filmov
tv
Glycogenesis Mnemonic for USMLE

Показать описание
Study this Glycogenesis USMLE mnemonic and other mnemonics with Pixorize.
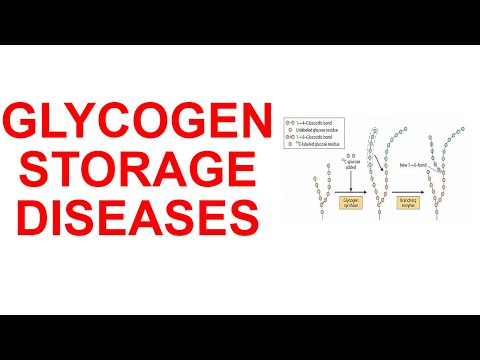
Glycogenesis is the biochemical pathway that produces glycogen, which is the body’s storage form of glucose. The main places in our body that want to store glucose for later use as glycogen are the liver and muscle.
Glycogenesis begins with glucose-6-phosphate, which is then catalyzed to glucose-1-phosphate via a mutase enzyme, phosphoglucomutase.
Next, Glucose-1-phosphate reacts with UTP to form the high-energy UDP-glucose intermediate, in a reaction catalyzed by a pyrophosphorylase enzyme, UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase.
Next, glycogen synthase uses the energy from UDP-glucose to connect the glucose residue to the end of a glycogen straight chain. When extending a straight chain, glucose molecules are added via alpha-1,4 linkages. Glycogen synthase is stimulated by insulin, but is inhibited by glucagon and epinephrine.
Finally, glycogen achieves its branched structure due to the actions of glycogen branching enzymes. These enzymes break off the ends of a glycogen straight chain and attach the fragment to the side of a straight chain to form a branch point, which is formed via an alpha-1,6 linkage.
#USMLE #Step1 #Biochem #Glycogenesis
Glycogenesis is the biochemical pathway that produces glycogen, which is the body’s storage form of glucose. The main places in our body that want to store glucose for later use as glycogen are the liver and muscle.
Glycogenesis begins with glucose-6-phosphate, which is then catalyzed to glucose-1-phosphate via a mutase enzyme, phosphoglucomutase.
Next, Glucose-1-phosphate reacts with UTP to form the high-energy UDP-glucose intermediate, in a reaction catalyzed by a pyrophosphorylase enzyme, UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase.
Next, glycogen synthase uses the energy from UDP-glucose to connect the glucose residue to the end of a glycogen straight chain. When extending a straight chain, glucose molecules are added via alpha-1,4 linkages. Glycogen synthase is stimulated by insulin, but is inhibited by glucagon and epinephrine.
Finally, glycogen achieves its branched structure due to the actions of glycogen branching enzymes. These enzymes break off the ends of a glycogen straight chain and attach the fragment to the side of a straight chain to form a branch point, which is formed via an alpha-1,6 linkage.
#USMLE #Step1 #Biochem #Glycogenesis
Комментарии
 0:01:25
0:01:25
 0:06:49
0:06:49
 0:20:57
0:20:57
 0:09:19
0:09:19
 0:02:18
0:02:18
 0:05:51
0:05:51
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:06:56
0:06:56
 0:00:36
0:00:36
 0:00:25
0:00:25
 0:14:18
0:14:18
 0:09:38
0:09:38
 0:20:08
0:20:08
 0:05:36
0:05:36
 0:04:47
0:04:47
 0:03:21
0:03:21
 0:03:50
0:03:50
 0:02:08
0:02:08
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 0:30:45
0:30:45
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:02:40
0:02:40
 0:01:42
0:01:42
 0:06:28
0:06:28