filmov
tv
Human Impacts on Biodiversity | Ecology and Environment | Biology | FuseSchool

Показать описание
Human Impacts on Biodiversity | Ecology and Environment | Biology | FuseSchool
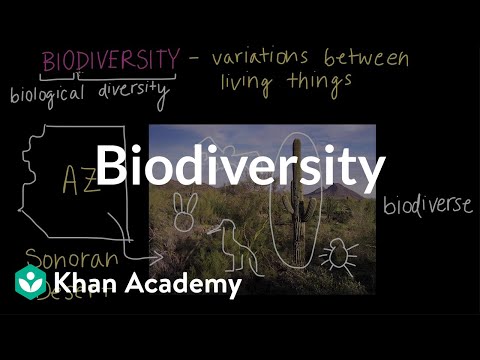
Biodiversity is the variety of life. There are thought to be 8.7 million species on planet Earth. And, as we saw in the video, "Why does biodiversity matter to me?", biodiversity is of utmost importance to humans.
The loss of one key species can have a detrimental impact on many levels; from other species of animals to plants to the physical environment.
Human activities are reducing biodiversity. Our future depends upon maintaining a good level of biodiversity, and so we need to start taking measures to try and stop the reduction.
In this video, we are going to look at how humans are negatively impacting biodiversity.
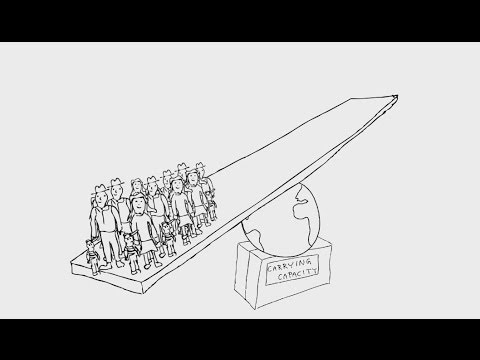
As the world population has grown from 1.5 billion in 1900 to nearly 7.5 billion people today, unsurprisingly the land use has changed.
Habitats have been destroyed in favour of agriculture, forestry, fishing, urbanisation and manufacturing. Unsurprisingly, habitat loss has greatly reduced the species richness. Habitat fragmentation has also meant that populations have been split into smaller subunits, which then, when faced with challenging circumstances, have not been able to adapt and survive.
After habitat loss, over-harvesting has had a huge effect on biodiversity. Humans historically exploit plant and animal species for short-term profit. If a resource is profitable, we develop more efficient methods of harvesting it, inevitably depleting the resources, as is currently happening with fishing and logging. The exploited species then needs protection. The difficulty is that the demand then outstrips the supply, and so the resource value rises. This increases the incentive to extract the resource and leads to the final collapse of the population, as happened with whales, elephants, spotted cats, cod, tuna and many more species.
Human activities are polluting the air and water. Toxic discharge into the water from industrial processes unsurprisingly has a negative effect on the local aquatic species by killing, weakening or affecting their ability to reproduce. Another big water pollution problem is eutrophication. Phosphorous and nitrogen in fertilisers run-off agricultural fields and pass into rivers. These surplus nutrients cause algae to bloom, which then starves other aquatic species of oxygen and light, causing them to die.
Acid rain is one consequence of humans polluting the air. This causes lakes and water bodies to become more acidic, killing off fish, molluscs, amphibians and many other species.
A huge impact humans have had on planet Earth is the introduction of alien species to habitats. In fact, it is estimated that on any given day there are 3000 species in transit aboard ocean-going vessels! Alien species can cause problems in a number of ways.
Throughout the earth’s history there have been periods of rapid climate change that have led to mass extinction events. We are currently in a period of fluctuating climate, but nearly all scientists agree that human activities, like burning fossil fuels, are speeding up global warming.
We don’t know how much climate change is going to affect biodiversity in future, but it’s predicted to be huge. Loss of sea ice and ocean acidification are already causing huge reductions in biodiversity. Climate change alters temperature and weather patterns, with changing patterns of rainfall and drought expected to have significant impacts on biodiversity.
You can search the internet to find more human-related impacts on biodiversity.
SUPPORT US ON PATREON
SUBSCRIBE to the FuseSchool YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid.
Biodiversity is the variety of life. There are thought to be 8.7 million species on planet Earth. And, as we saw in the video, "Why does biodiversity matter to me?", biodiversity is of utmost importance to humans.
The loss of one key species can have a detrimental impact on many levels; from other species of animals to plants to the physical environment.
Human activities are reducing biodiversity. Our future depends upon maintaining a good level of biodiversity, and so we need to start taking measures to try and stop the reduction.
In this video, we are going to look at how humans are negatively impacting biodiversity.
As the world population has grown from 1.5 billion in 1900 to nearly 7.5 billion people today, unsurprisingly the land use has changed.
Habitats have been destroyed in favour of agriculture, forestry, fishing, urbanisation and manufacturing. Unsurprisingly, habitat loss has greatly reduced the species richness. Habitat fragmentation has also meant that populations have been split into smaller subunits, which then, when faced with challenging circumstances, have not been able to adapt and survive.
After habitat loss, over-harvesting has had a huge effect on biodiversity. Humans historically exploit plant and animal species for short-term profit. If a resource is profitable, we develop more efficient methods of harvesting it, inevitably depleting the resources, as is currently happening with fishing and logging. The exploited species then needs protection. The difficulty is that the demand then outstrips the supply, and so the resource value rises. This increases the incentive to extract the resource and leads to the final collapse of the population, as happened with whales, elephants, spotted cats, cod, tuna and many more species.
Human activities are polluting the air and water. Toxic discharge into the water from industrial processes unsurprisingly has a negative effect on the local aquatic species by killing, weakening or affecting their ability to reproduce. Another big water pollution problem is eutrophication. Phosphorous and nitrogen in fertilisers run-off agricultural fields and pass into rivers. These surplus nutrients cause algae to bloom, which then starves other aquatic species of oxygen and light, causing them to die.
Acid rain is one consequence of humans polluting the air. This causes lakes and water bodies to become more acidic, killing off fish, molluscs, amphibians and many other species.
A huge impact humans have had on planet Earth is the introduction of alien species to habitats. In fact, it is estimated that on any given day there are 3000 species in transit aboard ocean-going vessels! Alien species can cause problems in a number of ways.
Throughout the earth’s history there have been periods of rapid climate change that have led to mass extinction events. We are currently in a period of fluctuating climate, but nearly all scientists agree that human activities, like burning fossil fuels, are speeding up global warming.
We don’t know how much climate change is going to affect biodiversity in future, but it’s predicted to be huge. Loss of sea ice and ocean acidification are already causing huge reductions in biodiversity. Climate change alters temperature and weather patterns, with changing patterns of rainfall and drought expected to have significant impacts on biodiversity.
You can search the internet to find more human-related impacts on biodiversity.
SUPPORT US ON PATREON
SUBSCRIBE to the FuseSchool YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid.
Комментарии
 0:04:28
0:04:28
 0:05:40
0:05:40
 0:04:35
0:04:35
 0:05:36
0:05:36
 0:04:09
0:04:09
 0:04:19
0:04:19
 0:03:25
0:03:25
 0:12:51
0:12:51
 0:58:13
0:58:13
 0:05:46
0:05:46
 0:09:12
0:09:12
 0:10:38
0:10:38
 0:09:20
0:09:20
 0:01:47
0:01:47
 0:07:51
0:07:51
 0:14:24
0:14:24
 0:03:51
0:03:51
 0:00:44
0:00:44
 2:00:23
2:00:23
 0:04:46
0:04:46
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:02:48
0:02:48
 0:11:37
0:11:37
 0:08:38
0:08:38