filmov
tv
Valves of heart

Показать описание
(Valves of heart) The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system, is a body system that is responsible for pumping and distributing blood throughout the body.
It is made up of the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
Heart
The heart is a muscular organ located in the chest that pumps blood throughout the body.
It is about the size of a clenched fist and is located between the lungs, behind the breastbone.
The heart has four chambers: the left and right atria, and the left and right ventricles.
The right atrium is the upper chamber on the right side of the heart.
It receives oxygen-depleted blood from the body and pumps it into the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve.
The right ventricle is the lower chamber on the right side of the heart.
It pumps the oxygen-depleted blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery to be oxygenated.
The left atrium is the upper chamber on the left side of the heart.
It receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it into the left ventricle through the mitral valve.
The left ventricle is the lower chamber on the left side of the heart.
It pumps the oxygenated blood out to the rest of the body through the aorta, the main artery of the body.
The heart has its own electrical conducting system, which helps to coordinate and regulate its contractions.
The sinoatrial node, also known as the heart's natural pacemaker, sends out electrical impulses that cause the heart to contract and pump blood.
The atrioventricular node receives the electrical impulses from the sinoatrial node and conducts them to the ventricles, causing them to contract and pump blood.
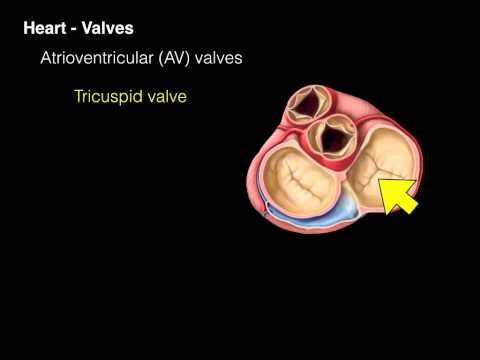
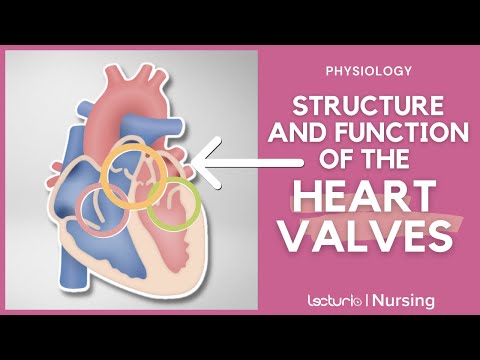
The heart also has four valves that help to regulate the flow of blood through the chambers and prevent blood from flowing back into the wrong chambers.
The tricuspid valve is located between the right atrium and right ventricle, and the mitral valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle.
The aortic valve is located between the left ventricle and the aorta, and the pulmonary valve is located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery.
blood vessels
The blood vessels are tubes that carry blood throughout the body.
There are three types of blood vessels: arteries, veins, and capillaries.
Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body's cells.
They have thick walls and are able to withstand the high pressure of the blood being pumped from the heart.
The aorta is the main artery of the body, and it branches off into smaller arteries that carry blood to the head, arms, legs, and other parts of the body.
Veins are blood vessels that carry oxygen-depleted blood back to the heart.
They have thinner walls than arteries and are not able to withstand as much pressure.
The superior and inferior vena cava are the main veins of the body, and they carry blood from the head, arms, and upper body to the heart.
The pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
Capillaries are tiny blood vessels that connect arteries and veins.
They are only one cell thick, which allows for the exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and waste products between the blood and the body's cells.
There are thousands of miles of capillaries in the body, and they are found in almost every tissue and organ.
Overall, the blood vessels play a vital role in the cardiovascular system, as they transport blood throughout the body and help to maintain the body's blood pressure.
They also help to exchange nutrients, oxygen, and waste products between the blood and the body's cells.
Blood
Blood is a vital fluid that circulates through the body's blood vessels and transports oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and other substances to and from the cells.
It also helps to maintain the body's pH balance and fights off infections and diseases.
Blood is made up of red and white blood cells and platelets suspended in plasma.
Red blood cells, or erythrocytes, are the most abundant type of blood cells.
They contain hemoglobin, a protein that binds to oxygen and carries it to the body's cells.
Red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow and have a lifespan of about 120 days.
White blood cells, or leukocytes, are responsible for defending the body against infection and disease.
There are several different types of white blood cells, including neutrophils, monocytes, lymphocytes, and eosinophils.
White blood cells are produced in the bone marrow and have a lifespan of several days to a few months.
Platelets, or thrombocytes, are small, irregularly shaped cells that are involved in blood clotting.
When a blood vessel is damaged, platelets clump together to form a clot that helps to stop the bleeding.
Platelets are produced in the bone marrow and have a lifespan of about 10 days.
It is made up of the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
Heart
The heart is a muscular organ located in the chest that pumps blood throughout the body.
It is about the size of a clenched fist and is located between the lungs, behind the breastbone.
The heart has four chambers: the left and right atria, and the left and right ventricles.
The right atrium is the upper chamber on the right side of the heart.
It receives oxygen-depleted blood from the body and pumps it into the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve.
The right ventricle is the lower chamber on the right side of the heart.
It pumps the oxygen-depleted blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery to be oxygenated.
The left atrium is the upper chamber on the left side of the heart.
It receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it into the left ventricle through the mitral valve.
The left ventricle is the lower chamber on the left side of the heart.
It pumps the oxygenated blood out to the rest of the body through the aorta, the main artery of the body.
The heart has its own electrical conducting system, which helps to coordinate and regulate its contractions.
The sinoatrial node, also known as the heart's natural pacemaker, sends out electrical impulses that cause the heart to contract and pump blood.
The atrioventricular node receives the electrical impulses from the sinoatrial node and conducts them to the ventricles, causing them to contract and pump blood.
The heart also has four valves that help to regulate the flow of blood through the chambers and prevent blood from flowing back into the wrong chambers.
The tricuspid valve is located between the right atrium and right ventricle, and the mitral valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle.
The aortic valve is located between the left ventricle and the aorta, and the pulmonary valve is located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery.
blood vessels
The blood vessels are tubes that carry blood throughout the body.
There are three types of blood vessels: arteries, veins, and capillaries.
Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body's cells.
They have thick walls and are able to withstand the high pressure of the blood being pumped from the heart.
The aorta is the main artery of the body, and it branches off into smaller arteries that carry blood to the head, arms, legs, and other parts of the body.
Veins are blood vessels that carry oxygen-depleted blood back to the heart.
They have thinner walls than arteries and are not able to withstand as much pressure.
The superior and inferior vena cava are the main veins of the body, and they carry blood from the head, arms, and upper body to the heart.
The pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
Capillaries are tiny blood vessels that connect arteries and veins.
They are only one cell thick, which allows for the exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and waste products between the blood and the body's cells.
There are thousands of miles of capillaries in the body, and they are found in almost every tissue and organ.
Overall, the blood vessels play a vital role in the cardiovascular system, as they transport blood throughout the body and help to maintain the body's blood pressure.
They also help to exchange nutrients, oxygen, and waste products between the blood and the body's cells.
Blood
Blood is a vital fluid that circulates through the body's blood vessels and transports oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and other substances to and from the cells.
It also helps to maintain the body's pH balance and fights off infections and diseases.
Blood is made up of red and white blood cells and platelets suspended in plasma.
Red blood cells, or erythrocytes, are the most abundant type of blood cells.
They contain hemoglobin, a protein that binds to oxygen and carries it to the body's cells.
Red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow and have a lifespan of about 120 days.
White blood cells, or leukocytes, are responsible for defending the body against infection and disease.
There are several different types of white blood cells, including neutrophils, monocytes, lymphocytes, and eosinophils.
White blood cells are produced in the bone marrow and have a lifespan of several days to a few months.
Platelets, or thrombocytes, are small, irregularly shaped cells that are involved in blood clotting.
When a blood vessel is damaged, platelets clump together to form a clot that helps to stop the bleeding.
Platelets are produced in the bone marrow and have a lifespan of about 10 days.
Комментарии
 0:01:24
0:01:24
 0:06:37
0:06:37
 0:03:19
0:03:19
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:05:54
0:05:54
 0:08:35
0:08:35
 0:46:42
0:46:42
 0:00:52
0:00:52
 0:26:28
0:26:28
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:24:03
0:24:03
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:09:55
0:09:55
 0:00:10
0:00:10
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:07:12
0:07:12
 0:04:46
0:04:46
 0:05:21
0:05:21
 0:02:41
0:02:41
 0:00:28
0:00:28
 0:03:07
0:03:07
 0:00:08
0:00:08
 0:01:33
0:01:33
 0:01:50
0:01:50