulder area. The most common bursa for calcific bursitis to occur is the subacromial bursa. A bursa is a small, fluid-filled sac that reduces friction, and facilitates movements between its adjacent tissues (i.e., between tendon and bone, two muscles or skin and bone). Inflammation of the bursae is called bursitis. Pain during rest
Tenderness on palpation
Stiffness (reducing joint range of motion)
Swelling
Causes
Calcific bursitis may be related to:[citation needed]
Calcific tendinitis. Sometimes calcium deposits of the involved tendons penetrate into the bursae.
Chronic bursitis. Lack of bursitis treatment or repetitive bursitis may lead to calcific bursitis.
Diagnosis
Diagnostic methods are the following[citation needed]
X-ray
MRI scan
Treatment
Management methods are the following[citation needed]
Ice (in the acute stage)
Rest (immobilization of the affected limb in the acute phase)
Non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Injections of steroid
Physical therapy
Surgical treatment
 0:02:15
0:02:15
 0:02:22
0:02:22
 0:02:40
0:02:40
 0:08:09
0:08:09
 0:02:42
0:02:42
 0:03:42
0:03:42
 0:02:49
0:02:49
 0:01:52
0:01:52
 0:01:27
0:01:27
 0:04:30
0:04:30
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:01:37
0:01:37
 0:07:13
0:07:13
 0:04:04
0:04:04
 0:05:42
0:05:42
 0:05:22
0:05:22
 0:09:22
0:09:22
 0:04:05
0:04:05
 0:02:03
0:02:03
 0:00:55
0:00:55
 0:01:53
0:01:53
 0:03:05
0:03:05
 0:02:20
0:02:20
 0:04:47
0:04:47