filmov
tv
How To Measure Angles Using A Circle Explained - Measuring Angles
Показать описание
In this video we discuss how to measure angles using a circle. We go through all of the angle measurements in a circle and give a brief introduction to using a protractor.
Transcript/notes
Angles are measured based on how open or closed they are, for instance this angle is not very open, and its measurement happens to be 20 degrees, and this angle is more open, and its measurement is 30 degrees. And angle measurements are in the form of degrees, which is represented by this little circle symbol you see here.
There are 2 very important angles to learn as references, a 90 degree angle and a 45 degree angle. The 90 degree angle, which is shown here, is called a right angle, and it is typically marked with a little box, as you see here in angle j, k, l. And the 2 lines that intersect to form a 90 degree angle are said to be perpendicular.
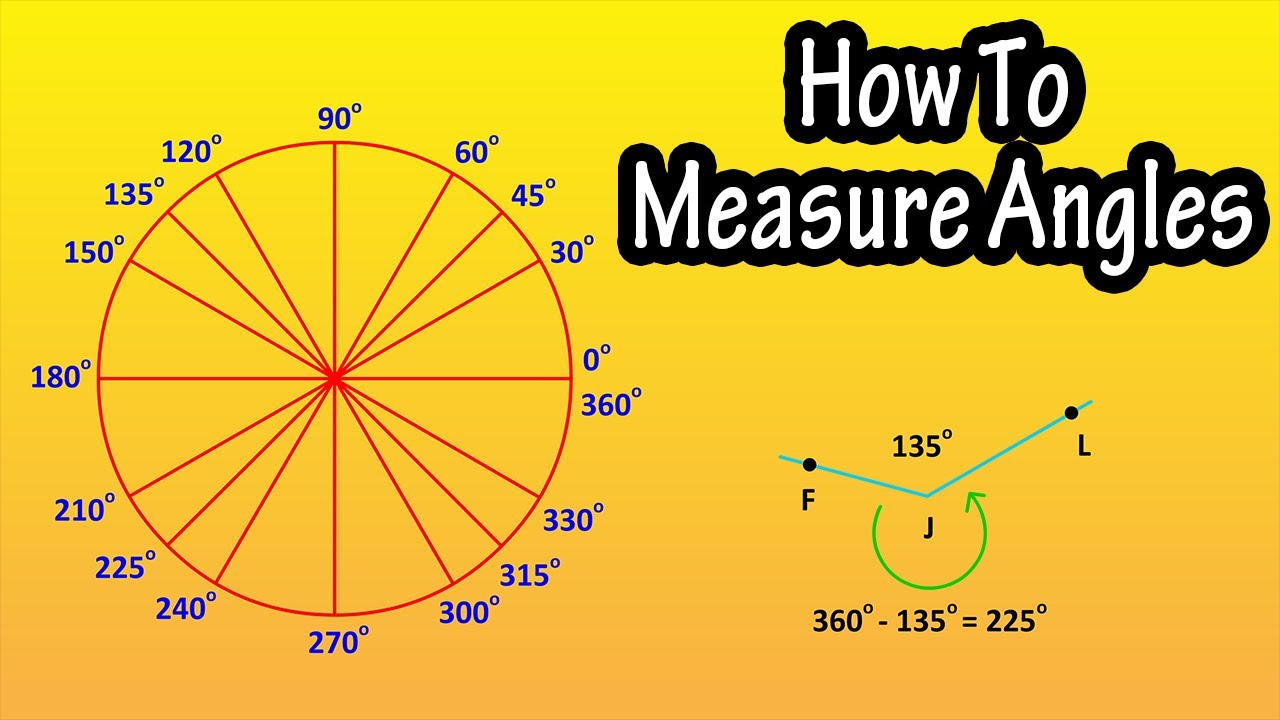
When first learning angle measurements it can help to start with a circle. We reference an angle here at 0 degrees, and an entire circle is 360 degrees.
90 degrees is here, and 45 degrees is here. A straight line across the circle has a measurement of 180 degrees, and a 270 degrees is here. And 90 degrees plus 45 degrees equals 135 degrees, and that goes here, and 225 degrees and 315 degrees are here.
Other important reference angles are in increments of 30 degrees, so 30 degrees and 60 degrees are here and 90 degrees is already drawn in. Here are the rest of the 30 degree increments around the circle.
We will often use this circle with these degree markings to calculate the measurement of angles. As an example here is an angle, and let’s say we need to calculate the measurement of this angle. We can use this circle as a reference to find that measurement.
We can take the angle and overlay it on the circle by putting one of the sides of angle aligned with 0 degrees, and we see it has a measurement of 135 degrees. Using this same 135 degree angle, if we wanted to know the angle the long way around, so to speak. Well, we know this angle cuts off the circle at 135 degrees, and the whole way around the circle is 360 degrees, so we would subtract 135 degrees from 360 degrees, which equals 225 degrees. So this angle is 225 degrees. And angles that are greater than 180 degrees are called reflex angles.
Now lets say that we want to measure this angle on the paper here. To do this, we use a protractor that you see here. We line up the vertex of the angle with this hole, and line up one of the sides of the angle with this kind of imaginary line on the protractor, then check where the other side of the angle lines up with the tick marks. And you can see that it lines up with 70 degrees, so this is a 70 degree angle.
I have a separate video that goes more in detail of how to measure angles with a protractor that I will link at the end of this video.
Timestamps
0:00 Angles are measured in degrees
0:23 What are right angles?
0:37 The degrees around a circle
1:27 Example using the circle to measure angles
1:44 Angles larger than 180 degrees
2:12 Example using a protractor
Transcript/notes
Angles are measured based on how open or closed they are, for instance this angle is not very open, and its measurement happens to be 20 degrees, and this angle is more open, and its measurement is 30 degrees. And angle measurements are in the form of degrees, which is represented by this little circle symbol you see here.
There are 2 very important angles to learn as references, a 90 degree angle and a 45 degree angle. The 90 degree angle, which is shown here, is called a right angle, and it is typically marked with a little box, as you see here in angle j, k, l. And the 2 lines that intersect to form a 90 degree angle are said to be perpendicular.
When first learning angle measurements it can help to start with a circle. We reference an angle here at 0 degrees, and an entire circle is 360 degrees.
90 degrees is here, and 45 degrees is here. A straight line across the circle has a measurement of 180 degrees, and a 270 degrees is here. And 90 degrees plus 45 degrees equals 135 degrees, and that goes here, and 225 degrees and 315 degrees are here.
Other important reference angles are in increments of 30 degrees, so 30 degrees and 60 degrees are here and 90 degrees is already drawn in. Here are the rest of the 30 degree increments around the circle.
We will often use this circle with these degree markings to calculate the measurement of angles. As an example here is an angle, and let’s say we need to calculate the measurement of this angle. We can use this circle as a reference to find that measurement.
We can take the angle and overlay it on the circle by putting one of the sides of angle aligned with 0 degrees, and we see it has a measurement of 135 degrees. Using this same 135 degree angle, if we wanted to know the angle the long way around, so to speak. Well, we know this angle cuts off the circle at 135 degrees, and the whole way around the circle is 360 degrees, so we would subtract 135 degrees from 360 degrees, which equals 225 degrees. So this angle is 225 degrees. And angles that are greater than 180 degrees are called reflex angles.
Now lets say that we want to measure this angle on the paper here. To do this, we use a protractor that you see here. We line up the vertex of the angle with this hole, and line up one of the sides of the angle with this kind of imaginary line on the protractor, then check where the other side of the angle lines up with the tick marks. And you can see that it lines up with 70 degrees, so this is a 70 degree angle.
I have a separate video that goes more in detail of how to measure angles with a protractor that I will link at the end of this video.
Timestamps
0:00 Angles are measured in degrees
0:23 What are right angles?
0:37 The degrees around a circle
1:27 Example using the circle to measure angles
1:44 Angles larger than 180 degrees
2:12 Example using a protractor
Комментарии
 0:02:57
0:02:57
 0:05:47
0:05:47
 0:09:32
0:09:32
 0:05:00
0:05:00
 0:03:43
0:03:43
 0:04:14
0:04:14
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:00:25
0:00:25
 0:03:33
0:03:33
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:07:18
0:07:18
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:02:56
0:02:56
 0:05:47
0:05:47
 0:02:59
0:02:59
 0:09:17
0:09:17
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:09:52
0:09:52
 0:10:48
0:10:48
 0:02:23
0:02:23
 0:03:11
0:03:11
 0:10:49
0:10:49
 0:00:17
0:00:17