filmov
tv
highly active antiretroviral therapy

Показать описание
(cART, combination antiretroviral therapy, HAART)
Treatment or management of HIV/AIDS that uses a combination of multiple drugs.
It stops the virus from making copies of itself in the body, lessening the damage to the immune system caused by the virus and slowing down the development of AIDS. It prevents opportunistic infections that often lead to death.
It may also help prevent transmission of HIV to others, including from mother to child during birth.
(Antiretroviral drugs: Broadly classified by the phase of the retrovirus life-cycle that the drug inhibits)
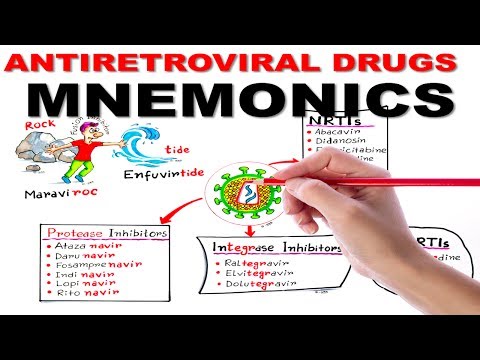
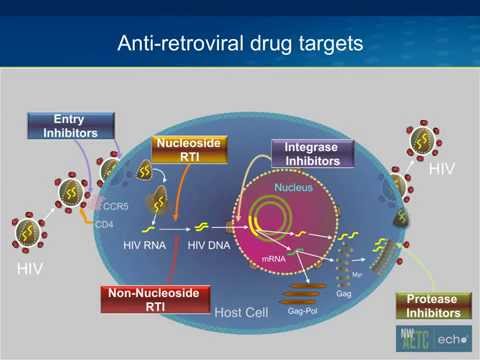
• nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTI): Targets a reverse transcriptase by disrupting the construction of a new piece of proviral DNA.
• non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI): Targets a reverse transcriptase by binding directly to it, blocking the reverse transcription process.
• protease inhibitor (PI): Blocks the activity of the protease enzyme.
• integrase inhibitor (integrase nuclear strand transfer inhibitor, INSTI): Targets an integrase which is essential for viral replication.
• fusion inhibitor (FI): An entry inhibitor.
• chemokine receptor antagonist (CCR5 antagonist): An entry inhibitor.
• attachment inhibitor: Binds to the gp120 portion of the HIV envelope protein.
• post-attachment inhibitor: Binds to the CD4 receptor on T-cells.
It has been so successful that in many parts of the world, HIV has become a chronic condition in which progression to AIDS is increasingly rare.
Treatment or management of HIV/AIDS that uses a combination of multiple drugs.
It stops the virus from making copies of itself in the body, lessening the damage to the immune system caused by the virus and slowing down the development of AIDS. It prevents opportunistic infections that often lead to death.
It may also help prevent transmission of HIV to others, including from mother to child during birth.
(Antiretroviral drugs: Broadly classified by the phase of the retrovirus life-cycle that the drug inhibits)
• nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTI): Targets a reverse transcriptase by disrupting the construction of a new piece of proviral DNA.
• non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI): Targets a reverse transcriptase by binding directly to it, blocking the reverse transcription process.
• protease inhibitor (PI): Blocks the activity of the protease enzyme.
• integrase inhibitor (integrase nuclear strand transfer inhibitor, INSTI): Targets an integrase which is essential for viral replication.
• fusion inhibitor (FI): An entry inhibitor.
• chemokine receptor antagonist (CCR5 antagonist): An entry inhibitor.
• attachment inhibitor: Binds to the gp120 portion of the HIV envelope protein.
• post-attachment inhibitor: Binds to the CD4 receptor on T-cells.
It has been so successful that in many parts of the world, HIV has become a chronic condition in which progression to AIDS is increasingly rare.
 0:02:31
0:02:31
 0:08:37
0:08:37
 0:01:40
0:01:40
 0:03:19
0:03:19
 0:04:04
0:04:04
 0:38:07
0:38:07
 0:59:54
0:59:54
 0:17:59
0:17:59
 0:04:28
0:04:28
 0:23:45
0:23:45
 0:07:37
0:07:37
 0:14:47
0:14:47
 1:36:41
1:36:41
 1:07:57
1:07:57
 0:05:54
0:05:54
 0:37:55
0:37:55
 1:15:49
1:15:49
 0:18:52
0:18:52
 0:20:20
0:20:20
 0:03:13
0:03:13
 1:18:01
1:18:01
 0:14:31
0:14:31
 1:36:07
1:36:07
 0:49:32
0:49:32